2. What the patient or carer should know before using ZYAMIS
Do not use if the patient has ever had an allergic reaction to midazolam or any of
the ingredients listed at the end of the CMI.
Talk to your patient’s doctor if your patient has any other medical conditions, takes
any other medicines, or is pregnant or plans to become pregnant or is breastfeeding.
For more information, see Section
2. What you or your patient should know before using ZYAMIS in the full CMI.
3. What if the patient is taking other medicines?
4. How do I use ZYAMIS for my patient?
5. What should you know while using ZYAMIS?
|
Things you should do
|
Remind any doctor, pharmacist or dentist you visit that the patient is using ZYAMIS.
In the event of a seizure, the parent or caregiver must follow the instructions in
the patient’s Emergency Medication Management Plan.
|
|
Things you should not do
|
Do not give more than one dose without prior medical advice.
|
|
Driving or using machines
|
After receiving this medicine, the patient should not drive, ride a bicycle, or operate
machinery until they are completely recovered.
|
|
Drinking alcohol
|
The patient must not drink alcohol if they have been given ZYAMIS.
|
|
Looking after ZYAMIS
|
Store ZYAMIS below 25°C. Keep the container in a cool, dry place and away from direct
heat and sunlight.
Do not put the product in the fridge or freezer.
Keep ZYAMIS in the original package in order to protect from light.
Keep ZYAMIS out of the sight and reach of children.
|
6. Are there any side effects?
Seek medical advice immediately or call an ambulance straight away if any of the following
side effects occur:
Allergic reaction e.g. swelling of the face, lips or tongue, a rash, pale skin, weak
rapid pulse or loss of consciousness.
Severe breathing difficulties e.g. slow or shallow breathing or blue lips. In very
rare cases breathing might stop.
Cardiac arrest (heart stopped) reported in very rare cases. Signs include loss of
consciousness associated with no pulse.
This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification
of new safety information. You can help by reporting any side effects you may get.
You can report side effects to your patient’s doctor, or directly at www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems .
Active ingredient(s):
midazolam
Full Consumer Medicine Information (CMI)
This leaflet provides important information about using ZYAMIS. You should also speak to the patient’s doctor or pharmacist if you would like further
information or if you have any concerns or questions about using ZYAMIS for the patient.
Where to find information in this leaflet:
1. Why is the patient using ZYAMIS?
ZYAMIS contains the active ingredient midazolam (as maleate). ZYAMIS belongs to a group of medicines known as benzodiazepines.
ZYAMIS is used to stop generalised convulsive seizures ('fit') in patients over 6
months old. ZYAMIS must only be used by parents/caregivers where the patient has an
established diagnosis of epilepsy by a medical practitioner.
2. What you or your patient should know before using ZYAMIS
Warnings
Do not use ZYAMIS if the patient:
1. is allergic to midazolam, or any of the ingredients listed at the end of this leaflet.
2. has severe muscle weakness, also known as myasthenia gravis.
3. has a condition called acute narrow angle glaucoma
4. is suffering from shock, or in a coma or have had a large amount of alcohol or
Always check the ingredients to make sure the patient can take this medicine.
Check with patient’s doctor if the patient:
has any other medical conditions such as:
a lung condition causing breathing problems as this medicine could make the patient’s
breathing worse
kidney, liver or heart problems.
high or low blood pressure.
sleep apnoea syndrome (which causes breathing to be frequently interrupted during
sleep)
mental disorders including depression or sleep disorders.
an illness that makes you feel very weak, run down and short of energy.
problems with alcohol use in the past or regularly drinks large amounts of alcohol.
problems with drug use in the past.
takes any medicines for any other condition.
During treatment, the patient may be at risk of developing certain side effects. It
is important that the carer understands these risks and how to monitor for them. See
additional information under Section
6. Are there any side effects?
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Check with the patient’s doctor if the patient is pregnant or intending to become
pregnant.
Talk to the patient’s doctor if the patient is breastfeeding or intending to breastfeed.
Contains maltitol
This product contains maltitol solution (sugar). If the patient has been told by his
or her doctor that he or she has an intolerance to some sugars, contact the patient’s
doctor before using this medicinal product.
Temporary Memory Loss
This medicine may affect the patient’s memory of the period after he or she has been
given it (temporary memory loss). The patient should be carefully observed after
being given this medicine.
3. What if the patient is taking other medicines?
Tell the patient’s doctor or pharmacist if the patient is taking any other medicines,
including any medicines, vitamins or supplements that you can buy without a prescription
from your pharmacy, supermarket or health food shop.
Medicines that may
increase
the effect of ZYAMIS include:
antiepileptics, (for treating epilepsy) e.g. phenytoin.
antibiotics, e.g. erythromycin, clarithromycin.
antifungals, e.g. ketoconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, posaconazole.
anti-ulcer medicines, e.g. cimetidine, ranitidine and omeprazole.
medicines used to treat blood pressure, e.g. diltiazem, verapamil.
some medicines used to treat HIV and AIDS, e.g. saquinavir, lopinavir/ritonavir combination.
narcotic analgesics (very strong pain killers), e.g. fentanyl.
medicines used to reduce fat in the blood, e.g. atorvastatin.
hypnotics (sleep inducing medicines).
sedative antidepressants (medicines used to treat depression that make you sleepy).
sedatives (medicines that relax you).
anaesthetics (for pain relief).
antihistamines (to treat allergies or cold).
muscle relaxant (e.g. baclofen).
Medicines that may
reduce
the effect of ZYAMIS include:
rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis).
St John’s Wort (a herbal medicine).
Echinacea.
Goldenseal.
Check with the patient’s doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure about what medicines,
vitamins or supplements the patient is taking and if they affect ZYAMIS.
4. How to use ZYAMIS?
How much to use
The dose is summarised in the table below:
|
Age Range
|
Dose
|
Weight Range
|
Colour of Packaging
|
|
> 6 months to < 1 year
|
2.5 mg
|
7 to <12 kg
|
Yellow
|
|
1 year to < 5 years
|
5 mg
|
12 to <21 kg
|
Blue
|
|
5 years to < 10 years
|
7.5 mg
|
21 to <29 kg
|
Purple
|
|
10 years and above
|
10 mg
|
≥ 29 kg
|
Orange
|
The recommended dose for adults is 10 mg. A second dose should only be given in accordance
with either the patient’s Emergency Medication Management Plan, or as authorised by
the medical practitioner.
The full contents of the oral syringe should be given.
In the event of a seizure, the parent or caregiver must follow the instructions in
the patient’s Emergency Medication Management Plan.
When to use ZYAMIS
ZYAMIS should be used when the patient is having a seizure (fit).
Care must be taken when administering the product to avoid the risk of the person
choking.
If the person is having a seizure ('fit'), allow their body to move freely and do
not try to restrain them. Only move the person if they are in danger from the surroundings,
for example, a road, open water, hot cooking appliances, fire or sharp objects.
Support the person’s head with something soft, such as a cushion or your lap.
Do not use if the medicine has passed the expiry date shown on the secondary packaging
and syringe or if the syringe is damaged.
Do not give this medicine if you notice that the solution is not clear (e.g. if cloudy
or white particles are present).
How to give ZYAMIS
Always give this medicine exactly as a doctor has told you. Check with a doctor or
pharmacist if you are not sure. The patient’s doctor should give the parents or caregivers
instructions on how to give ZYAMIS and what to do if the seizure does not stop.
ZYAMIS is for buccal use only which means that it is only to be used in the mouth.
ZYAMIS must not be injected. Do not attach a needle to the syringe.
|
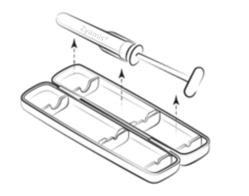
|
Step 1
Pull the tamper evident tab on the side of the plastic outer case, open it and take
the syringe out.
|
|
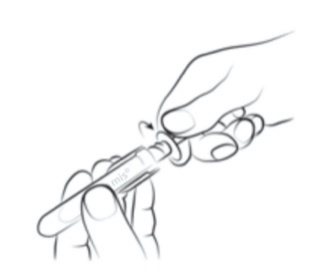
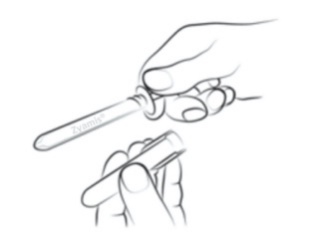
|
Step 2
Holding the clear finger grips, unscrew the amber sheath cap in an anti-clockwise
direction and remove the amber sheath cap.
|
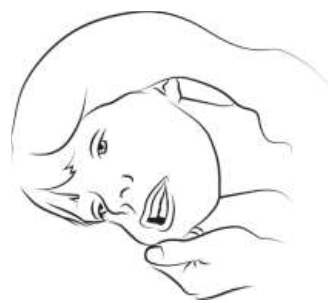
|
Step 3
Gently roll the person onto one side (recovery position) if safe and practical to
do so. Using your finger and thumb, gently pinch and pull back the patient’s cheek.
Open their lips and place the tip of the syringe into the back of the space between
the inside cheek and the lower gum (buccal cavity).
|
|
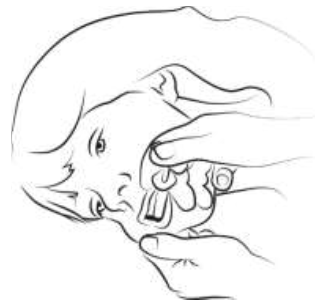
|
Step 4
Slowly administer approximately half of the solution to the buccal cavity on one side
of the mouth, and then administer the remainder slowly to the other side, by pressing
the syringe plunger until it stops. If it is particularly difficult to get the syringe
into one buccal cavity, then administer the whole dose over a duration of 4 – 5 seconds
into the other buccal cavity. Dispose of the syringe and cap safely.
|
|
Step 5: Watch breathing and seizure activity while they remain lying on their side
in the recovery position.
|
|
Step 6: Note the time that the seizure started, when the ZYAMIS was given and when
the seizure stopped.
|
If the person’s condition does not improve
Seek emergency medical assistance – telephone for an ambulance immediately – if the
patient’s seizure does not stop shortly after administering ZYAMIS.
Follow the instruction you have received from the patient’s doctor on how to act in
this situation.
If the person’s condition improves but their seizure ('fit') then starts again
Seek emergency medical assistance – telephone for an ambulance immediately.
A second dose of ZYAMIS should not be given without medical advice.
If you use too much ZYAMIS
If you think that you have used too much ZYAMIS, the patient may need urgent medical
attention.
You should immediately:
phone the Poisons Information Centre
(by calling
13 11 26), or,
contact your doctor, or,
go to the Emergency Department at your nearest hospital.
Signs that a patient has been given too much ZYAMIS may be:
Drowsiness, tiredness, fatigue.
Confusion or feeling disorientated losing their co-ordination.
developing muscle weakness.
low blood pressure – this can make them feel dizzy and faint breathing difficulties.
Keep the syringe to show to the ambulance staff or doctor.
You should do this even if there are no signs of discomfort or poisoning.
5. What should you know while using ZYAMIS?
Things you should do
If the patient is going to have an inhaled anaesthetic (one that the patient breathes
in) for an operation or for dental treatment, it is important to tell the doctor,
dentist or ambulance officer that they have been given ZYAMIS.
Remind any pharmacist, doctor or dentist you visit that the patient is taking ZYAMIS.
Things you should not do
Although highly unlikely, the patient must not drink alcohol if he or she has been
given ZYAMIS.
The patient must not be given a grapefruit juice to drink if using ZYAMIS to control
generalised convulsive seizures. It may increase the sedative effect of ZYAMIS, causing
more sleepiness.
Driving or using machines
ZYAMIS may make the person sleepy, forgetful or affect their concentration or coordination.
This may affect their ability to perform skilled tasks such as driving, riding a bicycle,
or operating machinery. After receiving this medicine, the person should not drive,
ride a bicycle or operate machinery until they are completely recovered. Please discuss
with the doctor if you need further advice.
Drinking alcohol
Although highly unlikely, inform the patient’s doctor if he or she drinks alcohol.
Alcohol may increase the sedative effects of ZYAMIS and make the patient very sleepy.
Although very unlikely, inform the patient’s doctor if he or she has an addiction
or history of abuse of alcohol, opiates or other drugs.
Looking after ZYAMIS
Keep ZYAMIS in the original package in order to protect from light.
Store ZYAMIS below 25°C. Keep the container in a cool, dry place and away from direct
heat and sunlight. Do not put the product in the fridge or freezer.
The medicine contains no preservatives. The medicine is for single use in one patient
only. Discard any residue.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the label. The
expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Keep it where young children cannot reach it.
Getting rid of any unwanted medicine
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater.
If you no longer need to use this medicine or it is out of date, take it to any pharmacy
for safe disposal.
These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Are there any side effects?
All medicines can have side effects. If the patient experiences any side effects,
most of them will be minor and temporary. However, some side effects may need medical
attention.
See the information below and, if you need to, ask your doctor or pharmacist if you
have any further questions about side effects.
Less serious side effects
Serious side effects
|
Serious side effects
|
What to do
|
|
Signs of an allergic reaction which may include a sudden rash, itching or lumpy rash
(hives), swelling of the face, lips, tongue or other parts of the body, pale skin,
a weak and rapid pulse or feeling of loss of consciousness.
Breathing problems or complications, sometimes causing the breathing to be very slow,
shallow or stop.
Heart attack. Signs could include chest pain which may spread to the neck and shoulders
and down the left arm.
|
Call your doctor straight away, or go straight to the Emergency Department at your
nearest hospital if you notice any of these serious side effects.
|
Tell the doctor or pharmacist if you notice anything else that may be making the patient
unwell. Other side effects not listed here may occur in some people.
Reporting side effects
After the patient has received medical advice for any side effects he or she may experience,
you can report side effects to the Therapeutic Goods Administration online at
www.tga.gov.au/reporting-problems . By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of
this medicine.
Always make sure you speak to the doctor or pharmacist before the patient decides
to stop taking the medicine.
7. Product details
This medicine is only available with a doctor's prescription.
What ZYAMIS contains
|
Active ingredient
(main ingredient)
|
Midazolam (as maleate)
|
|
Other ingredients
(inactive ingredients)
|
ethanol
saccharin sodium
glycerol
purified water
sodium hydroxide
maltitol solution
|
Do not give this medicine if the patient is allergic to any of these ingredients.
What ZYAMIS looks like
ZYAMIS midazolam 2.5 mg/ 0.25mL oromucosal solution.
Each pre-filled, oral syringe (0.25 mL) contains midazolam maleate corresponding to
2.5 mg midazolam per 0.25 mL solution. The secondary packaging and syringe label are
yellow.
ZYAMIS midazolam 5 mg/ 0.5 mL oromucosal solution.
Each pre-filled, oral syringe (0.5 mL) contains midazolam maleate corresponding to
5 mg midazolam per 0.5 mL solution. The secondary packaging and syringe label are
blue.
ZYAMIS midazolam 7.5 mg/ 0.75 mL oromucosal solution.
Each pre-filled, oral syringe (0.75 mL) contains midazolam maleate corresponding to
7.5 mg midazolam per 0.75 mL solution. The secondary packaging and syringe label are
purple.
ZYAMIS midazolam 10 mg/ 1 mL oromucosal solution.
Each pre-filled, oral syringe (1 mL) contains midazolam maleate corresponding to 10
mg midazolam per 1 mL solution. The secondary packaging and syringe label are orange.
ZYAMIS midazolam (as maleate) oromucosal solution is a slightly viscous, clear colourless
to pale yellow solution for buccal administration presented in a pre-filled syringe,
single-use (needle free) oral syringe. Each oral syringe is individually packed in
its own container. Each pre-filled oral syringe contains a single dose of ZYAMIS.
Australian Registration Numbers
ZYAMIS 2.5 mg/0.25 mL ARTG 342690
ZYAMIS 5 mg/0.5 mL ARTG 342691
ZYAMIS 7.5 mg/0.75 mL ARTG 342692
ZYAMIS 10 mg/1 mL ARTG 342693
Who distributes ZYAMIS?
Clinect Pty Ltd,
120-132 Atlantic Drive,
Keysborough,
VIC 3173,
Australia.
Telephone: 1800 899 005
This leaflet was updated in April 2023.