An overgrowth of the fungus Candida albicans or other Candida speciesin the mouth is responsible for causing oral thrush. A small quantity of Candida fungus is naturally present in the mouth and digestive tract of most individuals, and it does not usually cause an infection and resulting symptoms. However, changes in the oral environment under certain circumstances can cause the fungus tomultiply and lead to the presentation of oral thrush.
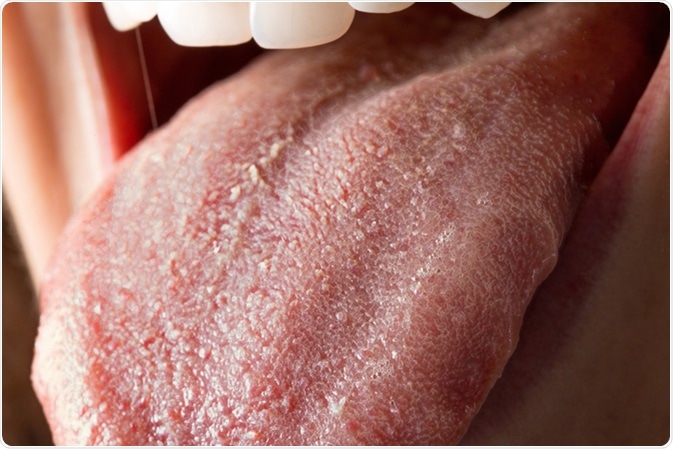
Tongue with Candida albicans infection. Image Credit: sruilk / Shutterstock
Medications
Some medications can increase the risk of Candida fungal overgrowth in the mouth and are associated with an increased risk of oral thrush.
Patients who have recently taken a course of broad-spectrum antibiotics, particular high-dose or longer courses, are at risk of the infection. Immunosuppressant drugs are also linked to a higher risk of oral thrush.
Additionally, people who take an inhaled corticosteroid medication, such as those commonly prescribed for the prevention and management of asthma, are more likely to be affected by oral thrush. Using a spacer to deliver the inhaled medication and rinsing the mouth with water after use can help to decrease the risk of developing oral thrush symptoms.
Some therapies used in the treatment of cancer, such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy, can also increase the risk of oral thrush.
Underlying Health Conditions
There are several health conditions that may predispose an individual to develop oral thrush, including:
- Diabetes and other endocrine disorder
- Iron deficiency
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Hypothyroidism
- HIV and other disorders involving immunosuppression
Dentures and Oral Health
People who wear dentures or false teeth, particularly dentures that have not been properly fitted to the mouth and gums of the individual, are more prone to oral thrush. Therefore, it is important for people with dentures to make sure theirs are fitted correctly and that they have regular dental check-ups to make sure they remain well fitted. Dentures should also be removed from the mouth at nighttime and cleaned appropriately before they are placed in the mouth again.
Poor oral hygiene can also contribute to a high risk of developing symptoms of oral thrush. In order to help reduce the risk of oral thrush, individuals should be encouraged to brush and floss teeth regularly, in addition to rinsing the mouth after meals.
Diet and Lifestyle Habits
People who smoke are more likely to be affected by oral thrush than people who do not.
Diet can also play a role in contributing to causing oral thrush. People who eat a diet high in sugar and other carbohydrates are more likely to be affected by the condition, for example.
Other
There are various possible causes of dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, including some medical conditions and certain medications. No matter the specific cause, having a dry mouth can increase the likelihood that an individual will be affected by oral thrush.
Significant hormonal changes in women, such as during pregnancy or when taking oral contraceptive pills, can also increase the likelihood of oral thrush.
Age is another factor that is associated with risk of oral thrush. Both very young children and babies and elderly people have a higher risk of developing oral thrush than older children and adults.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 27, 2019