The human brain is comprised of a number of different regions. Each of these regions are vitally important with highly specialized functions. The brain is roughly divided into three parts which include the following:
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Brain stem or hind brain
The central part of the brain includes the brain stem and the midbrain. The function of the midbrain and has been largely preserved over years of evolution. The functions of the forebrain, however, have changed somewhat. The cortex is highly developed with a high capacity for complex thinking and problem solving.
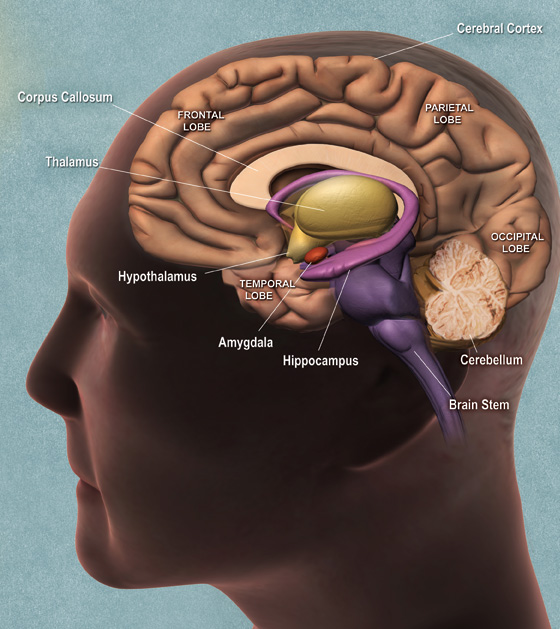
The brain stem
This part of the human brain is similar to animals of lower order and has not changed much with evolution. The brain stem contains vital structures including the medulla oblongata which controls breathing, heart rate, and digestion and the cerebellum which coordinates sensory input and maintains muscle movement and balance.
The mid-brain
This region of the brain is responsible for vision, hearing, temperature control, motor control and alertness. The midbrain also connects the brain stem to the thalamus, allowing for information to be relayed from the senses to the brain and back to the muscles. The midbrain also includes a limbic system which lies above the brain stem and under the cortex. It consists of a number of interrelated structures that regulate temperature control, hormones, and emotions. The limbic system also deals with long term memory.
The limbic system includes:
The hypothalamus - The hypothalamus regulates emergency responses such as the "fight or flight" response, as well as non-emergency vital processes such as feeding and reproduction. The hypothalamus also controls the release of hormones. Neurons affecting heart rate and respiration are concentrated in the hypothalamus.
The amygdala - This part of the limbic system regulates behaviour.
The hippocampus - This area is responsible for the formation, storing and organizing of memories.
The midbrain and the limbic system also form part of the reticular activating system (RAS). It is this area that regulates wakefulness and sleep.
The fore-brain
This region contains the cerebral cortex and surrounds the brain stem and midbrain. In humans, it is highly developed and has a very complicated structure. The forebrain is involved in thought and problem solving.
The cerebral cortex has two cerebral hemispheres and a folded, wrinkled surface. The folds in the layer are called the sulci. The top layer of the cortex is about two millimeters thick and has a total surface area of about 1.5 square meters. The two hemispheres work in co-ordination, although one side is dominant. For example, right handed people have a dominant left cerebral hemisphere.
The cortex is made up of four lobes which include:
The frontal lobe - This region of the brain occupies the front part of the skull and lies behind the forehead. The frontal lobe is associated with planning, decision making, voluntary muscle movement, processing speech, smell, and emotions.
The parietal lobe - This area of the brain processes sensory information and is responsible for determining spatial awareness, navigation and positioning. It is also involved in processing information related to taste, temperature and touch.
The temporal lobe - The temporal lobe is involved in processing visual and auditory information and controls some aspects of language perception, memory and emotion.
The occipital lobe - This is the visual processing centre of the brain and contains the largest proportion of the visual cortex region.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jun 20, 2023