New results from a global survey of over 150 people living with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a life-threatening rare lung disease, demonstrate that while many patients were involved in treatment decisions, opportunities exist to improve the level of dialogue between patients and healthcare professionals.
The new findings from the survey, supported by Boehringer Ingelheim, are released to coincide with Rare Disease Day whose theme in 2017 is ‘research’. Encouragingly, the results show that 2 out of 3 patients (64%) were involved in the decision-making process for their IPF treatment.1 However, one out of every three patients (30%) said they were not involved in treatment discussions at all.1
It is vital that IPF patients are actively involved in the treatment decisions that affect them,”
“Open discussion about the lifestyle needs and priorities of patients is key to making the right choice of therapy that can slow the progression of IPF and other options that could assist with its symptoms and management.”
Liam Galvin, Secretary of the European Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis & Related Disorders Federation (EU-IPFF).
Patient and physician priorities
The new findings expand on insights from a 2015 global survey of over 400 pulmonologists. Analysis of the results shows that whilst patients and physicians agreed on one of the key treatment priorities – to maintain lung function for as long as possible – patient and physician views on other priorities regarding IPF treatment differed.1,2
In addition to maintaining lung function, patients identified reducing the risk of the condition suddenly worsening and being on a medication with manageable side-effects among their top priorities for IPF treatment.1,2
However, physicians cited being on a treatment that allows patients to continue day-to-day activities as normally as possible and being on an effective treatment independent of the stage of disease as their view of patients’ top priorities for IPF treatment besides maintaining lung function for as long as possible.2
This variation in what is seen as most important by patients and physicians highlights the benefit of open dialogue to compare these potentially competing priorities.
Patient involvement in decision-making process
The new survey findings also highlight that as many as 1 in every 3 patients involved in the decision-making process (30%) said that in coming to an agreement about appropriate medical treatment for their IPF, further discussion about treatment choice was not really needed and they strictly followed their doctor or nurse’s treatment recommendation.1
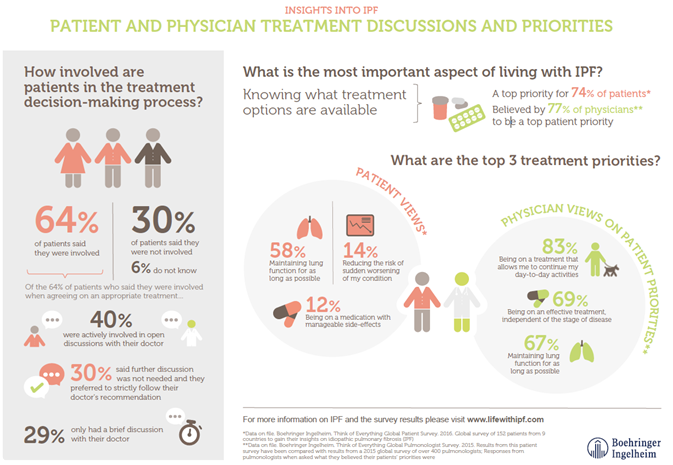
Furthermore, only 40% of those involved said that they were “actively” involved in the decision making-process before agreeing to a certain treatment.1
IPF can make a patient feel their world has turned upside-down, and they may want to leave treatment decisions to their doctor,”
“It is important that patients engage in discussion. This provides their doctor with relevant information so that the right decision is made at the right time on the appropriate treatment option that best suits their needs. This applies both for medication as well as other non-medical support that may be of benefit.”
Dr. Marlies Wijsenbeek, pulmonologist, Erasmus MC, The Netherlands.
Boehringer Ingelheim in fibrosing lung conditions
The global survey of 152 patients was designed to provide insights into IPF and the realities of living with the condition. These new findings have been released to support the 2017 Rare Disease Day theme of ‘research’.
As a leader in medical research, Boehringer Ingelheim is committed to transforming fibrosing lung diseases from fatal diseases to chronic, treatable ones. As part of this commitment, Boehringer Ingelheim is currently enrolling patients to participate in the SENSCIS™ STUDY – (Safety and Efficacy of Nintedanib in Systemic SClerosIS), which is the largest trial to date in people with systemic sclerosis who have also developed interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD).