Hazardous waste created by healthcare institutions totals 20 to 25% and may contribute to many health and environmental risks if not managed and destroyed appropriately. Healthcare facilities and hospitals are increasing worldwide. Therefore, hazardous waste management and disposal is becoming a serious issue.
What is Biohazardous Waste?
Biologically derived waste or a waste type contaminated with biological materials is the definition of biohazardous waste and includes any biological process, whether medical, clinical, veterinary or resulting from animal processing produce biological tissue, fluids or potentially infectious materials.
Any items or implements used in these processes have a high contamination risk. If left unmanaged, they can often become more hazardous with serious environmental and health implications. Per hospital bed per day, high-income countries generate an average of up to 0.5 kg of hazardous waste. Conversely, low-income countries generate 0.2 kg.
In 2017, approximately 273,559 tons of medical waste was disposed of in England, representing only a fraction of the total biohazardous waste disposed of annually in the UK alone. On a global scale, a wide variety of waste will lead to higher numbers. This exponential growth, if left unmanaged, can manifest as severe environmental pollution.

Image Credit: Inciner8
Where is Biohazardous Waste Generated From?
The types of organizations generating waste include:
- Dental practices
- General practices
- Health clinics
- Hospitals
- Opticians
- Veterinary practices
- Pharmacies
- Podiatrists
- Practices offering alternative treatments
- Private and independent healthcare organizations
- Research facilities
- Voluntary organizations
- Residential homes with and without nursing care
- Other non-healthcare practices that produce healthcare-type waste (such as tattooists and body piercing studios)

Image Credit: Inciner8
What are Some Biohazard Examples?
Biohazardous waste includes human body fluid, human blood and blood products, microbiological wastes (specimen cultures, discarded viruses or equipment used to transfer or mix cultures), pathological waste (unfixed human tissue or waste biopsy materials) and sharps waste (IV tubing, needles and scalpels).
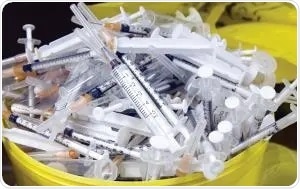
Image Credit: Inciner8
What are the Regulations for Disposing of Biohazardous Waste?
Hazardous Waste Regulations necessitate that most premises producing hazardous waste are registered with the EA in England and Wales. If they produce less than 500 kg of hazardous waste in any period of 12 months, some premises are exempt from registration.
The Waste Bag Classification System
The testing, analysis and classification of biohazardous waste are always critical. The waste bag classification system, which is issued by the government, gives guidelines on how waste should be sorted and temporarily stored before treatment and disposal.
Orange bins are for the storage and disposal of sharps not containing or contaminated with medicines, for example, sharps for blood samples and acupuncture.

Image Credit: Inciner8
Yellow bins are used for the storage and disposal of sharp wastes contaminated with or containing medicines or anesthetics.
Red Bags are for the disposal of solid or liquid items contaminated with blood or other waste with infectious materials.
Purple bins are for the disposal of sharps and medicines with cyto-toxic or cyto-static content or contamination.
Blue bins are used for the disposal of out-of-date drugs, used drug denaturing kits and discarded items used for pharmaceutical handling, including bottles or boxes with residues, gloves, masks, connecting tubes, syringe bodies, drug vials and anatomical waste.

Image Credit: Inciner8
Waste auditing is also an important means of managing waste, disposal, and volumes and frequency of waste types. Precise regulations for disposing of biohazardous waste are strictly controlled. Waste management is important for biohazardous waste to prevent disease and infection risks to anyone who may come into contact with it.
Why is it so Important to Follow Incinerator Legislation?
Though widely practiced, the incineration of waste has been inadequate or the incineration of unsuitable materials results in pollutants being released into the air and ash residue. The incineration of heavy metals or materials with a high metal content (in particular lead, mercury and cadmium) can lead to the spread of toxic metals in the environment.
Modern incinerators operating at 850-1100 °C, fitted with gas-cleaning equipment, are the only ones able to comply with the international emission standards for dioxins and furans. Informing your local authority and environmental agency of what materials you are burning is vital. Once aware, they can approve or disapprove your incinerator and, to avoid any environmental concern, it is important to follow regulations for bio hazardous waste disposal.

Image Credit: Inciner8
The Benefits of Incineration
Due to high temperatures during incineration, chemicals or any contaminated supplies that pose a risk to health can be destroyed. Incineration ensures the complete destruction of hazardous waste that would otherwise go to a landfill, which can be very dangerous as there is a high risk of ground pollution. Infected waste can pollute the ground, which could enter the food and drink supply.
Why Choose Inciner8?
Knowing the importance of promptly providing the right products to the right locations, Inciner8 has many years of experience dealing with biohazard emergencies.
Inciner8 has delivered solutions to hospitals and large health clinics worldwide for years and understands the importance of total destruction at the source. The company’s range of hazardous waste incinerators are specifically designed to manage many types of medical and hazardous waste in most climates and conditions.

Image Credit: Inciner8
About Inciner8
Inciner8 are a globally respected manufacturing organisation offering a range of Incinerators for all applications in the waste management industry, our products are specifically designed with clean air incineration at the forefront of our product development for Medical, Animal by product and General Municipal waste streams.
After many years in the industry with a track record second to none we have become the company that existing and new clients from around the world come to for their incineration solutions
On top of supplying a range of standard models we have developed a bespoke service for specialist markets and requirements thus ensuring we cater for the needs of this growing industry.
Environmental awareness is always a factor in waste management, inciner8 realise the importance of this and continue to demonstrate full commitment in striving to understand and deliver solutions based on individual country regulations and standards, this has been recently enhanced by our range of products specifically launched to provide an extensive range of pollution control systems and heat recovery options.
Inciner8 - Corporate Intro
We are very proud of our company and Brand, our continued focus is to ensure we enhance that position on a global basis with new product development, listening to our clients as part of that process and communicating consistently in every aspect of our daily activity to keep our valued clients abreast of market changes and future developments from Inciner8.
Being a global leader comes with great responsibility, we value feedback as we continue daily to educate our people to ensure they give the most authoritive and educational information to our clients, which is why we employ highly skilled technicians and thermal treatment experts to support all of our client requirements in the decision making process in sourcing environmentally friendly quality products from Inciner8.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.