axoCells™ Human iPSC-Derived Sensory Neurons, male donor, ≥3.2 million cells
Various environmental stimuli, such as touch, heat, and pain, trigger nerve cells known as sensory neurons. They are commonly used in microfluidic devices for cosmetic testing, pain models, and peripheral neurotoxicity models.
- Derived from human iPSCs
- Expression of the key nociceptive ion channels including Nav1.7, Nav1.8, Nav1.9, TRPV1, TRPM8 and TRPA1
- Assay-ready in just 21 days
- Functional relevance across multiple assays including capsaicin and menthol treatment, thermoception and neurite outgrowth with paclitaxel
- Designed for advanced in vitro model formats including co-culture, microfluidics devices and organ-on-chip platforms
Phenotypic characterization
Using immunocytochemistry, Axol Bioscience has thoroughly characterized their axoCells iPSC-derived sensory neurons to pinpoint the important markers.
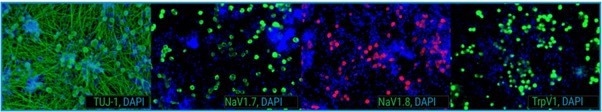
Figure 1. Immunocytochemistry of axoCells Sensory Neurons show expression of the key marker TUJ-1, indicative of neuronal development, and the nociceptive ion channels TrpV1, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8, responsible for the generation and maintenance of abnormal neuronal electrogenesis and hyperexcitability in the development of pathological pain. Image Credit: Axol Bioscience Ltd
Functional relevance
axoCells iPSC-derived sensory neurons have undergone comprehensive validation in various assays, such as the capsaicin and menthol challenge, thermoception, and neurite outgrowth.
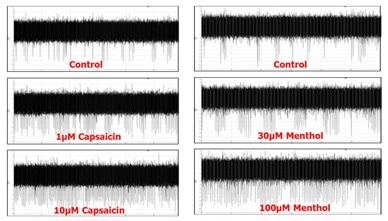
Figure 2. axoCells Sensory Neurons were challenged with capsaicin and menthol at 22 and 27 days, respectively. As early as 22 days, 90% of the neurons responded to the capsaicin challenge with increased spike measurements on a multi-electrode array (MEA) platform. Dose responses for both chemicals were observed, demonstrating their value in advanced in vitro models of pain, sensation, and peripheral neurotoxicity. Image Credit: Axol Bioscience Ltd
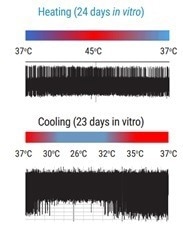
Figure 3. Electrophysiology recordings demonstrating increased firing of axoCells Sensory Neurons in response to heating and decreased firing in response to cooling. This demonstrates thermoception, an in vivo function, and shows the functional relevance of axoCells Sensory Neurons. Image Credit: Axol Bioscience Ltd
Reduced neurite length (axotomy) results from treating axoCells Sensory Neurons with the chemotherapy drug paclitaxel, illustrating the functional significance of the sensory neurons. This offers a model for both chronic peripheral neurotoxicity and acute insult.
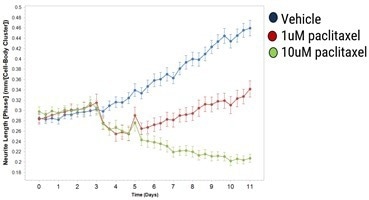
Figure 4. Response of day 25 axoCells Sensory Neurons to paclitaxel, a chemotherapy reagent, applied at 2.6 days (arrowhead) with wash-off at 4.6 days (arrow). Image Credit: Axol Bioscience Ltd
fQC for axoCells Sensory Neurons
In the progression of the quality chain, Axol has delved into functional QC (fQC), assessing cell efficacy and performance in biologically relevant assays. This standard will enhance the translational potential in advanced in vitro models and bolster confidence in the cells' physiological relevance.
axoCells Sensory Neurons have been fine-tuned for in vitro pain models. fQC will employ a multi-electrode array to gauge responses to capsaicin at concentrations of 1 µM and 10 µM.
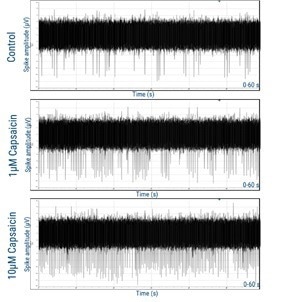
Figure 5. axoCells Sensory Neurons demonstrating response to 1 µM and 10 µM capsaicin at 22 days, measured on the Axion Maestro Pro multi-electrode array (MEA) system. Image Credit: Axol Bioscience Ltd
Read more about fQC
Product information
Source: Axol Bioscience Ltd
| Product Name |
Cells only code /
1 vial |
Quantity* /
per vial |
Kit**
code |
axoCells™ Human iPSC-Derived Sensory
Neurons, new-born male donor, ≥3.2 million cells |
ax0555 |
≥3.2 million cells |
- |
axoCells™ Human iPSC-Derived Sensory
Neurons, male donor, ≥0.5 million cells |
ax0055 |
≥0.5 million cells |
ax0157 |
*Number of viable cells post thaw
**Kit contains cells and one of each item listed in the media and supplements table
axoCells™ - Neurons and neuroinflammatory cells