Cancer that forms in blood and bone marrow is called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, the word “chronic” denotes slow progress and the word "lymphocytic" means deceased white blood cells. Lymphocytes are the group of white blood cells that fight against any bacterial infections. Generally, elderly people are more likely to be affected by chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
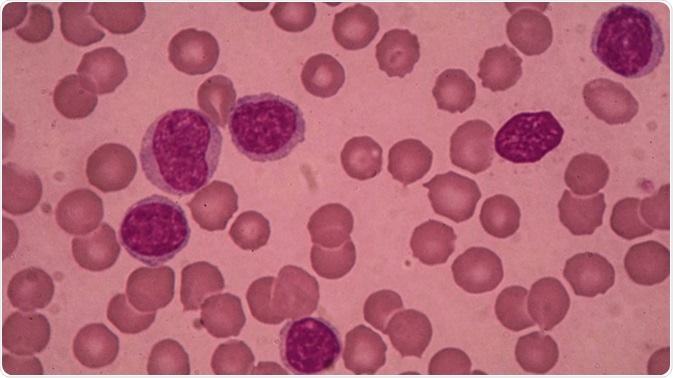
Blood smear showing chronic lymphoblastic leukemia (CLL). Image Credit: Medtech THAI STUDIO LAB 249 / Shutterstock
Genetic Causes
The root cause of the CLL is still unknown. Some doctors believe that a genetic mutation in DNA of the blood producing cells may be responsible for the production of ineffective and abnormal lymphocytes.
Lymphocytes with abnormal growth can affect organs and blood in the body, leading to complications. They can suppress the healthy cells present in bone marrow, thereby affecting the production of normal blood cells. Researchers and doctors are engaged in finding out the specific reason for the development of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Certain types of leukemia may be caused by exposure to radiation and chemicals such as benzene; however, CLL does not appear to be linked to these causes.
In some cases, the risk of developing certain types of cancer is high when the DNA mutations are inherited from parents, which is the case for CLL. Usually, the changes in DNA relating to CLL are not inherited before birth but may occur at any point of time in a person's life.
In CLL, chromosomal alterations are significant. However, scientists are still unsure about the specific genes that are involved in the changes that lead to leukemia. When B-lymphocytes in the immune system are in contact with antigens, or foreign substances, they grow and divide based on its program.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) - Mayo Clinic
Conditions that Cause CLL
The report of European study states that males who are affected by diabetes have an increased risk of developing chronic lymphocytic leukemia. On the other hand, females are not prone to an increased risk of developing CLL even if they have diabetes.
Several other studies have proved that people with concurrent medical conditions may also develop the chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Associated medical conditions include:
- pneumonia (chest infection)
- sinusitis
- auto immune hemolytic anemia
- chronic osteoarthritis
- inflamed prostate (prostatitis)
- shingles infection
However, these conditions may possibly be developed due to the decreased immunity in the starting phases of CLL.
First-degree relatives with Hodgkin lymphoma have an increased risk of developing CLL. There are some known proofs of CLL running in the family, but not witnessed often. Likewise, the first-degree relatives affected by monoclonal gammopathy (blood disorder) has greater chance of developing CLL.
Risk Factors
Electromagnetic fields: Exposure to electromagnetic fields is widely known as a risk factor for causing leukemia, with research to support the role that electromagnetic fields play a role in causing CLL. As everyone is exposed to electromagnetic radiation to some extent, there is no increased risk for the adults who have been exposed to typical exposure levels at home.
Decrease in immunity: People with low immunity levels have thrice the chance of developing CLL than the general population. After organ transplantation, medicines that are used to lower immune system and reduce the risk of rejection are associated with a higher risk of CLL.
Other risk factors of chronic lymphocytic leukemia include:
- Over the age of 60 years.
- People with fair skin.
- Family history of cancer in bone marrow and blood.
- Exposure to some chemicals such as insecticides and herbicides, Agent Orange, which was used in Vietnam War.
Complexity of Causes
The cause of chronic lymphocytic leukemia leads to the following complexities.
People who have chronic lymphocytic leukemia are also often affected by other infections, usually in the upper and lower parts of the respiratory tract. Severe infections are developed in some cases. People with CLL may develop diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, which is an aggressive form of cancer, also named as Richter's syndrome after Dr. Maurice Richter.
People affected by other cancer types such as lung and digestive tract cancer, skin cancer and melanoma are most likely to be affected by CLL. Immune system disorders can be caused by chronic lymphocytic leukemia in some patients, due to the immune cells helping to fight against the disease and infection by attacking the red blood cells and platelets.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Dec 29, 2022