Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that involves the degradation of joints, articular cartilage, and subchondral bone as a result of mechanical stress on the area.
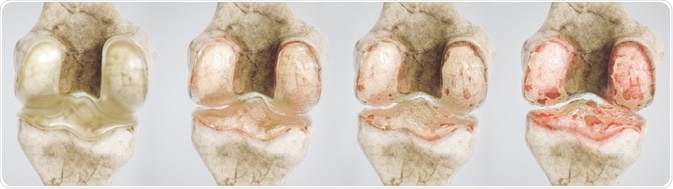
Image Credit: Crevis / Shutterstock.com
Introduction
The word osteoarthritis is derived from the following Greek words:
- osteo which means “of the bone”
- arthr which means “joint”
- itis which means “inflammation”
Despite the name of this condition, the inflammation associated with the bones and joints in osteoarthritis is not a conspicuous feature. Although inflammation can result from the physical damage associated with osteoarthritis, it is not believed to cause the condition. This is a distinguishing factor between osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, which is more strongly linked to inflammation.
Epidemiology
Worldwide, it is estimated that approximately 250 million people are affected by osteoarthritis of the knee, comprising 3.6% of the global population. In fact, as of 2020, over 86.7 million people around the world were found to be affected by osteoarthritis of the knee, thus leading to a global incidence of 203 people for every 10,000. Approximately 80% of the population is likely to show radiographic evidence of bone degradation in the joints by the age of 65, although only 60% of those are likely to be symptomatic.
Up to one-quarter of all consultations with general practitioners are related to osteoarthritis. Additionally, almost all nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) prescriptions are indicated for the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Causes
Mechanical stress on the joints is the main reason for the development of osteoarthritis. Obesity is also strongly linked to this condition, as it increases the weight that the joints are required to support. In particular, the knees and hips of obese individuals are predominantly affected.
There is also a hereditary factor that is seen to predispose people to osteoarthritis, although in most cases additional risk factors are typically present.
Stages of Knee Osteoarthritis
Symptoms
Osteoarthritis is characterized by pain, tenderness, and stiffness of the affected joints. The joints in the hand, hips, and knees are most commonly affected, although it may also occur in the shoulder, jaw, or other joints of the body.
As a result of the pain and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis, freedom of the joints is often affected. To this end, individuals may find it difficult to partake in daily activities as usual, particularly if the activities involve fine movements of the joints.
The quality of life can be greatly reduced in individuals with osteoarthritis, as the pain can be inhibiting and thus make it difficult for people to live their daily lives as usual.
Image Credit: Lightspring / Shutterstock.com
Diagnosis
Clinical examination of the affected joints is typically the first step of diagnosing osteoarthritis. The affected joints often appear swollen and the patient will report significant pain in the area.
Confirmation of the diagnosis can be made with X-ray imaging. Characteristic changes to the joints, particularly involving the cartilage and bone in the area, are usually evident.
Treatment
For mild symptoms, treatment usually begins with the management of the risks of osteoarthritis and identifying methods to relieve pressure on the joints.
Losing weight is one of the most important first steps, as obesity is a strong risk factor of the condition and any excess weight will put unneeded stress on the joints.
Some physical therapies, such as hot and cold packs, can offer a benefit to help reduce pain or stiffness.
Medical therapy usually addresses the pain associated with osteoarthritis and simple analgesics are the treatment of choice. Paracetamol is the first-line choice, as it is associated with less severe side effects. NSAIDs can also be used, particularly for more severe pain, although they carry a greater risk of complications such as gastrointestinal ulceration and risk of stroke. Since NSAIDs may provide a suitable option, the potential risks of this type of therapy should be considered carefully.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Mar 17, 2021