Cancer is considered a significant public health issue worldwide. Several fundamental studies and clinical trials have displayed that immunotherapy is one of the most efficient and hopeful therapeutic methods for cancer treatment.
Cancer immunotherapy triggers the immune system of the body and improves the antitumor immune response to combat cancer cells. It comprises numerous strategies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, cytokine therapies, therapeutic monoclonal antibodies targeting tumor antigens, cell therapies (for example, CAR-T cells) and cancer vaccines.
Also, targeting cytokines or cytokine receptors have arisen as possible cancer immunotherapy with the help of intensive studies of cytokines in cancers.
Cytokines are a class of small proteins (normally <30 kDa) exhibiting several biological activities and being synthesized and secreted by immune cells and a few nonimmune cells (for example, epidermal cells, endothelial cells and fibroblasts).
Cytokines mediate intercellular communication in a paracrine or autocrine manner. This helps control the differentiation, proliferation, survival and effector functions of immune cells. Based on their functions, cytokines could be categorized into interferons (IFNs), interleukins (ILs), colony-stimulating factors (CSTs), tumor necrosis factors (TNFs) and chemokines.
Cytokine network in the tumor microenvironment
The tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complicated and combined system of endothelial cells, fibroblasts, the extracellular matrix, immune cells and cytokines spanning the cancer cells. The interaction of cancer cells seems to be constant with the encircling microenvironment.
Notably, cytokines mediate intercellular communication between these several cells in the TME in a paracrine or autocrine way (Figure1).1
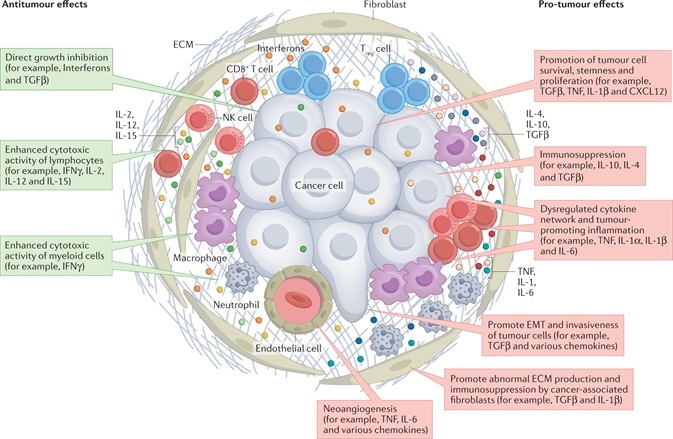 Figure 1. Cytokine Network in the TME. The actions of the cytokines are shown in red and green rectangles, indicating pro-tumor effects and anti-tumor effects, respectively1. Image Credit: doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
Figure 1. Cytokine Network in the TME. The actions of the cytokines are shown in red and green rectangles, indicating pro-tumor effects and anti-tumor effects, respectively1. Image Credit: doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
As far as TME is concerned, a few particular cytokines, like IFNγ, IL-2, IL-12 and IL-15, illustrate antitumor effects by directly hindering cell growth or improving the cytotoxic effects of lymphocytes and/or myeloid cells.
At the same time, a few aberrantly expressed cytokines display tumor-promoting effects in several ways, like neoangiogenesis, cancer cell survival promotion, stemness, immunosuppression and proliferation.
Such atypical cytokines could be generated by stromal cells, immune cells and even malignant cells, and they could be included in all stages of cancer occurrence and advancement.
Based on the antitumor or protumor impacts of various cytokines, two conflicting cytokine-based immunotherapy strategies are utilized for cancer treatment: (1) cytokine therapy, where cytokine derivatives or recombinant cytokines with antitumor effects are utilized directly to fight cancer cells, and (2) anticytokine therapy, where the antagonists of cytokines or cytokine receptors are controlled to curb the protumor effects of cytokines.
Cytokine therapy
For the past four decades, several clinical and preclinical studies have tried to directly exploit cytokines with antitumor effects for cancer treatment, and few have shown hopeful outcomes. Currently, two cytokine drugs have been approved for the clinical treatment of cancer: IFN alfa-2b (Intron A) and aldesleukin (Proleukin) (Table 1).
Table 1. FDA-approved Cytokine Drugs. Source: Sino Biological Inc.
| Cytokines |
Deliverables |
Brand Name |
Approval Date |
Indications |
| IFN-α |
interferon alfa-2b |
Intron A |
06/04/1986 |
Hairy Cell Leukemia, Malignant Melanoma, Follicular Lymphoma, AIDS-Related Kaposi's Sarcoma |
| IL-2 |
aldesleukin |
Proleukin |
05/05/1992 |
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma, Metastatic Melanoma |
Intron A was authorized for treating malignant melanoma, follicular lymphoma, hairy cell leukemia and AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma,2 whereas Proleukin was certified for treating metastatic melanoma and metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).3
Several other cytokines are determined as possible cytokine therapies. For instance, as an antitumor cytokine, IL-12 boosts the proliferation and cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells and T cells, while improving TH1 cell differentiation and IFNγ production.
In several clinical trials, recombinant IL-12 has displayed modest antitumor effects. But its contagiousness and short half-life impede its approval for clinical application.
Currently, multiple strategies, like protein conjugation with polyethylene glycol and antibody-cytokine fusion proteins, are being employed for IL-12 engineering to extend its half-life and decrease its toxicity.
In the studies performed, recombinant cytokines of high purity and activity are vital for several functional assays, like cytotoxicity assay and control experiment of the cytokine drug candidates.
Sino Biological offers an extensive collection of recombinant cytokines spanning all the high-purity, high-activity and multilabel cytokine families (Figure 2).
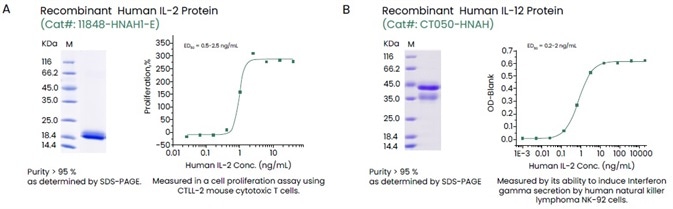 Figure 2. Examples of High-quality Recombinant Human IL-2 and IL-12. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 2. Examples of High-quality Recombinant Human IL-2 and IL-12. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Anticytokine therapy
Anticytokine therapies, particularly those targeting TNF and IL-6, are utilized extensively in the clinical treatment of a few autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. The great success of anticytokine therapies in the field of immunology has significantly contributed to its wide use in the field of oncology.
As per several preclinical studies, neutralizing monoclonal antibodies or antagonists aiming the cytokines with protumor effects or their receptors display anticancer activities. Furthermore, TNF is a proinflammatory cytokine with tumor-promoting effects.
Hence, antibodies to TNF are utilized to bind abnormally expressed TNF for cancer treatment. Infliximab is an anti-TNF monoclonal antibody approved for multiple autoimmune diseases.
A phase I clinical trial disclosed that infliximab was highly compatible and showed no dose-limiting toxic effects in patients with advanced cancer.4 In two sequential phase II clinical trials, three of 37 patients with RCC obtained a partial response and 14 patients achieved stable disease.5
Thus, infliximab might be efficient for RCC, but it still needs to be confirmed in additional clinical trials. IL-6 plays pro-inflammatory and tumor-promoting roles in the TME. Therefore, agents targeting IL-16 or its receptor might be potential cancer drugs.
For instance, siltuximab, an approved monoclonal antibody to IL-6, was utilized in a phase II clinical trial involving 18 patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.6 Amongst such patients, one showed a partial response, and seven had stable disease. Siltuximab treatment also considerably decreased the plasma levels of CCL2, CXCL12 and VEGF.
Sino Biological has come up with a complete range of high-quality reagents, such as receptor proteins, antibodies, recombinant cytokine and ELISA kits to help support anticytokine therapies (Figure 3). Such high-quality reagents have been validated with the help of several techniques to offer constant and reproducible outcomes.
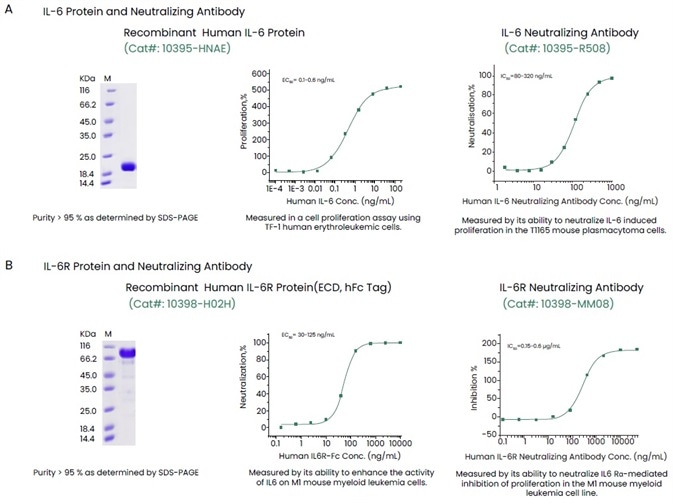 Figure 3. Examples of High-quality IL-6, IL-6R and Their Antibodies. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
Figure 3. Examples of High-quality IL-6, IL-6R and Their Antibodies. Image Credit: Sino Biological Inc.
References
- Propper DJ, Balkwill FR. Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2022; 10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9. doi.org/10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
- PRODUCT INFORMATION INTRON A (Interferon alfa-2b). www.fda.gov, accessed January 21, 2022. Reference ID: 4160510
- PRODUCT INFORMATION PROLEUKIN (aldesleukin). www.fda.gov, accessed January 21, 2022. Reference ID: 3165255
- Brown ER, Charles KA, Hoare SA, et al. A clinical study assessing the tolerability and biological effects of infliximab, a TNF-alpha inhibitor, in patients with advanced cancer. Annals of Oncology. 2008;19(7):1340-1346. doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdn054
- Harrison ML, Obermueller E, Maisey NR, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha as a new target for renal cell carcinoma: two sequential phase II trials of infliximab at standard and high dose. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25(29):4542-4549. doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2007.11.2136
- Coward J, Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, et al. Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target in human ovarian cancer. Clinical Cancer Research, 2011;17 (18):6083-6096. doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0945
About Sino Biological Inc.

Sino Biological is an international reagent supplier and service provider. The company specializes in recombinant protein production and antibody development. All of Sino Biological's products are independently developed and produced, including recombinant proteins, antibodies and cDNA clones. Sino Biological is the researchers' one-stop technical services shop for the advanced technology platforms they need to make advancements. In addition, Sino Biological offers pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates.
Sino Biological's core business
Sino Biological is committed to providing high-quality recombinant protein and antibody reagents and to being a one-stop technical services shop for life science researchers around the world. All of our products are independently developed and produced. In addition, we offer pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology firms pre-clinical production technology services for hundreds of monoclonal antibody drug candidates. Our product quality control indicators meet rigorous requirements for clinical use samples. It takes only a few weeks for us to produce 1 to 30 grams of purified monoclonal antibody from gene sequencing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.