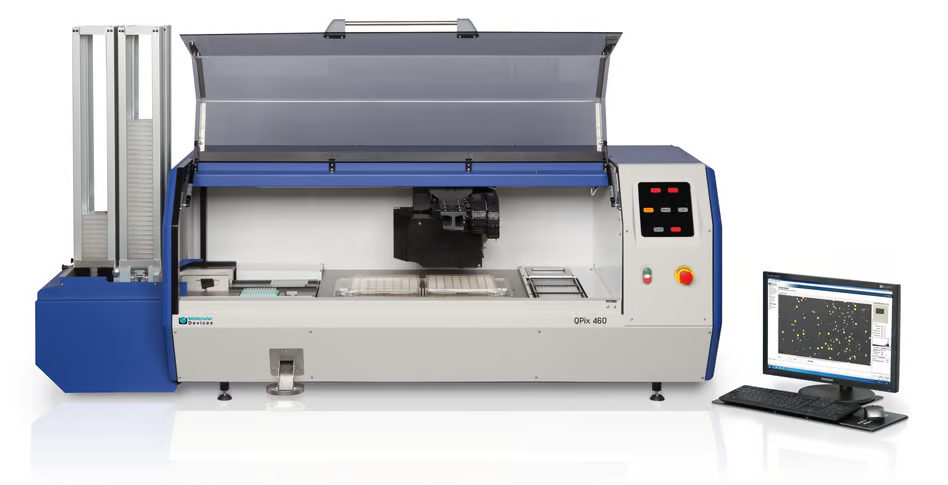
The QPix® Microbial Colony Picker from Molecular Devices leverages first-in-class colony-picking technology to ease bottlenecks and rapidly, precisely, and effectively screen via huge genetic libraries.
The user-friendly and intuitive software guides users via setting up colony-picking runs where precision robotics picks the correct colonies every time. In addition to microbial screening, the system has automated numerous sample preparation and plate handling processes, such as transferring bacterial liquid culture and plating on agar.
Automatic data recording is carried out, offering users an entire audit trail and sample tracking and guaranteeing that data is not lost. The modular and scalable series of colony pickers enable groups of all sizes to increase the precision and throughput of their workflow while still enabling future throughput growth.
Identify colonies with a desired phenotype
The QPix colony pickers support an extensive range of microorganisms and several selection modalities, such as fluorescence intensity, size and proximity, blue or white selection, and zone of inhibition.
Select colonies efficiently
A collection of organism-specific pin and agar sensors guarantee efficient picking. The system offers a picking efficiency of more than 98%, enabling users to walk away confidently.
Maintain sterility
A host of sterility features comes with a UV light for sanitizing the instrument’s interior part, pin washing, and halogen drying of pins.
Anatomy of a QPix system
- Availability of integrated plate stacker to scale up screening capacity.
- Automated plate de-lidder retains sterility
- Barcode reader offers dependable traceability of data
- Organism-specific and interchangeable picking pins provide flexibility to tackle multiple organisms such as yeast and E.coli.

Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
- Wash baths consisting of bleach and ethanol remove contamination among pins
- Automated agar height sensor and fluorescent camera with color filters allow high picking efficiency (>99%)
- Fusion software provides stepwise guidance to establish colony analysis and picking

Anatomy of a QPix system. Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
Features
Organism-specific pins
Various shapes and picking area pins increase E. coli, yeast, and phage efficiency. Plating-specific pins guarantee even distribution of liquid culture onto agar.
Plating and spreading
Automated plating and streaking of 96 samples could be performed in just 30 minutes, offering greater walk-away time.
Agar sensing
Ultrasonic agar height sensor has the potential to detect differences in height, leading to variable pouring volume allowing the utmost picking efficiency.
Multiple imaging modes
Colonies could be picked depending on pre-specified parameters with the help of fluorescence, white light, and color. The use of filters allows applications such as blue-white colony screening.
Replication, grid and hit picking
Automated plate handling and tracking simplify sample management and downstream assay. QPix colony pickers offer adaptable gridding, plate replication, and hit-picking abilities.
Scalable automation options
The QPix HT model is a robot-compatible solution with the help of a modular deck. The Advanced Workflow Engineering Solutions Team could customize a colony picker with various custom services.
Automate users’ workflow with the QPix Colony Picker
Colony picking is a necessary step in biological research as scientists frequently separate microbial clones to enormously produce DNA or proteins to be utilized in a range of applications downstream.
Conventionally, colony picking is executed manually using sterile pipette tips or inoculation loops, which are generally slow, time-consuming, and laborious. Not only will automated colony pickers make the entire process quicker, but the outcomes are highly consistent and trustworthy.
How it works
1. Plating: Plate samples to agar
The QPix system has the potential to plate and streak 96 samples in about 30 minutes, which is a significant enhancement in throughput in comparison to the manual process.
2. Screening: Selective screening by fluorescent detection of target protein
The QPix system assists fluorescent and colorimetric detection, enabling researchers to determine and isolate colonies that display the preferred phenotype or biological function. The system could pick just those colonies of interest, saving time and money.
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
3. Picking: Pick the best colonies
The QPix system could accurately pick 3,000 colonies every hour, removing common errors linked to manual processes, such as double picks or misses.
Sensors automatically detect agar height, aiding high-precision robotics to pick single colonies gently while achieving >98% efficiency.
4. Replicating: Make multiple copies of microplates
The replicating function in the QPix system makes duplicates and sub-libraries of colonies, enabling scientists to have a working microbe plate available for assays and another plate for sample banks.
Three kinds of plate replications are possible:
- Compression (4 × 96-well plates into 1 × 384-well plates)
- Identical replicates (96- to 96-well, 384- to 384-well plates)
- Expansion (1 × 384-well plate into 4 × 96-well plates)
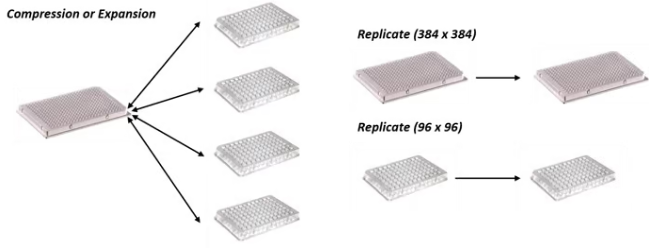
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
5. Gridding (arraying): Set up high density arrays for offline screening
Picked colonies could be arrayed onto filters or agar for hybridization screening. Up to 6 filters, with up to 57,600 spots for every filter, are aided, enabling users to an affordable and powerful way to screen libraries.
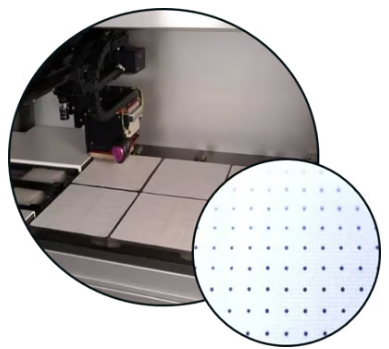
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
6. Re-Arraying
Cherry pick from microplate to microplate to consolidate desired clones
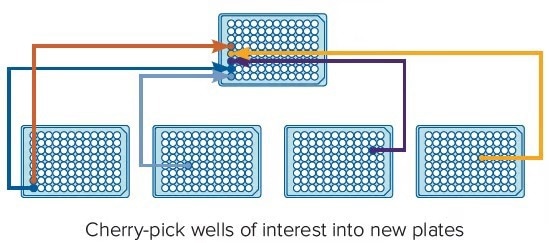
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
Applications
Colony picking is crucial in several different branches in biology. In this context, there are a few significant applications in which the QPix Microbial Colony Picker could help.

Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
Phage display
An approach in which a large library of antibodies is encoded into the DNA of a virus (developing a phage library) in such a method that the antibody is shown on the virus's coat. The phage library infects bacterial hosts where the virus can further replicate.
Virus-infected individual colonies are then picked and deposited into a microtiter plate coated with the antigen of interest. The plate is washed so phages showing an antibody specific to the antigen stay attached.
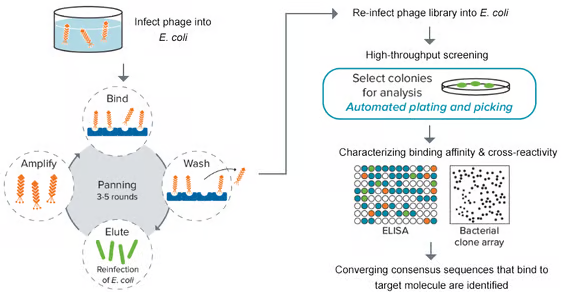
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
How QPix can help
A normal phage library contains around 109-1011 variants separately expressed in E. coli, posing a considerable blockage while screening for the right candidates. The QPix system can potentially pick up to 3,000 clones/hr, increasing throughput, speed, and walk-away time.
DNA assembly
A term denoting to the aligning and merging pieces of DNA. Scientists interested in developing genes from the ground up frequently use computer algorithms and the known properties of present sequences to anticipate the behavior of their designer gene

Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
How QPix can help
Arrangement of the genes could be difficult since they are often very large (thousands of base pairs in size). At present, the majority of the techniques could synthesize strands of DNA up to hundreds of base pairs.
To assemble the gene of interest, thousands of shorter strands should be joined collectively to develop the larger gene of interest. Before gene assembly, the shorter strands of DNA are initiated into bacteria, which should be picked consequently and prepped for gene assembly. The QPix system could help expedite this process.
Synthetic biology
Synthetic biology is an extensive term for manipulating metabolic pathways to coax microbes to manufacture proteins in a highly predictable way via engineering principles. Sometimes individual genes are altered and sometimes complete genomes are edited for preferred characteristics.

Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
How QPix can help
The engineering of metabolic pathways to generate constant and predictable protein product frequently needs the manipulation of several pathways and various components within every pathway.
This multifactorial method requires the screening of a diverse library of mutants to determine the unique clone with the preferred characteristics. Automating this process is vital to guaranteeing consistency and also fulfilling throughput requirements.
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is an emerging field that involves studying all genetic materials arising from a particular environment (for example, gut) instead of the traditional method of learning a known specific organism within that environment.
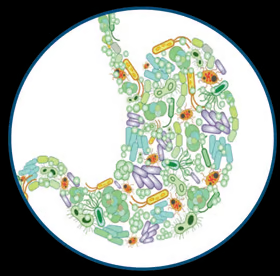
Image Credit: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
How QPix can help
A normal project begins with sampling microorganisms inside a given environment to find as many species as possible for further investigation downstream.
Some experts recommend there are highly unknown microbes on Earth compared to stars in the universe. There are generally a huge and diverse set of microbial colonies that benefit hugely from the throughput and flexibility of the Qpix system.
Which QPix is right for users?
Source: Molecular Devices UK Ltd
| |
QPix 420 |
QPix 450/460 |
QPix HT |
QPix XE |
| |

A fundamental design for automating colony picking with a compact footprint can be made. It is the perfect system for substituting manual with automated picking, enabling labware use and adaptable bed setup. |

Right from plating to picking—it is possible to increase throughput with up to 210 destination plates available in three stacker lanes. Optional fluidics for streaking and plating enables users to plate and pick samples. |

Adaptable, modular, and completely automated colony picking and library management system is all set for robotics integration for walkaway time and utmost throughput. |
Perfect for small laboratory spaces with no compromise on efficiency, with progressed imaging and robotic abilities. The modular platform enables additional integration into an automated work cell for throughput growth or walk-away time. |
| IMAGING |
White light and fluorescence.
|
White light and fluorescence.
|
White light and fluorescence.
|
White light and fluorescence
|
| PICKING CAPACITY |
3000 colonies per hour in white light, 2000 colonies per hour in fluorescent light
|
3000 colonies per hour in white light, 2000 colonies per hour in fluorescent light
|
3000 colonies per hour in white light, 2000 colonies per hour in fluorescent light
|
1500 colonies per hr white light and 1000 colonies per hour in fluorescence mode
|
| COLONY SELECTION CRITERIA |
Size, proximity, roundness, fluorescence intensity.
|
Size, proximity, roundness, fluorescence intensity.
|
Size, proximity, roundness, fluorescence intensity.
|
Size, proximity, roundness, fluorescence intensity.
|
| PICKING AND REGIONAL PICKING |

|

|

|

|
| BARCODE TRACKING |

|

|

|

|
| RE-ARRAYING AND REPLICATION |

|

|

|

|
| GRIDDING |

|

|

|
|
| PLATING AND STREAKING |
|

Only QPix 460
|

|
|
| AGAR TO AGAR |
|
|

|
|
| ROBOTICS INTEGRATION |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| |
|
|

|
|
| DESTINATION PLATE CAPACITY |
Picking: 12 plates
Replicating and re-arraying: Maximum of 20 plate positions
|
QPix 450: Up to 156 standard SBS plates, 52 standard SBS plates per stacker, up to 3 stacker lanes.
QPix 460: Up to 104 standard SBS plates, 52 standard SBS plates per stacker, up to 2 stacker lanes.
|
Configurable and expandable with automation. No limit to number of plates.
|
Picking – 4 plates
Replicating and re-arraying:
Max – 8 plates
|
| STACKERS |
|
2 or 3 Stacker Lanes
|
Plate Hotels
|
|
| SOURCE PLATE CAPACITY |
Without manual intervention:
1 x 15 cm petri dish;
5 x 9 cm petri dishes;
2 x OmniTrays;
1 x 22 cm QTrays
|
Without manual intervention:
2 x 15 cm petri dish;
10 x 9 cm petri dishes;
4 x OmniTrays;
2 x 22 cm QTrays
|
Automation mode:
1-well Omnitray,
8-well Omnitray
Manual mode:
Qtrays
Petri Dishes
Omnitrays
SBS plates
|
Manual Mode:
1 x 15 cm petri dish;
5 x 9 cm petri dishes;
2 x OmniTrays;
1 x 22 cm QTrays
Automation mode:
1-well Omnitray,
8-well Omnitray
|
| WALKAWAY TIME |
25 minutes at a time - only return to swap destination plates after 12 are full
|
QPix 450: 156 plates x 96 colonies per plate = 14,976 colonies picked in 4.5 hours
QPix 460: 104 plates x 96 colonies per plate = 9,984 colonies picked in 3 hours
|
Entire duration of run
|
|