Mycoplasma, and particularly Mycoplasma bovis, alongside Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus agalastiae, are dangerous pathogens for cows and calves, and can lead to inflammation and the Mastitis disease.
Mastitis results in lower levels of milk production, making it not only a risk to animal well-being and health, but also a serious financial issue for farmers. In veterinary diagnostics, it is vital to separate the unsafe bacteria from the milk and to distinguish them with precision.
Treatment of Mycoplasma bovis is especially tricky, as it lacks cell walls and thus has an in-built resistance to antibiotics. The only way to inhibit the spread of the bacteria is to place symptomatic cows in isolation.
As a result of the multiple constituents of milk, including fat, sugar and proteins, it can be difficult to extract bacterial DNA. It is for this reason that a specially designed extraction kit or process is advisable. The Mastit 4C Kit from DNA Diagnostic is a prime example of such a kit, and is ideally placed to successfully extract bacterial DNA from milk.

DNA Diagnostic’s Mastit 4C Kit, alongside the qTOWER³, for quantitative real-time PCR, can be used to detect the extracted nucleic acid.
The Mastit 4C Kit can detect up to four targets, including Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus agalastiae, Mycoplasma bovis and Mycoplasma species, concurrently, and also offers an amplification control.
This application note proves the specificity of the Mastit 4C Kit by DNA Diagnostic on the qTOWER³, through the description of a technique for the detection of diverse pathogens.
Materials and Methods
The Mastit 4C Kit from DNA Diagnostic was used to separate bacterial DNA from milk. The quantity of samples of the protocol was adjusted. Each step was carried out in a 1.5 ml reaction tube.
Once the Pre-lysis buffer was transferred from the 96 Deep Well Plate to the 1.5 ml reaction tube, 500 µl of raw milk was added. In order to test the performance of the extraction and detection, one sample was adulterated with a number of pathogens.
The detection feature of the Mastit 4C kit of DNA Diagnostic was engaged alongside the qTOWER³ from Analytik Jena in order to identify Mycoplasma, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus in the samples. The qPCR protocol was modified to fit the qTOWER³.
Samples and Reagents
- Mastit 4C Kit (DNA Diagnostic)
- Raw Milk (Dairy farm)
Instrumentation
- qTOWER³ (Analytik Jena)
- qTOWER³ Software: qPCR soft 3.4
Table 1. qPCR Protocol
| Step |
Cycle |
Profile |
Temperature |
Holding time |
Ramp rates |
| 1 |
1 |
Initial denaturation |
95 °C |
1 min |
2.5 °C/sec |
| 2 |
40 |
Denaturation |
95 °C |
10 sec |
2.5 °C/sec |
| Annealing/Elongation* |
60 °C |
25 sec |
2.5 °C/sec |
* Data aquisition: Color Module 1 (470 – 520 nm) with Gain3, 3 (553 – 580) with Gain 2, 4 (565 – 605) with Gain 5, 5 (630 – 670) with Gain 3 and Color Module 6 (660 – 705) with Gain 5
Results and Discussion
The internal amplification control was engaged to authenticate the findings prior to the values being checked for the various pathogens. The benchmark for a result to be considered valid was an Internal Amplification Control (IAC) lower than a Ct-value of 32.
Each sample displayed Ct-values between 23 and 31, meaning the results of the other targets were satisfactory.
Samples number 2 and 3 displayed positive IAC, but were negative for all the other channels, leading to a negative diagnosis. Samples number 1 and 4 displayed a positive signal for the ROX channel, indicating contamination with Streptococcus agalactiae, while the signal for sample number 4 was minimal.
Sample 5 displayed Ct-values for HEX (Staphylococcus aureus), ROX (Streptococcus agalactiae) and Cy5 (Mycoplasma species).
Table 2. Results of the qPCR detection based on the Mastit 4C Assay (DNA Diagnostic) and qTOWER³ (Analytik Jena)
| Sample |
Target |
IAC Quasar
705 |
Mycoplasma bovis
FAM |
Staphylococcus aureus
HEX |
Streptococcus agalactiae
ROX |
Mycoplasma species
Cy5 |
| Sample 1 |
29.29 |
no Ct |
no Ct |
21.13 |
no Ct |
| Sample 2 |
30.18 |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
| Sample 3 |
31.59 |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
| Sample 4 |
29.59 |
no Ct |
no Ct |
35.7 |
no Ct |
| Sample 5 |
24.87 |
no Ct |
14.79 |
10.65 |
18.33 |
| Positiv control |
23.47 |
19.15 |
19.67 |
14.14 |
18.19 |
| NTC |
28.44 |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
no Ct |
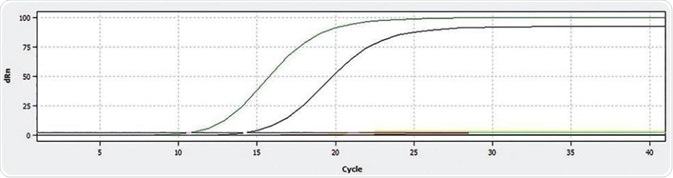
Figure 1. Display of the qPCR curves for ROX (green – Sample 5, black – Postiv control)
Conclusion
The findings from the IAC indicate that the amplification of the Mastit 4C Kit in Analytik Jena’s qTOWER³ functions very well as a combination. Firstly, the entire experiment is considered to be valid in light of the results of the NTC (No template control) and Positive control.
Additionally, the Internal Amplification Control can be detected in all samples, so the results of the various raw milk samples from cows with symptoms of Mastitis are positive or negative for the numerous pathogens.
The findings of this study can be summarized as follows: for customers with a need to detect pathogens in milk, the combination of qTOWER³ (Analytik Jena) and Mastit 4C kit (DNA Diagnostic) could represent an effective solution.
About Analytik Jena US
Analytik Jena is a provider of instruments and products in the areas of analytical measuring technology and life science. Its portfolio includes the most modern analytical technology and complete systems for bioanalytical applications in the life science area.
Comprehensive laboratory software management and information systems (LIMS), service offerings, as well as device-specific consumables and disposables, such as reagents or plastic articles, complete the Group’s extensive range of products.
About Life Science
The Life Science product area demonstrates the biotechnological competence of Analytik Jena AG. We provide a wide product spectrum for automated total, as well as individual solutions for molecular diagnostics. Our products are focused to offer you a quality and the reproducibility of your laboratory results.
This will surely ease your daily work and speed up your work processes in a certain way. All together we support you through the complete process of the lab work. Besides we offer customized solutions and are able to adapt our products to your needs. Automated high-throughput screening systems for the pharmaceutical sector are also part of this segment’s extensive portfolio.
About Analytical Instrumentation
Analytik Jena has a long tradition in developing high-performance precision analytical systems which dates back to the inventions made by Ernst Abbe and Carl Zeiss. We have grown to become one of the most innovative manufacturers of analytical measuring technology worldwide.
Our business unit Analytical Instrumentation offers excellent competencies in the fields of optical spectroscopy, sum parameters and elemental analysis. Being proud of our core competency we grant all our customers a long-term warranty of 10 years for our high-performance optics.
About Lab Automation
With more than 25 years of market experience, Analytik Jena with its CyBio® Product Line is a leading provider for high quality liquid handling and automation technologies. In the pharmaceutical and life science industries, our products enjoy the highest reputation for precision, reliability, robustness and simplicity.
Moreover, the Automation Team designs, produces and installs fully automated systems tailored to our clients' application, throughput and capacity requirements. From stand-alone CyBio® Well up to fully customized robotic systems we handle your compounds, biomolecules and cells with great care.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.