2. What should I know before I use COVERAM?
Do not use if you have ever had an allergic reaction to perindopril or amlodipine,
any other ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers, or any of the ingredients listed
at the end of the CMI. Talk to your doctor if you have any other medical conditions, take any other medicines,
or are pregnant or plan to become pregnant or are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
4. How do I use COVERAM?
Your doctor will select a dose when they prescribe COVERAM for you. The usual dose
is one tablet once daily. Swallow your tablet(s) with a glass of water. Grapefruit
juice and grapefruit should not be consumed by people who are taking COVERAM.
5. What should I know while using COVERAM?
|
Things you should do
|
Take this medicine exactly as prescribed and remind any healthcare professional you
are taking it.
If you have stopped treatment with COVERAM due to an allergic reaction you should
not start taking COVERAM again.
|
|
Driving or using machines
|
COVERAM may affect your ability to drive or use machines. If the tablets make you
sick, dizzy, weak or tired, or give you a headache, do not drive or use machines and
contact your doctor immediately.
|
|
Drinking alcohol
|
Your doctor may advise you to limit your alcohol intake.
|
|
Looking after your medicine
|
Store in a cool dry place away from moisture, heat, and sunlight. Keep your tablets
in the bottle until it is time to take them. Keep out of reach of children.
|
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. Sometimes they are serious, most of the time
they are not. If you do not feel well while you are taking COVERAM then tell your
doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible. Angioedema (a severe allergic reaction)
has been reported in patients treated with ACE inhibitors, including COVERAM. This
may occur at any time during treatment. If you develop swelling of your limbs, hands or feet, lips, face, mouth, tongue
or throat, purple spots with occasional blisters on the front of your arms and legs
and/or around your neck and ears (a rare condition known as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome),
painful red areas, developing large blisters and peeling of layers of skin (accompanied
by fever and chills), red, often itchy spots, similar to the rash of measles, which
starts on the limbs and sometimes on the face and the rest of the body, difficulty
in breathing or a fast and irregular heartbeat after taking COVERAM – please seek
urgent medical attention.
Active ingredient(s):
perindopril arginine/amlodipine besilate
Full Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet answers some common questions about COVERAM. It does not contain all
the available information about this medicine. Reading this leaflet does not take
the place of talking to your doctor or pharmacist.
All medicines have risks and benefits. Your doctor has weighed the risks of you taking
COVERAM against the benefits they expect it will have for you.
If you have any concerns about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Keep this leaflet with the medicine. You may need to read it again.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why am I using COVERAM?
The name of your medicine is COVERAM.
The medicine contains the active ingredient perindopril arginine. Perindopril belongs
to a group of medicines called angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors.
It also contains the active ingredient amlodipine besilate. Amlodipine belongs to
a group of medicines called calcium channel blockers. Calcium channel blockers do
not change the amount of calcium in your blood or bones.
COVERAM has been prescribed for you by your doctor to replace the separate tablets
of perindopril and amlodipine you were taking. One COVERAM tablet replaces separate
tablets of perindopril and amlodipine.
What COVERAM is used for
You have been prescribed COVERAM if you have high blood pressure, also known as hypertension.
Why COVERAM is used for high blood pressure
Everyone has blood pressure. This pressure helps get your blood all around the body.
Your blood pressure may be different at different times of the day, depending on how
busy or stressed you are.
You have high blood pressure when your blood pressure stays higher than is needed,
even when you are calm or relaxed.
There are usually no symptoms of high blood pressure. The only way of knowing that
you have it is to have your blood pressure checked on a regular basis. If high blood
pressure is not treated it can lead to serious health problems. You may feel fine
and have no symptoms, but eventually it can cause stroke, heart disease and kidney
failure.
The active ingredients in COVERAM, perindopril arginine and amlodipine help lower
your blood pressure.
You may also have been prescribed COVERAM if you have coronary heart disease.
Why COVERAM is used for coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is narrowing of the vessels carrying blood to the heart.
In patients with coronary artery disease, COVERAM has been shown to reduce some of
the risks, including heart attacks.
How COVERAM works
COVERAM works by widening your blood vessels, which reduces pressure in the vessel,
making it easier for your heart to pump blood around your body.
This helps increase the supply of oxygen to your heart, so that when you place extra
demands on your heart, such as during exercise, your heart may cope better and you
may not get short of breath as easily.
Ask your doctor if you have any questions about why COVERAM has been prescribed for
you.
COVERAM is available only with a doctor's prescription.
There is no evidence that COVERAM is addictive.
2. What should I know before I use COVERAM?
There are some people who shouldn't take COVERAM. Please read the list below.
If you think any of these situations apply to you or you have any questions, please
consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Warnings
Do not use COVERAM if:
you are allergic to perindopril or amlodipine, or any of the other ingredients of
COVERAM listed at the end of this leaflet.
you have had an allergic reaction to any other ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers.
Symptoms of an allergic reaction to COVERAM may include skin rash, itchiness, shortness
of breath, swelling of the face, lips or tongue, muscle pain or tenderness or joint
pain.
are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. COVERAM may affect your developing baby
if you take it during pregnancy.
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. COVERAM passes into breast milk and therefore
there is a possibility that the breastfed baby may be affected.
are undergoing treatments where your blood is treated outside of the body (also known
as extracorporeal treatments) that may increase your risk of allergic reactions, treatments
such as:
renal dialysis or haemofiltration using polyacrylonitrile membranes
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) apheresis, a technique where LDL is 'filtered' out of
the blood, using dextran sulfate.
you are treated with a blood pressure lowering medicine containing aliskiren and have
diabetes or impaired kidney function.
you are being treated with sacubitril/valsartan, a medicine for heart failure as the
risk of angioedema (rapid swelling under the skin in an area such as the throat) is
increased (see also ‘Tell your doctor straight away if’ and ‘What if I am taking other
medicines?’ sections).
have renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the blood vessels to one or both kidneys).
have aortic stenosis (narrowing of the main blood vessel leaving from the heart).
have severe hypotension (low blood pressure).
have unstable angina. Unstable angina is a pain or uncomfortable feeling in the chest
that lasts longer than a few minutes or occurs with rest and may not be relieved with
medication.
have cardiogenic shock which is a sudden and severe drop in blood pressure and blood
flow through the body because the heart is not pumping normally.
have heart failure during the first 28 days after a heart attack (Heart failure means
that the heart muscle cannot pump blood strongly enough to supply all the blood needed
throughout the body. It does not mean that the heart stops working).
have experienced swelling of the face, tongue, lips or throat either spontaneously
or in response to another medicine in the past. (This rare condition is known as angio-oedema).
the packaging is damaged or shows sign of tampering.
the expiry date (EXP) on the pack has passed.
If you think any of these situations apply to you, or you have any doubts or questions
about taking COVERAM speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
Tell your doctor straight away if:
you are pregnant or become pregnant while taking COVERAM, as it may cause serious
harm to your baby.
you are undergoing desensitisation treatment or have had an allergic reaction during
previous desensitisation treatment (e.g. treatments using bee, wasp or ant venom).
you are undergoing, or you are intending to undergo, treatments where your blood is
treated outside of the body (also known as extracorporeal treatments) you are to undergo
anaesthesia and/or surgery.
you have recently suffered from diarrhoea or vomiting.
you are on a salt restricted diet or use salt substitutes which contain potassium.
you have an intolerance to some sugars as COVERAM contains lactose.
you are taking any of the following medicines used to treat high blood pressure:
an 'angiotensin II receptor blocker' (also known as ARBs or sartans - for example
valsartan, telmisartan, irbesartan), in particular if you have diabetes-related kidney
problems
aliskiren
you are treated with immunosuppressant therapy or allopurinol or procainamide.
you have any other health problems, including:
kidney disease or if you are on renal dialysis
liver disease
high or low levels of potassium, or other problems with salt balance
diabetes
heart disease, severe increase in blood pressure or other heart problems
Systemic lupus erythematous or scleroderma (a disease affecting the skin, joints and
kidneys)
abnormally increased levels of a hormone called aldosterone in your blood (primary
hyperaldosteronism)
If you think any of these situations apply to you, or you have any doubts or questions
about taking COVERAM consult your doctor or pharmacist.
During treatment, you may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It is important
you understand these risks and how to monitor for them. See additional information
under Section
6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Do not take COVERAM if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. COVERAM may
affect your developing baby if you take it during pregnancy.
Do not take COVERAM if you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. COVERAM passes
into breast milk and therefore there is a possibility that the breastfed baby may
be affected.
For older people and patients with renal impairment
COVERAM can generally be used safely by elderly people.
Reduced kidney function is often found in elderly people and in this case, the starting
dose should always be 2.5 mg of perindopril arginine and 2.5 mg of amlodipine taken
as separate tablets.
For children
COVERAM is not recommended for children.
Driving and using machines
COVERAM may affect your ability to drive or use machines. If the tablets make you
feel sick, dizzy, weak or tired, or give you a headache, do not drive or use machines
and contact your doctor immediately.
3. What if I am taking other medicines?
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any other medicines, including any
medicines, vitamins or supplements that you buy without a prescription from your pharmacy,
supermarket or health food shop.
Taking COVERAM may change the effect of some medicines, and some medicines may affect
how well COVERAM works. You may need different amounts of your medication or to take
different medicines.
The medicines that may interact with COVERAM include the following:
some treatments where your blood is treated outside of the body, also known as extracorporeal
treatments (see also ‘Do not use COVERAM if’ and ‘Tell your doctor straight away if’
sections)
some antibiotic medicines such as erythromycin, clarithromycin and rifampicin
some medicines used to treat fungal infections such as ketoconozole or itracanazole
some anti-inflammatory drugs (including high dose aspirin, ibuprofen to relieve pain
swelling and other symptoms of inflammation, including arthritis, and gold injections
to treat rheumatoid arthritis)
medicines used to treat mood swings and some types of depression (lithium, tricyclic
antidepressants, antipsychotics)
potassium-sparing medicines (spironolactone, triamterene, amiloride, eplerenone),
sources of potassium, like potassium tablet and salt substitutes containing potassium,
other drugs which can increase potassium in your body (such as heparin, a medicine
used to thin blood to prevent clots; co-trimoxazole also known as trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
for infections caused by bacteria; and ciclosporin, an immunosuppressant medicine
used to prevent organ transplant rejection)
some medications used to treat high blood pressure (including angiotensin receptor
blocker, beta-blockers, alpha-blockers) aliskiren (see also ‘Do not use COVERAM if’
and ‘Tell your doctor straight away if’ sections), or diuretics (sometimes called
'fluid' or 'water' tablets because they increase the amount of urine passed each day)
vasodilators including nitrates
medicines used to treat diabetes (tablets and insulin)
muscle relaxants such as baclofen and dantrolene; dantrolene is also used to treat
hyperthermia during anaesthesia (symptoms include very high fever and muscle stiffness)
medicines used to treat epilepsy such as carbamazepine, phenobarbitone, phenytoin
or primidone
St. John's Wort
medicines which lower your immune system, such as corticosteroids, cyclosporin, tacrolimus
or medicines used to treat cancer (including radiation therapy)
simvastatin (cholesterol lowering medicine)
tetracosactide, a medicine used to treat adrenal insufficiency
medicines which may affect the blood cells, such as allopurinol, procainamide
medicines affecting the part of the nervous system that controls the activities of
the heart and blood vessels, including ephedrine, noradrenaline or adrenaline
alpha-blockers used for the treatment of enlarged prostate such as prazosin, alfuzosin,
doxazosin, tamsulosin, terazosin
amifostine (used to prevent or reduce side effects caused by other medicines or radiation
therapy that are used to treat cancer)
corticosteroids (used to treat various conditions including severe asthma and rheumatoid
arthritis)
medicines used to treat HIV infection such as indinavir, ritonavir (also called 'protease
inhibitors')
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors used to avoid rejection of transplanted
organs (e.g. temsirolimus, sirolimus, everolimus)
sacubitril/valsartan (used to treat long-term heart failure) (see also ‘Do not use
COVERAM if’ and ‘Tell your doctor straight away if’ sections)
gliptins used to treat diabetes (e.g. linagliptin, saxagliptin, sitagliptin, vildagliptin,
alogliptin)
Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines, vitamins
or supplements you are taking and if these affect COVERAM.
Your doctor or pharmacist has more information on medicines to be careful with or
avoid while taking COVERAM.
4. How do I use COVERAM?
Follow all directions given to you by your doctor and pharmacist carefully. They may
differ from the information contained in this leaflet.
If you do not understand the instructions on the label, ask your doctor or pharmacist
for help.
How much to take / use
Your doctor will select a dose when they prescribe COVERAM for you. The usual dose
is one tablet once daily.
Follow the instructions provided and use COVERAM until your doctor tells you to stop.
Swallow your tablet(s) with a glass of water.
Grapefruit juice and grapefruit should not be consumed by people who are taking COVERAM.
This is because grapefruit and grapefruit juice can lead to an increase in the blood
levels of the active ingredient amlodipine, which can cause an unpredictable increase
in the blood pressure lowering effect of COVERAM.
How long to take it for
COVERAM helps control your blood pressure and/or treat your coronary heart disease
but does not cure it. Continue taking the tablets for as long as your doctor tells
you.
When to take / use COVERAM
Take COVERAM at about the same time each day unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
Taking your tablet at the same time each day will have the best effect. It will also
help you remember when to take the tablets.
COVERAM should be taken in the morning before a meal.
If you forget to use COVERAM
COVERAM should be used regularly at the same time each day.
If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the dose you missed and take your next
dose when you are meant to. Otherwise, take it as soon as you remember, and then go
back to taking it as you would normally.
Do not take a double dose to make up for the dose you missed.
If you use too much COVERAM
If you think that you have used too much COVERAM, you may need urgent medical attention.
You should immediately:
phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling
13 11 26), or
contact your doctor, or
go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
5. What should I know while using COVERAM?
Things you should do
If you become pregnant while you are taking COVERAM, tell your doctor.
If you are about to be started on any new medicine, remind your doctor and pharmacist
that you are taking COVERAM.
Tell all doctors, dentists and pharmacists involved with your treatment that you are
taking COVERAM.
Take COVERAM exactly as your doctor has prescribed. Otherwise you may not get the
benefits from treatment.
If any of the signs below occur, then tell your doctor immediately or go to the Accident
and Emergency department at your nearest hospital.
swelling of your lips, face, mouth, tongue or throat
purple spots with occasional blisters on the front of your arms and legs and/or around
your neck and ears (a rare condition known as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, Toxic Epidermal
Necrolysis (TEN))
severe blisters, skin rash, itching or other allergic reactions.
These side effects are extremely rare but can become serious.
If you have stopped treatment with COVERAM due to an allergic reaction you should
not start taking COVERAM again.
Things you should not do
do not give COVERAM to anyone else, even if they have the same condition as you.
do not use COVERAM to treat other complaints unless your doctor tells you to.
do not stop taking COVERAM or change the dosage, without checking with your doctor.
do not stop taking your tablets because you are feeling better, unless advised by
your doctor.
Things that may help your condition
Some self - help measures suggested below may help your condition. Talk to your doctor
or pharmacist about these measures and for more information.
Alcohol - your doctor may advise you to limit your alcohol intake.
Diet - eat a healthy low-fat diet which includes plenty of fresh vegetables, fruit,
bread, cereals and fish. Also eat less fat and sugar.
Exercise - regular exercise helps to reduce blood pressure and helps get the heart
fitter, but it is important not to overdo it. Walking is good exercise but try to
find a route that is reasonably flat. Before starting any exercise, ask your doctor
about the best kind of program for you.
Salt - your doctor may advise you to watch the amount of salt in your diet. To reduce
your salt intake you should avoid using salt in cooking or at the table.
Smoking - your doctor may advise you to stop or at least cut down smoking.
Weight - your doctor may suggest losing some weight to help lower your blood pressure
and help lessen the amount of work your heart has to do. Some people may need a dietician's
help to lose weight.
Driving or using machines
Be careful before you drive or use any machines or tools until you know how COVERAM
affects you.
COVERAM may affect your ability to drive or use machines. If the tablets make you
feel sick, dizzy, weak or tired, or give you a headache, do not drive or use machines
and contact your doctor immediately.
Drinking alcohol
Tell your doctor if you drink alcohol. Your doctor may advise you to limit your alcohol
intake.
Looking after your medicine
Keep your COVERAM tablets in the bottle until it is time to take them.
COVERAM will not keep as well outside its packaging.
Keep your COVERAM tablets in a cool, dry place away from light where the temperature
stays below 25°C.
Do not store medicines in a bathroom or near a sink. Do not leave them in a car or
on a window sill.
Heat and dampness can destroy some medicines.
Keep your COVERAM tablets where children cannot reach them.
A locked cupboard at least one-and-a-half metres above the ground is a good place
to store medicines.
When to discard your medicine
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
If your doctor tells you to stop taking COVERAM, or the tablets have passed their
expiry date, return any leftover tablets to your pharmacist for disposal.
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. If you do experience any side effects, most of
them are minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you
have any further questions about side effects.
Serious side effects
|
Serious side effects
|
What to do
|
|
Angioedema (a severe allergic reaction) has been reported in patients treated with
ACE inhibitors, including COVERAM. This may occur at any time during treatment. If
you develop such symptoms described below you should tell your doctor immediately
or go to the Accident and Emergency department at your nearest hospital. These side
effects are extremely rare but can become serious:
Respiratory and heart
difficulty in breathing
a fast and irregular heartbeat
Skin
purple spots with occasional blisters on the front of your arms and legs and/or around
your neck and ears (a rare condition known as Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
painful red areas, developing large blisters and peeling of layers of skin. This is
accompanied by fever and chills
red, often itchy spots, similar to the rash of measles, which starts on the limbs
and sometimes on the face and the rest of the body
swelling of your extremities (limbs, hands or feet), lips, face, mouth, tongue or
throat
|
Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your
nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects.
|
Less serious side effects
|
Less serious side effects
|
What to do
|
|
Respiratory and heart
cough, often described as dry and irritating, shortness of breath, discomfort on exertion
chest pain
changes in the rhythm or rate of the heartbeat, fast or irregular heartbeat
chest tightness (dyspnoea)
difficulty breathing or wheezing
fast, slow or irregular heartbeat
myocardial infarction, angina pectoris (a feeling of tightness, pressure or heaviness
in the chest)
cardiac failure - disease of the heart with heart failure, symptoms include shortness
of breath, swelling of the feet or legs due to fluid build-up
Skin and hair
rash, pruritus (itching), red raised skin rash
eczema
purpura - unusual bleeding or bruising under the skin, or purple or red-brown spots
visible through the skin
excessive sweating
increased sensitivity of the skin to sun, skin rash or inflammation of the skin often
including blisters that weep and become crusted
skin discolouration
hypersensitivity reactions, mainly skin reactions, in patients with allergies and
asthmatic reactions
worsening of psoriasis
pemphigoid - a skin disease usually affecting older people
increase in some white blood cells (eosinophilia)
hives or skin rash (urticaria)
red, often itchy spots, similar to the rash of measles, which starts on the limbs
and sometimes on the face and the rest of the body
dry skin
cold and clammy skin
dermatitis
Steven Johnson syndrome
severe flaking or peeling of the skin
swelling of hands, ankles or feet, joint swelling (ankle swelling)
oedema (fluid retention)
Quicke's oedema
unusual hair loss or thinning
Gastrointestinal
nausea, vomiting, taste disturbances, indigestion, diarrhoea, constipation, change
of bowel habits, stomach pain or discomfort
flatulence or 'passing wind'
inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis)
gastritis - inflammation of the stomach where symptoms include pain, nausea, vomiting,
vomiting blood, blood in the bowel motions
Mouth
dry mouth
difficulty in swallowing
bleeding, tender or enlarged gums
swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat which may cause difficulty in
swallowing or breathing
Kidney and liver related
pollakiuria
need to urinate during the night
passing urine more often than usual
kidney problems
painful or difficult urination
acute kidney disease
problems with production or passing of urine
concentrated urine (dark in colour), feel or are sick, have muscle cramps, confusion
and fits which may be due to inappropriate anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) secretion can
occur with ACE inhibitors. If you have these symptoms contact your doctor as soon as possible.
hepatitis (liver disease)
yellowing of the skin and/or eyes, also called jaundice
Blood, investigations and metabolism
bleeding or bruising more easily than normal caused by a low blood platelet count
(thrombocytopenia)
frequent infections such as fever, severe chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers caused
by a lack of white blood cells (leukopenia)
hyperglycaemia (high blood sugar levels)
hypoglycaemia (low blood sugar levels)
high levels in the blood of potassium, urea and/or creatinine
low sodium levels in the blood
eosinophilic pneumonia
illnesses resulting from a lack or destruction of red blood cells - (anaemia, pancytopenia)
illnesses resulting from a lack of white blood cells (agranulocytosis, neutropenia,
pancytopenia)
elevation of bilirubin levels in the blood
increases in liver enzymes
weight gain
weight decrease
decreased appetite
increased appetite
thirst
Vascular disorders
low blood pressure (and related effects), flushing, impaired peripheral circulation,
blood vessel inflammation (vasculitis)
discolouration, numbness and pain in fingers or toes (Raynaud’s phenomenon)
orthostatic hypertension - dizziness on standing up, especially when getting up from
a sitting or lying position
peripheral coldness
peripheral ischaemia - a condition caused by reduced blood flow to the limbs, hands
and feet
Musculoskeletal
muscle spasms
osteoarthritis
aching muscles, not caused by exercise
back pain
joint pain
unusual muscle stiffness causing poor control of movement
muscle weakness
muscle twitching
Nervous system
confusion
loss of memory
ataxia - clumsiness and lack of coordination, affecting balance and manner of walking,
limb or eye movements and/or speech. Unsteadiness when walking
migraine
dizziness
headache
pins and needles
feeling sleepy (somnolence)
drowsiness
numbness or weakness of the arms and legs
tremor
numbness, or reduced sense of touch
cerebrovascular accident
extrapyramidal syndrome - unusual movements, including trembling and shaking of the
hands and fingers, rigid posture, mask-like face, slow movements of the body, shuffling
unbalanced walk and stiffness of the arms and legs
Eye, ear and nose
vision impairment (including double vision)
conjunctivitis - discharge with itching of the eyes and crusty eyelids, swollen runny
eyes
diplopia, eye pain
blurred vision
dry eyes
tinnitus (persistent noise in the ears)
vertigo
nosebleeds
runny or blocked nose, sneezing, facial pressure or pain
inability to smell
Reproductive system
erectile dysfunction
sexual dysfunction
breast enlargement in men
Psychiatric
mood disturbance, depression, nervousness, depersonalisation, sleep disturbances (difficulty
sleeping, abnormal dreams), fainting
hallucination
agitation
apathy - lack of interest, enthusiasm, concern
General
feeling tired, lethargic or weak
fatigue
fever or high temperature
generally feeling unwell
falls
malaise, pain, chills
|
Speak to your doctor or pharmacist if you have any of these less serious side effects
and they worry you.
|
Consult your doctor, pharmacist or nurse if you experience any of these or notice
anything else that is making you feel unwell.
Do not be alarmed by this list of possible side effects. You may not experience any
of them. Other uncommon side effects have been reported and you should ask your doctor,
pharmacist or nurse if you want to know more.
Reporting side effects
After you have received medical advice for any side effects you experience, you can
report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at
www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems . By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of
this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to your doctor or pharmacist before you decide to stop
taking any of your medicines.
7. Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What COVERAM contains
|
Active ingredient
(main ingredient)
|
Each tablet of COVERAM 5/5 contains 5 mg perindopril arginine and 5 mg amlodipine
besilate.
Each tablet of COVERAM 5/10 contains 5 mg perindopril arginine and 10 mg amlodipine
besilate.
Each tablet of COVERAM 10/5 contains 10 mg perindopril arginine and 5 mg amlodipine
besilate.
Each tablet of COVERAM 10/10 contains 10 mg perindopril arginine and 10 mg amlodipine
besilate.
|
|
Other ingredients
(inactive ingredients)
|
Lactose monohydrate
Microcrystalline cellulose
Colloidal anhydrous silica
Magnesium stearate
|
|
Potential allergens
|
Lactose monohydrate
|
Do not take this medicine if you are allergic to any of these ingredients.
What COVERAM looks like
COVERAM 5/5 tablets are white and rod-shaped engraved with 5/5 on one face and the
Servier Logo on the other face, supplied in a bottle of 30 tablets.

(Tablet image not actual size)
COVERAM 5/10 tablets are white and square-shaped engraved with 5/10 on one face and
the Servier Logo on the other face, supplied in a bottle of 30 tablets.

(Tablet image not actual size)
COVERAM 10/5 tablets are white and triangular-shaped engraved with 10/5 on one face
and the Servier Logo on the other face, supplied in a bottle of 30 tablets.

(Tablet image not actual size)
COVERAM 10/10 tablets are white and round engraved with 10/10 on one face and the
Servier Logo on the other face, supplied in a bottle of 30 tablets.
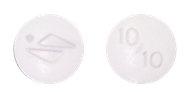
(Tablet image not actual size)
Thirty (30) tablets are supplied in a white bottle containing desiccant sachets and
equipped with a white child-resistant screw-on cap.
COVERAM is registered on the Australian register of Therapeutic Goods. Australian
Register Numbers:
COVERAM 5/5: AUST R 154438
COVERAM 5/10: AUST R 154439
COVERAM 10/5: AUST R 154440
COVERAM 10/10: AUST R 154441
Who distributes COVERAM
Servier Laboratories (Aust.) Pty. Ltd.
Level 4, Building 9
588A Swan Street
Burnley, 3121, Victoria
Phone: 1800 153 590
This leaflet was prepared in May 2024.