The small size, easy humanization, low immunogenicity, superior affinity and stability, high penetration, and sufficient levels of solubility make nanobodies crucial instruments for tumor diagnostics and treatment. They are also expected to transform antibody-based medication therapy.
The first nanobody in the world was licensed for sale in the European Union in 2018 to treat adult patients with acquired thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Over 20 nanobodies are now being investigated in clinical studies across the globe, most frequently in phase I or phase II.
What are nanobodies?
A form of antibody called a nanobody (Nb), commonly referred to as a single-domain antibody, is present in cartilaginous fish like sharks and rays as well as camelids like alpacas and dromedaries. It does not have light chains by nature and attaches to the antigens by means of many heavy chain regions.
With a size that is only one-tenth of the size of a typical antibody, single-domain antibodies with only heavy-chain variable regions (4 nm in length, 2.5 nm in diameter, and 12–15 kDa in molecular weight) are currently the smallest naturally-derived antigen-binding fragments. As a result, they are known as nanobodies.
Nanobodies and monoclonal antibodies both have three highly variable antigen-binding loops and four conserved framework regions (FR1–FR4) in their VH domains (CDR1–CDR3). Moreover, nanobodies have higher structural flexibility, which suggests a higher antigen affinity, contrasted to monoclonal antibodies, whose CDR1 and CDR3 loops are enlarged.
To prepare multi-specific antibodies and obtain a larger number of functions, thus achieving specific nanobody conjugations, nanobodies can also be designed with a combination of multiple functional domains.
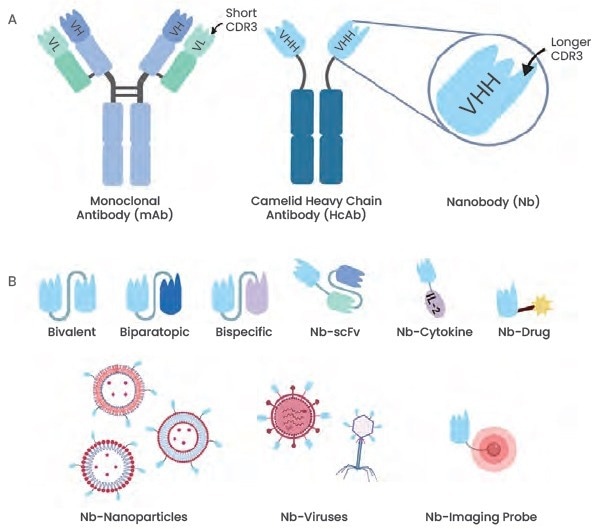
Figure 1. Illustration of the general nanobody structure and different nanobody types. Image Credit: https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01182
Use of nanobodies
In a variety of pathologic situations, including disorders of the central nervous system, infectious diseases, circulatory system, oncological, and inflammatory diseases, nanobodies can be widely applied and have shown promising results.
Nanobodies can be used for the recognition and therapeutic inactivation of checkpoint inhibitors, the activation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), the blocking of immunosuppressive cells, the neutralization of immunosuppressive molecules, the regulation of cytokines, and the development of CAR-T or CAR-NK cells, particularly in the field of cancer immunotherapy.
In the fields of treating and diagnosing tumors, nanobodies are also frequently used. In the absence of FC domains, nanobodies lose their ADCC or CDC activity and show minimal cytotoxicity. As nanobodies have limited cytotoxicity, conjugating them with toxins or anti-tumor drugs not only compensates for this limitation but also effectively delivers therapeutic drugs.
Similar to antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), nanobody-drug conjugates (NDCs) selectively kill tumor cells by conjugating toxins, chemotherapeutic drugs and target proteins to nanobodies through linkers. The next generation of clinical cancer diagnostics and therapies will therefore increasingly rely on nanobodies.
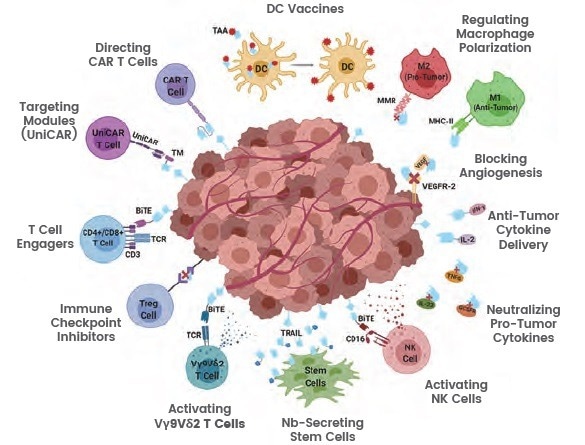
Figure 2. Illustration of nanobodies targeting a tumor microenvironment. Image Credit: https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.01182
Nanobody preparation
Nanobodies will be increasingly applied in the future; thus, it is essential to identify and choose the best methods for their preparation.
Immune libraries are typically used to create nanobodies. By immunizing camelids and utilizing phage display technology or MS spectral identification, suitable nanobodies are screened.
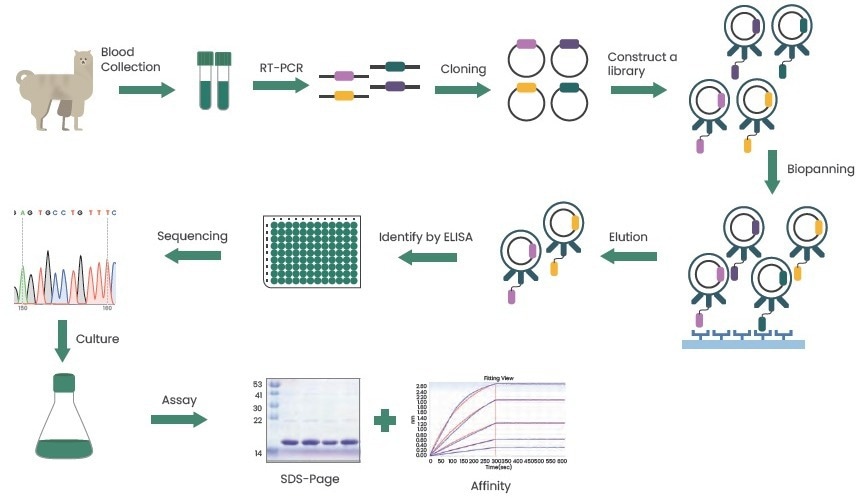
Figure 3. Preparation of nanobodies using phage display technology. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Technical services for the preparation of nanobodies at Sino Biological
Sino Biological has created and produced a nanobody platform with a 108–109 storage capacity. Through this platform, Sino Biological was able to successfully obtain the candidate antibody of the druggable target (PD-L1) via competitive screening.
The blocking and cell activities of this antibody were shown to be superior to those of the positive control antibody, while the affinity was shown to be similar to that of the positive control antibody. The information collected from the particular comparison test is displayed below:
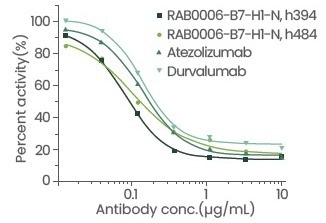
Figure 4. Evaluation of antibody blocking activity. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
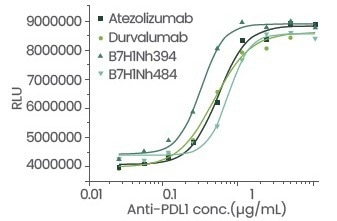
Figure 5. Cell activity evaluation. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Table 1: Detailed data of antibody blocking activity and cell activity. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Sample ID |
IC50 (μg/mL) |
EC50 (μg/mL) |
| Atezolizumab |
0.14426 |
0.38 |
| Durvalumab |
0.1419 |
0.33 |
| B7-H1-N, h394 |
0.08344 |
0.23 |
| B7-H1-N, h484 |
0.10723 |
0.51 |
References
- Emily Y. Yang and Khalid Shah, Nanobodies: Next Generation of Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Frontiers in Oncology, 2020.
- Peter Bannas, Julia Hambach and Friedrich Koch-Nolte, Nanobodies and Nanobody-Based Human Heavy Chain Antibodies As Antitumor Therapeutics. Frontiers in Immunology, 2017.
- Bao et al. Nanobody: a promising toolkit for molecular imaging and disease therapy. EJNMMI Res, 2011.
- Manman Liu, et al. Nanobody-Ferritin Conjugate for Targeted Photodynamic Therapy. Chem. Eur. J., 2020.
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.