The introduction of monoclonal antibodies as therapeutics for cancer has revolutionized the field.
To enhance the specificity and potency of antibodies, bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) are emerging, with the ability to bind two different antigens or two different epitopes on the same antigen. More than 85% of bsAbs in clinical trials are cancer therapeutics.
As of 2022, a total of six bsAbs have received approval by FDA and/or EMA in cancer immunotherapy (see Table 1), including the initially approved bsAb, Catumaxomab.
However, Catumaxomab was withdrawn from the European Union market in 2017, and three bsAbs were approved for marketing in 2022. By the end of 2023, there may be marketing application submissions for 5 bsAbs in late-stage clinical studies.
Over 600 bsAbs are currently being investigated, and the industry is predicted to grow to more than $30 billion over the next five years. As a result, big pharmaceutical companies have a growing interest in investigating and investing in this promising immunotherapy.
Table 1. BsAbs approved by EMA and/or FDA in cancer immunotherapy. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| BsAbs Name |
Brand Name |
Company |
Target 1 |
Target 2 |
Mechanism of Action |
Indications |
Approved by |
First Approval |
| Catumaxomab |
Removab |
Neovii |
CD3
(T cell) |
EpCAM (cancer cell) |
Recruitment and activation of T cells |
Malignant ascites |
EMA |
Apr 2009 (withdrawn in Jun 2017) |
| Blinatumomab |
Blincyto |
Amgen |
CD3
(T cell) |
CD19 (cancer cell) |
Recruitment and activation of T cells |
B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) |
EMA and FDA |
Dec 2014 |
| Amivantamab |
Rybrevant |
Janssen |
EGFR (cancer cell) |
c-MET (cancer cell) |
Blocking of dual signal pathways |
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) |
EMA and FDA |
May 2021 |
| Tebentafusp |
Kimmtrak |
Immunocore |
CD3
(T cell) |
gp100 (cancer cell) |
Recruitment and activation of T cells |
Unresectable or metastatic uveal melanoma |
EMA and FDA |
Jan 2022 |
| Mosunetuzumab |
Lunsumio |
Roche |
CD3
(T cell) |
CD20 (cancer cell) |
Recruitment and activation of T cells |
Relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma |
EMA and FDA |
Jun 2022 |
| Teclistamab |
Tecvayli |
Janssen |
CD3
(T cell) |
BCMA (cancer cell) |
Recruitment and activation of T cells |
Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma |
EMA and FDA |
Aug 2022 |
Mechanisms of action of bsAbs and emerging targets
BsAbs may be categorized based on their mechanisms of action (MoAs). Many bsAbs have been created to bridge T cells and tumor cells, which simultaneously bind to a tumor-associated antigen (TAA) expressed on tumor cells and CD3 on T cells.
This redirects the cytotoxic activity of effector T cells to destroy tumor cells (see Figure 1). The TAAs that are targeted by the approved cell-bridging bsAbs include CD19, EpCAM, CD20, gp100, and BCMA.
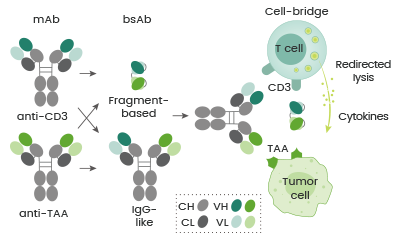
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of bsAbs bridging tumor cells and T cells. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
In addition to the bsAbs that are already approved, the TAAs of cell-bridging bsAbs that are being tested in current clinical trials include CD33, CD37, CD38, CD123, FLT-3, and CLEC12A for hematologic malignancies, and HER2, CEA, PMEL, PSMA, GPA33, GPC3, and B7H3 for solid tumors.
NK cells may also act as the effector in cell-bridging bsAbs. CD16 on NK cells is frequently utilized as the target for this bsAbs category. For instance, bsAbs that target CD30×CD16 are currently being evaluated in clinical trials for hematologic malignancies.
BsAbs that can block two mutually related signaling pathways through the targeting of two epitopes on tumor cells or in the tumor microenvironment are also widely studied.
The antigen pairs include VEGF×Ang-2, EGFR×c-MET, IGF‐1×IGF‐2, VEGF×DLL4, HER2×HER2, and HER2×HER3. The FDA approved Janssen’s Amivantamab (Rybrevant) that targets EGFR×c-MET for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment in May 2021.
BsAbs that block immune checkpoints, such as PD-1×LAG3, PD-L1×TIGIT, and PD-L1×CTLA-4, are a further category tested in clinical trials. Immune checkpoints have an inhibitory effect on immune cell activity.
BsAbs that simultaneously target two immune checkpoints are largely investigated for the treatment of solid tumors and potentially better the efficacy of checkpoint inhibition in comparison to monotherapy.
Akeso’s Cadonilimab (开坦尼®), a PD-1×CTLA-4 blocker, was approved in China in June 2022 for treating relapsed or metastatic cervical cancer. It is the first dual immune checkpoint inhibitor bsAb to be approved. BsAbs of immune checkpoints in combination with TAAs have also been developed, such as PD1×VEGF and PD1×HER2.
BsAbs that co-target T-cell-costimulatory molecules and immune checkpoints, such as CTLA-4×OX40 (CD134) and PD-L1×4-1BB (CD137), are currently under development.
BsAbs and targets beyond cancer
Due to their success in oncology, bsAbs are also being pursued for the treatment of other diseases, such as infections, autoimmune disorders, ophthalmic disorders, neurologic diseases, and rare diseases.
Since FDA approval of Roche’s Emicizumab (Hemlibra) for hemophilia A in 2017, which acts on coagulation factor IXa (FIXa)×FX, new avenues for the application of bsAbs in other diseases have been unlocked.
FDA approved Genentech’s Faricimab (Vabysmo) in January 2022, and this targets VEGF×Ang-2, to treat wet AMD and DME.
In Japan, in September 2022, Taisho Pharmaceutical’s Ozoralizumab (Nanozora), a humanized trivalent NANOBODY® compound consisting of one anti-HSA NANOBODY® and two anti-TNFα NANOBODIES®, was approved for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Regarding autoimmune diseases, some of the targets of bsAbs currently in development include CD79B, CD32B, TNF, IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-17F, IL-1α, and IL-1β.
The rapid success of bsAbs in cancer and noncancer programs has attracted much attention and investment to expand this field of therapeutics.
With the currently ongoing research in the discovery, preclinical, and clinical stages, bsAb therapy has a very promising future and brings hope to patients suffering from these different diseases that may not have many treatment options.
Supporting bispecific antibody development at Sino Biological
Sino Biological is world-leading in recombinant technology and is at the forefront of the bioreagents and contract research services industries.
Sino Biological has developed a wide range of extremely high-quality recombinant antibodies and proteins to aid the research and therapeutic development of bispecific antibody targets in immunotherapy and other diseases.
The company’s products include high-activity and high-purity proteins for c-MET, CD278/ICOS, CD3, CD16a, CD38, DLL4, CTLA-4, HER3, HER2, TIGIT, VEGFR2, 4-1BB, and more well-established and emerging targets.
Sino Biological offers a rapid and efficient bispecific antibody production service, using its vast expertise and experience in mammalian cell expression and proprietary technology platforms that are specifically optimized.
Starting from the antibody sequence, Sino Biological can deliver multiple bsAb formats, such as BiTE, Diabody, CrossMab, and DVD-IgG. Numerous bsAb projects have been completed with greater than 90% overall success rates, and yields of 250 mg/L or more have been achieved.
References
- Jin S, Sun Y, Liang X, et al. Emerging new therapeutic antibody derivatives for cancer treatment. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):39. Published 2022 Feb 7. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00868-x
- Kang J, Sun T, Zhang Y. Immunotherapeutic progress and application of bispecific antibody in cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1020003. Published 2022 Oct 20. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1020003
- Kaplon H, Crescioli S, Chenoweth A, Visweswaraiah J, Reichert JM. Antibodies to watch in 2023. MAbs. 2023;15(1):2153410. doi:10.1080/19420862.2022.2153410
- Nick T. The accelerating rise of bispecific antibodies outside of oncology. Biopharm Deal.Published 2018 Sep 28. https://www.nature.com/articles/d43747-020-00566-7
- Sheridan C. Bispecific antibodies poised to deliver wave of cancer therapies. Nat Biotechnol. 2021;39(3):251-254. doi:10.1038/s41587-021-00850-6
- Wang S, Chen K, Lei Q, et al. The state of the art of bispecific antibodies for treating human malignancies. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(9):e14291. doi:10.15252/emmm.202114291
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.