Mar 10 2014
Synthesis, Anti-tubulin and Antiproliferative Structure–Activity Relationship of Steroidomimetic Dihydroisoquinolinones
Tubulin, the building-block protein of cellular microtubules, is a well-validated cancer drug target: Disrupting tubulin polymerization affects cytoskeletal function and thus cell division. The vinca alkaloids, taxanes, and other taxane site binders have found wide therapeutic application and constitute one of the most successful classes of anticancer agent. Nevertheless, current drugs that target tubulin still suffer from limited therapeutic window, acquired resistance, lack of oral bioavailability, and problematic formulation.
As reported in ChemMedChem, Barry Potter’s research group at the University of Bath (UK), along with colleagues at the NCI (USA), Ipsen (France), and Imperial College London, focused on a natural steroidal lead for introducing a new set of modifications that confer good oral activity and delivery and that impart resistance to metabolism. 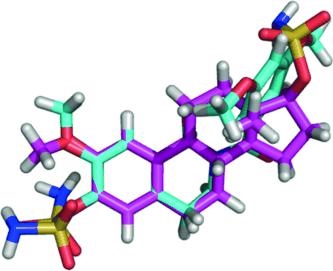
"Two compounds showed in vitro anti-angiogenic activity, and X-ray analysis of one reveals that electrostatic repulsion between two adjacent carbonyl groups [...] dictates adoption of a 'steroid-like' conformation that might partially explain the excellent in vitro activities," says Potter. Indeed, the most active compounds are nearly equivalent to another compound currently in clinical trials as inhibitors of tubulin assembly, and some were shown to be anti-angiogenic. Moreover, the compounds are easily synthesized and amenable to aqueous formulation.