A stomach ache is a term used to describe cramps or a dull ache in the abdomen. Usually, a stomach ache is short-lived and not a cause for concern. Stomach pain that is severe is more likely to be cause for concern, especially if it occurs unexpectedly and suddenly, in which case it should be treated as a medical emergency.

Image Credit: CHAjAMP / Shutterstock.com
Whether the stomach pain is mild, sharp, or feels like cramps, the pain can have various different causes. Some of the most common causes of stomach ache are described below.
Indigestion
Also called dyspepsia, indigestion refers to a full and uncomfortable feeling in the stomach after eating. Indigestion may be accompanied by a burning sensation in the upper part of the stomach.
Indigestion may be a sign of an underlying issue such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), gall bladder disease, or ulcers; therefore, the treatment for this condition will depend on its cause.
Indigestion is a common problem; however, several factors can cause certain individuals to be more susceptible to this condition. Some of the risk factors for indigestion include:
- Gastroparesis, which is a condition in which the stomach fails to empty fully. Gastroparesis is a common problem among people who have diabetes.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Stomach infection
- Pancreatitis
- Thyroid disease
- Stomach cancer, although this is rare
Some medications that may lead to indigestion include:
- Aspirin and other analgesics
- Thyroid medications
- Birth control pills
- Steroids
- Certain antibiotics
Some lifestyle factors that may lead to indigestion include:
- Eating too much, too quickly, or while stressed
- Excess alcohol intake
- Stress
- Tiredness
- Smoking
Constipation
Constipation refers to difficult bowel movements or bowel movements that occur less frequently than usual. Constipation is not usually serious.
Bowel movements vary between individuals, with some people finding it is normal for them to have bowel movements three times a day, whereas others may only have them twice a week. Generally, no bowel movements for more than three days is too long. This can lead to the hardening of feces, which makes it difficult to pass.
Some causes of constipation can include:
- Dietary changes
- The use of antacids that contain calcium or aluminum
- IBS
- Inactivity
- Lack of water or fiber
- Pregnancy
- Overuse of laxatives
- Some medications, such as antidepressants and iron supplements
- Hypothyroidism
- Stress
Gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis is a condition where the stomach and intestines become irritated and inflamed, usually as a result of a bacterial or viral infection. Pain in the stomach is usually accompanied by diarrhea and vomiting, with some individuals also reporting a fever and headache.
Gastroenteritis can be spread in many ways, some of which include:
- Contact with someone who has the condition
- Intake of contaminated food or water
- Failing to wash the hands after using the toilet
Gastroenteritis is most commonly caused by a virus, usually norovirus or rotavirus. Norovirus is the most common cause of severe gastroenteritis in the United States, whereas rotavirus is the most common cause of gastroenteritis in young children and infants. Gastroenteritis can also be triggered by Campylobacter bacteria and salmonella, which are usually spread as a result of the consumption of undercooked poultry or eggs.
IBS
IBS is a collection of symptoms that occur together including stomach pain, cramping, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. The condition can cause intestinal damage and can have a significant effect on a person’s life.
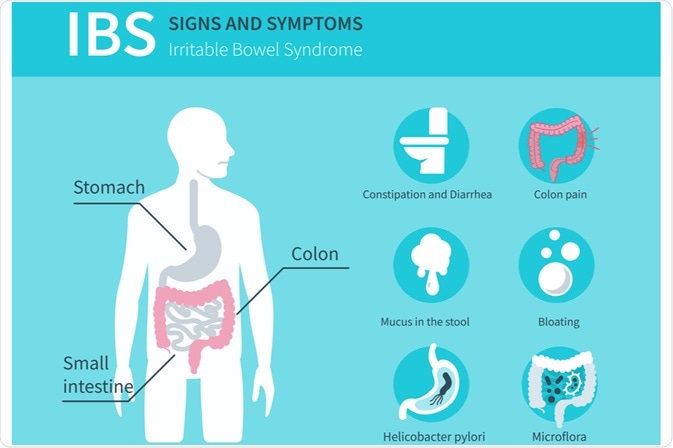
Image Credit: Irina Strelnikova / Shutterstock.com
The cause of IBS is unknown; however, some suggested triggers for this condition include an overly sensitive immune system or colon. Bacterial infection in the gastrointestinal tract can also cause post-infectious IBS.
Food poisoning
Food poisoning occurs as a result of eating toxic, contaminated, or spoiled food, which leads to vomiting and diarrhea. Food poisoning is a common problem, with one in six individuals in the United States experiencing it every year.
Usually, food poisoning is triggered by one of the following three factors:
- Bacteria – Salmonella is the most common cause of serious food poisoning in the U.S.; however, other culprits include E. coli, listeria, Campylobacter, and C. botulinum.
- Parasites – The most commonly occurring parasite to cause food poisoning is toxoplasma, which is usually found in cat litter boxes. Parasites can go undetected in the intestine for years, but people with weakened immune systems and women who are pregnant are at the greatest risk of serious side effects if parasites make their way into the intestine.
- Viruses – Some of the viruses that cause food poisoning include norovirus, sapovirus, rotavirus, and astrovirus, all of which cause similar symptoms.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: May 6, 2021