Introduction
Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) is an advanced technique that enables real-time screening of protein drug targets and cellular compound interactions. The QCM-D technique is unique in its ability to sense changes in energy dissipation (softness) and can be used to detect both structural and conformational changes in whole cells and molecular layers.
These capabilities provide an important advantage, potentially proving useful in applications such as drug discovery, the identification of new pharmaceutical candidates and for gaining insight into the mechanisms of target interactions.
A Sensitive Platform for Cellular interactions
The QCM-D platform can be used to monitor cell-surface interactions in real-time. In order to demonstrate the effectiveness of this technique, human carcinoma cells were placed on the sensor ex-situ and their subsequent interaction with epidermal growth factor (EGF) was studied (Figure 1).
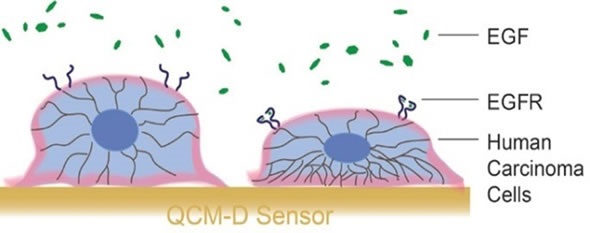
Figure 1. Illustration of carcinoma cells on a QCM-D sensor, and the exposure to EGF. Addition of EGF causes changes in the cytoskeleton.
The binding of EGF to the EGF receptor (EGFR) induced rearrangement of the cytoskeleton and altered the viscoelasticity of the cell layer, changes that were effectively detected by the QCM-D sensor.
Conformational Changes in Protein Structure
A number of publications have pointed at the QCM-D technique as an effective tool for screening protein drug targets. These assays rely on the conformational changes to a protein’s tertiary structure following the binding of small compounds. In this example, lysine analogues were added so that the unfolding of plasminogen could be probed. (Figure 2).
Conformational changes in the HIV-1 envelope protein were also examined. The His-tagged recombinant HIV-1 envelope protein was placed on the QCM-D sensor and its interactions with other compounds were monitored. For both studies, the changes in energy dissipation that occurred were essential to understanding the conformational events
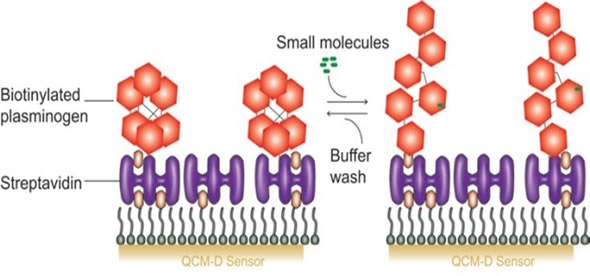
Figure 2. Plasminogen protein conformational change due to small molecule interaction.
Biomolecular Interactions and Drug Development
In drug development, a good understanding of the interactions between proteins or between DNA and proteins is crucial. Taking the estrogen receptor as an example, once a ligand binds to this receptor, it then binds to DNA.(Figure 3) By immobilizing biotinylated DNA and injecting estrogen receptors with or without ligands, the QCM-D approach can be used to study the interactions.
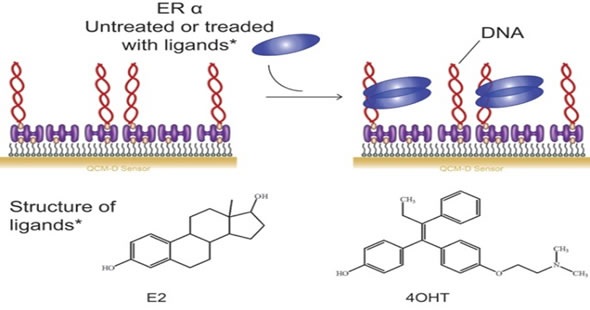
Figure 3. Outline of the estrogen-DNA binding assay and structure of the two ligands.
The QCM-D can also be used to study the self-oligomerization and protein aggregation processes that occur in diseases caused by protein misfolding. Measurements obtained through the QCM-D technique showed that the amyloid-beta peptide associated with Alzheimer´s disease forms oligomers that are softer than the monomers formed on interaction with a model surface. This finding may be related to the toxicity of amyloid-beta in Alzheimer´s disease.
Conclusion
The QCM-D provides an excellent platform for real-time measurement of cell-surface interactions and enables a better understanding of biomolecular processes occurring at the cellular level. These capabilities are potentially useful in applications relevant to the research and development of drugs.
About Biolin Scientific
 Biolin Scientific is a leading Nordic instrumentation company with roots in Sweden, Denmark and Finland. Our customers include companies working with pharmaceuticals, energy, chemicals, and advanced materials, as well as academic and governmental research institutes. Our precision instruments help discover better drugs faster, develop better solutions for energy and materials, and perform research at the frontiers of science and technology.
Biolin Scientific is a leading Nordic instrumentation company with roots in Sweden, Denmark and Finland. Our customers include companies working with pharmaceuticals, energy, chemicals, and advanced materials, as well as academic and governmental research institutes. Our precision instruments help discover better drugs faster, develop better solutions for energy and materials, and perform research at the frontiers of science and technology.
Biolin Scientific proprietary systems are based on nanotechnology and advanced measurement techniques. They have earned leadership in several industries through our commitment to scientific excellence and continuous product development.
Our commitment to customer service and application support is a key feature of our operations. We focus on working together with customers and building long-standing relations. Today, Biolin Scientific provides products and services in more than 70 countries around the world.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.Net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.