The endocrine system releases hormones into circulation which affects different organs and regulates numerous homeostatic and growth functions within the body. Endocrine disruption chemicals alter the regulation of hormones which leads to the development of numerous diseases.
Skip to
Image Credit: Serhii Bobyk / Shutterstock
What is the role of the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is made up of numerous glands that produce and secrete hormones into the circulatory system to regulate the function of distant cells and organs. The major endocrine organs in humans are the hypothalamus, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, pituitary gland, pineal gland, testis in males, and ovaries in females. Hormones include amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes or prostaglandins.
The hypothalamus controls metabolism, body temperature, and secretes hormones. The hormones secreted by the hypothalamus stimulate or suppress the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. An example being the release of somatostatin from the hypothalamus that causes the pituitary gland to stop releasing growth hormones.
The pituitary gland is responsible for releasing growth hormones, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropin hormone, luteinizing hormone, follicle-stimulating hormone, and prolactin. Thyroid hormones are released from the thyroid and are responsible for controlling the body’s metabolism. The adrenal glands produce corticosteroids which regulate the metabolism, the immune system, and sexual function. The pineal gland produces melatonin which regulates the wake-sleep cycle.
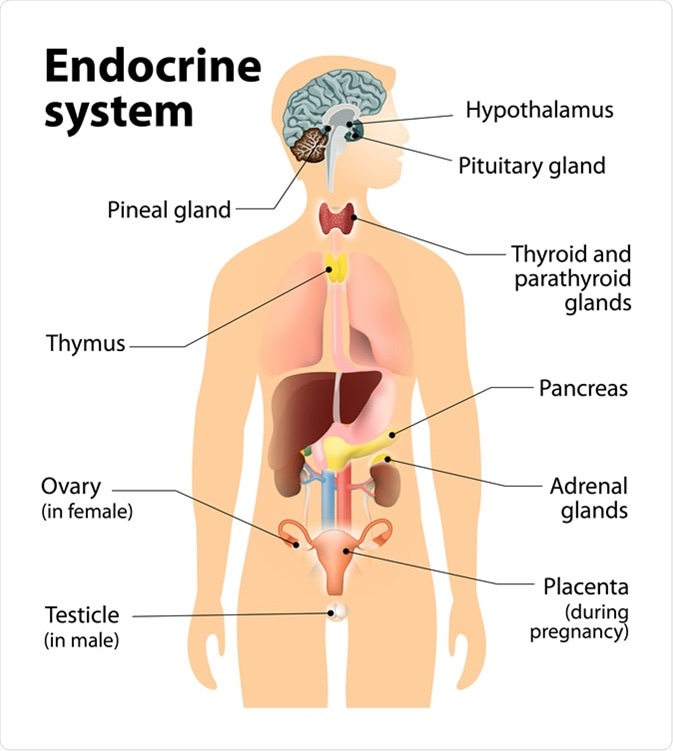
Endocrine system. Human silhouette with highlighted internal organs. Image Credit: Designua / Shutterstock
Endocrine disrupting chemicals
Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) are chemicals that interfere with the endocrine system affecting the way the body’s hormones work. EDCs act in varied ways, some of them mimic the function of hormones to induce a similar response to the hormone, and others block the action of natural hormones which prevents them from performing their roles. EDCs can also affect how hormones are made, stored, or broken down, as well as affecting how sensitive the body is to certain hormones. As a result of these actions, any exogenous chemical that interferes with any aspect of hormone control is referred to as an EDC.
Exposure to EDCs can come from many different environmental sources such as the air, food, and water. There are even EDCs that can dissolve through the skin to affect an individual. Examples of sources of EDCs include:
- Industrial chemicals and pesticides
- Packaging containers from consumer products
- Processed foods
- Soy-based products
- Household Dust
- Building materials
Effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals
As EDCs have the ability to affect many different hormones in many different ways, they have been linked to numerous different adverse health conditions which include decreased sperm quality and fertility, early puberty, altered nervous system function, altered immune system function, certain cancers, respiratory problems, diabetes, obesity, growth problems, cardiovascular problems, and many more.
Research has suggested that EDCs can act directly or indirectly promote adipogenesis making them obesogens (chemicals that disrupt normal lipid metabolism which can cause obesity). EDCs promote adipogenesis via facilitating lipid accumulation or affecting the energy balance within the body. Adipose tissues are mainly responsible for energy storage but they are also involved in numerous homeostatic endocrine functions such as the production of various endocrine molecules including cytokines (e.g. interleukin-6), prostaglandins, chemokines, proteins of the complement pathway (I.e. adipsin), angiotensinogen, glucose homeostasis factors (I.e. retinol binding protein), hemostasis factors (I.e. plasminogen activator growth inhibitor-1), and angiogenesis factors (I.e. vascular endothelial growth factor). The dysregulation of these pathways due to EDCs leads to obesity.
The production of reactive oxygen species and other biomarkers can cause oxidative stress. This impairs eNOS and other anti-atherosclerotic enzymes which exacerbates the progression of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is progressed by the infiltration of monocytes into the vascular endothelial wall then macrophages gather low-density lipoproteins lead to the formation of foam cells. This leads to the attraction of more T-cells, the proliferation of macrophage-smooth muscle cells, and the accumulation of collagen, which contribute to the formation of plaques. Obesity and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines due to EDCs will cause atherosclerosis to worsen. Atherosclerosis can lead to numerous cardiovascular diseases including coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, blood clots, and strokes.
Research into the effects of EDCs is ongoing and much is unknown about the effects on the human body. Avoidance of EDCs, where practical, is advised to minimize possible effects on health.
Further Reading
Last Updated: May 8, 2019