Skip to:
Since the invention of the first prototype in the early 20th Century the electron microscope has allowed us to peer into the micromolecular world more deeply than ever.
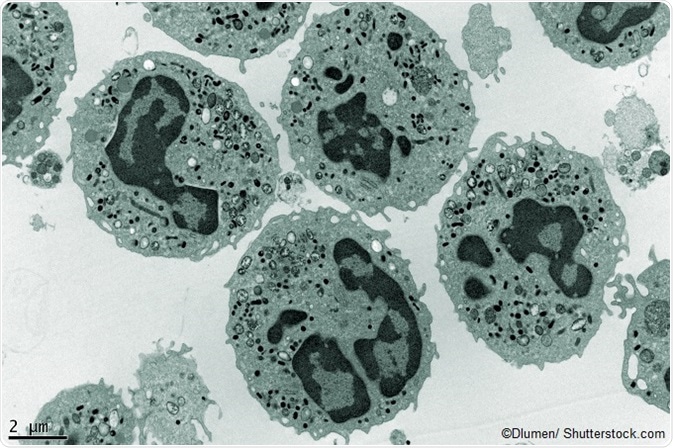
Image of blood clot using a scanning electron microscope.
By firing a concentrated “beam” of electrons at a sample (either a thin cross-section in the case of transmission electron microscopy or a three dimensional sample in the case of scanning electron microscopy) in a vacuum, biological and chemical structures can be revealed in ever more clarity, and a number of variations on the main techniques have been developed in recent decades.
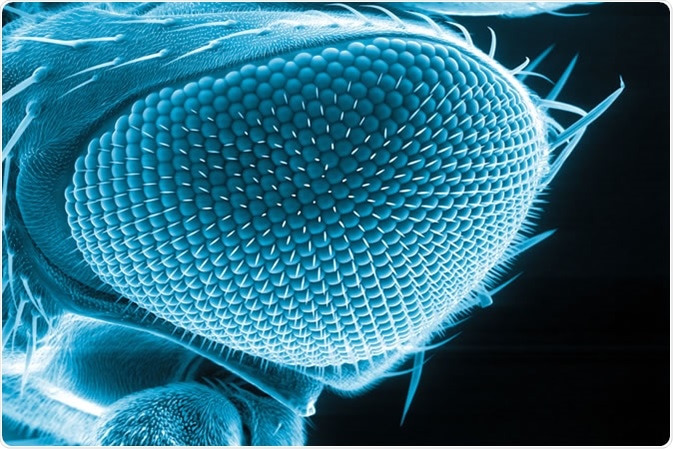
Eye of a fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, scanning electron microscopy Image Credit: Heiti Paves / Shutterstock
As with any scientific technique or technology, it is not without its disadvantages, but it does have several advantages for the researcher using it. Some of these are listed below.
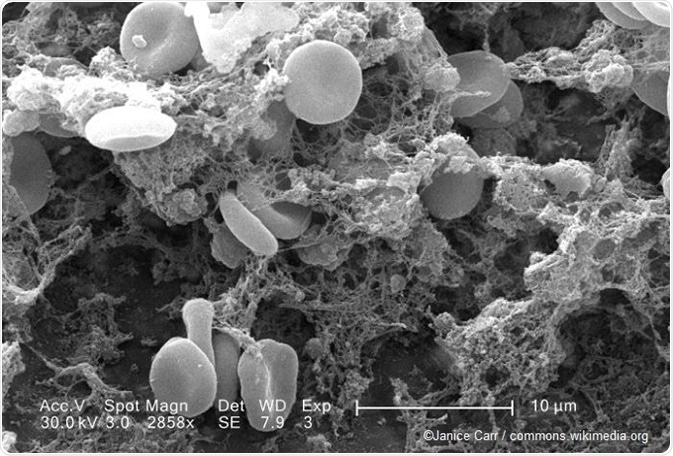

Image of human neutrophils using a transmission electron microscope.
Advantages of electron microscopy
Electron microscopy has several main advantages. These include:
- Magnification and higher resolution – as electrons rather than light waves are used, it can be used to analyze structures which cannot otherwise be seen. The resolution of electron microscopy images is in the range of up to 0.2 nm, which is 1000x more detailed than light microscopy.
- Diverse applications – Electron microscopy has a diverse range of applications in many different fields of research including technology, industry, biomedical science and chemistry. Examples of applications include semiconductor inspection, computer chip manufacture, quality control and assurance, analysis of atomic structures, and drug development.
- High-quality images – With proper training, an electron microscope operator can use the system to produce highly detailed images of structures which are of a high quality, revealing complex and delicate structures that other techniques may struggle to reproduce.
Disadvantages of electron microscopy
However, there are several disadvantages which may mean that other techniques, especially light microscopy and super-resolution microscopy, are more advantageous to the researcher. These include:
- Inability to analyze live specimens – As electrons are easily scattered by other molecules in the air, samples must be analyzed in a vacuum. This means that live specimens cannot be studied by this technique. This means that biological interactions cannot be properly observed, which limits the applications of electron microscopy in biological research.
- Black and white images – Only black and white images can be produced by an electron microscope. Images must be falsely colorized.
- Artefacts – These may be present in the image produced. Artefacts are left over from sample preparation and require specialized knowledge of sample preparation techniques to avoid.
- Cost – Electron microscopes are expensive pieces of highly specialized equipment. As most projects have limited budgets, it may prove detrimental to use an electron microscope in the research. However, running costs can be similar to alternatives such as confocal light microscopes, so the investment in a basic electron microscope is still worth considering even if budgetary concerns are a major factor in decisions against utilizing the technology.
- Size – Despite the advantages in technology over the years, electron microscopes are still large, bulky pieces of equipment which require plenty of space in a laboratory. Also, as electron microscopes are highly sensitive, magnetic fields and vibrations caused by other lab equipment may interfere with their operation. Consideration must be given to this if the researcher is looking to install an electron microscope in their laboratory.
- Training – Specialist operators are required to operate electron microscopes, and these can undergo years of training to properly use this technology.
Electron microscopy: A highly useful analytical technique
These advantages and disadvantages must be carefully considered by researchers and project managers. However, electron microscopy is a highly useful analytical technique which remains at the forefront of scientific research and with the right training and use can produce results which no other technology available can.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Oct 22, 2019