Carbohydrates are one of the most essential food groups in the diet of all animals, including humans. They provide essential elements the body needs for instant energy production and various vital functions. While carbohydrates play a key role in a balanced diet, the human body can adapt to a low-carbohydrate intake by metabolizing fats and proteins for energy. Thus, while essential for optimal health, especially for brain function and physical activity, humans can survive on low-carb diets.
Carbohydrates | Organic Chemistry | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Chemistry
Carbohydrates are macromolecules composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O). In general, carbohydrates will have the formula of Cx(H2O)y.
Carbohydrates are classified based on the following chemical characteristics:
- The number of carbons
- The number of sugar units
- Location of the carbonyl (C=O) group
- The molecules' stereochemistry or chiral handedness, the latter of which refers to the configuration of the molecule, which may exist in different structural forms or isomers.
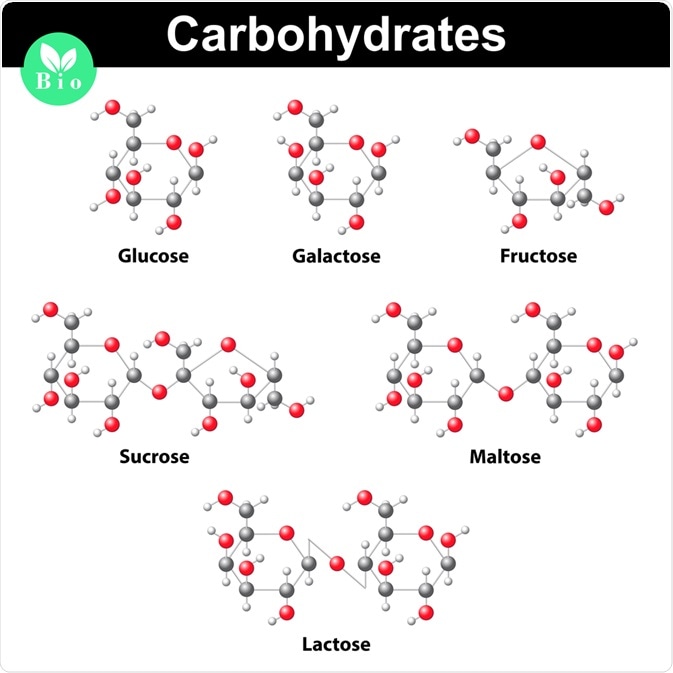
Image Credit: chromatos / Shutterstock.com
Classification by sugar number
When classified according to the number of sugars, carbohydrates are described as monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, or polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides consist of a single sugar unit. Some examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and glyceraldehyde. Depending on the number of carbon atoms, the molecule may be triose, tetrose, pentose, or hexose.
Whereas disaccharides contain two sugar units, oligosaccharides are carbohydrates comprising 3 to 10 sugar units.
The fourth and final type of sugar classification for carbohydrates includes polysaccharides, which contain more than 10 sugar units. These sugars may be storage polysaccharides, such as starch or glycogen, or structural polysaccharides, such as the cellulose found in plant cell walls. Structural peptidoglycans are polysaccharides found in the bacterial cell wall.
Monosaccharides and disaccharides are considered simple sugars as they break down easily, readily providing the body with energy. Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are more complex molecules and are referred to as complex carbohydrates.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 11, 2024