There are several different causes of epididymitis, including sexually transmitted infections (STIs), urinary tract infections (UTIs), prostate enlargement, as well as surgery or other procedures involving the renal system. In some cases, the exact cause of epididymitis is not known, which is referred to as idiopathic epididymitis.
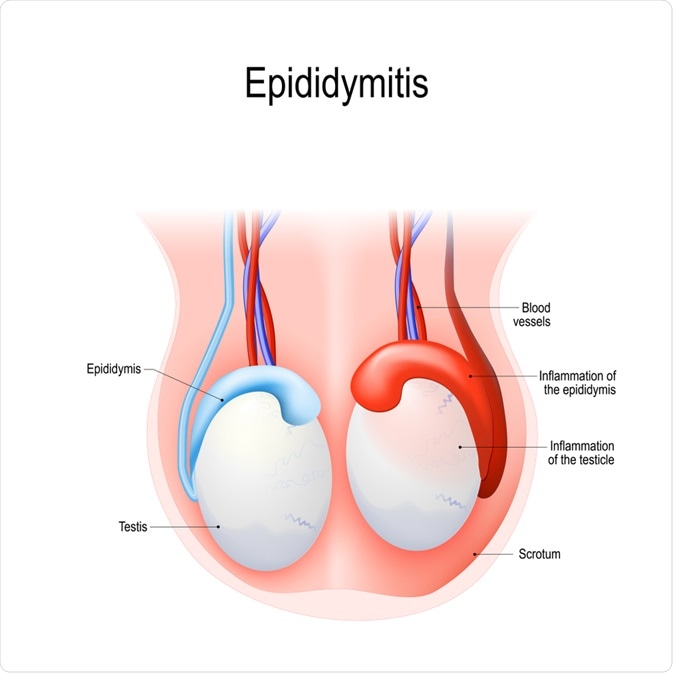
Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock.com
Although men of any age can be affected by epididymitis, the condition is most common in young men aged between the ages of 19 and 35. Men who engage in sexual activities with multiple partners without the use of a condom are most likely to get the condition. Men with an uncircumcised penis are also at an increased risk.
STIs
The most common causes of epididymitis are STIs such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. This cause is most likely to cause epididymitis in young men who have unprotected sex, regardless of their sexual orientation. Men who have sexual intercourse with more than one partner without using condoms are at the highest risk of suffering from epididymitis.
Chlamydia infections are estimated to account for more than half of all epididymitis cases in men younger than the age of 35. Other pathogens that may be associated with causing an STI and subsequent epididymitis include Neisseria gonorrhea, Treponema pallidum, Gardnerella vaginalis, and Trichomonas species.
UTIs
UTIs are much less common in men than women due to the increased length of the urethra, which makes it more difficult for bacteria to reach the bladder and proliferate to cause an infection. Children or older men with epididymitis are more likely to have the condition caused by a UTI.
E. coli or Pseudomonas bacteria are the most common UTI-causing pathogens that can lead to epididymitis as a result of:
- Enlarged prostate gland pressing on the bladder
- Insertion of catheter into the urinary system
- Surgery to the prostate gland, bladder, or groin region
Surgery or trauma to the groin region
Epididymitis may also be caused by physical trauma or surgery to the groin region. This includes:
- Structural abnormalities of the urinary tract
- Surgery to the prostate, bladder, or groin region
- Urine backflow associated with an enlarged prostate or heavy lifting
- Enlarged prostate pushing against the bladder
- Groin injury
Recent surgery to the urinary tract may interfere with the structure of the epididymis or the surrounding tissues, resulting in inflammation and symptoms of epididymitis.
Additionally, men with an uncircumcised penis are at a heightened risk of the condition, although this is thought to be linked to an increased susceptibility to infection in the area.
Causes, symptoms and management of Epididymitis - Dr. Teena S Thomas
Medications
Amiodarone, which is a medication that is used to manage arrhythmias or an abnormal heart rhythm, has also been associated as a causative factor of epididymitis. Low doses of this medication are not linked to an increased risk of epididymitis; rather, higher doses may cause the condition.
Other health conditions
There are several other health conditions that are associated with an increased risk of epididymitis, which include mumps, tuberculosis (TB), and Behcet’s disease.
Idiopathic epididymitis
Idiopathic epididymitis is a term used to describe cases of epididymitis when the exact cause cannot be identified. The condition may result from various circumstances, but there are no obvious risk factors that are likely to be associated with causing the condition.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Nov 17, 2022