Sponsored Content by ByonoyReviewed by Maria OsipovaMar 21 2024
A routine performance in numerous laboratories is quantifying protein concentration in aqueous samples, encompassing applications in fundamental and clinical research.

Image Credit: Byonoy GmbH
Protein quantification is an important first step in the subsequent processing of protein samples and involves their isolation, separation, and analysis. Various methods can be employed to measure protein concentration depending on the required accuracy, sensitivity, and purity of samples, and different detection techniques can be utilized, including colorimetric and fluorometric determination.1
Due to the growing demand for high-throughput protein quantification in diverse fields, including proteomics, drug discovery, and therapeutics, lab automation workflows for protein quantification have become more critical.
Automated processes enhance experiments' reliability, throughput, and efficacy while mitigating manual errors. Therefore, automating some of the well-established and commonly used colorimetric and protein–copper chelation methods (such as bicinchoninic acid (BCA), Bradford (Coomassie) and Lowry) could prove advantageous in protein quantification and analysis workflows.2
An automated BCA assay is presented here, enabled by integrating the Absorbance 96 Automate microplate reader into the epMotion® liquid handling system (LHS).
The performance of Absorbance 96 Automate is evaluated by comparing it with another benchtop microplate reader; results exhibit identical readouts with similar reproducibility and linearity, highlighting the efficacy and sensitivity of the Absorbance 96 Automate in conducting automated quantification.
A comparison of manual and automated workflows also showcases expedited procedural steps in the automated workflow solution, resulting in a substantial reduction in the overall time required to perform the entire assay.
BCA Automated workflow
Protein quantification was carried out using the PierceTM microplate BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Following the manufacturer's protocol, an automated workflow was established combining the epBlue software and the epMotion® LHS.
The automated process measured absorbance readouts at 562 nm, facilitated by the on-deck integrated Absorbance 96 Automate. The bovine serum albumin (BSA) standard graph was constructed, incorporating seven data points in triplicates, and measurement of unknown samples (four replicates) was performed across four dilution ranges.
Results
In the comparative analysis, the BSA standard curve analysis was performed by measuring the absorbance of the standard protein samples at 562 nm (Absorbance 96 Automate) and 560 nm (GloMax® Discover). Results showed comparable optical density (OD) readouts with a high correlation (see Figure 1).
The subsequent examination and comparison of OD values from unknown protein samples also revealed similar results (Figure 1B), with a high correlation (R² = 0.9989) (Figure 1C). The findings confirm that the Absorbance 96 Automate shows similar reproducibility, linearity, and sensitivity within the dynamic range compared to the GloMax® microplate reader.
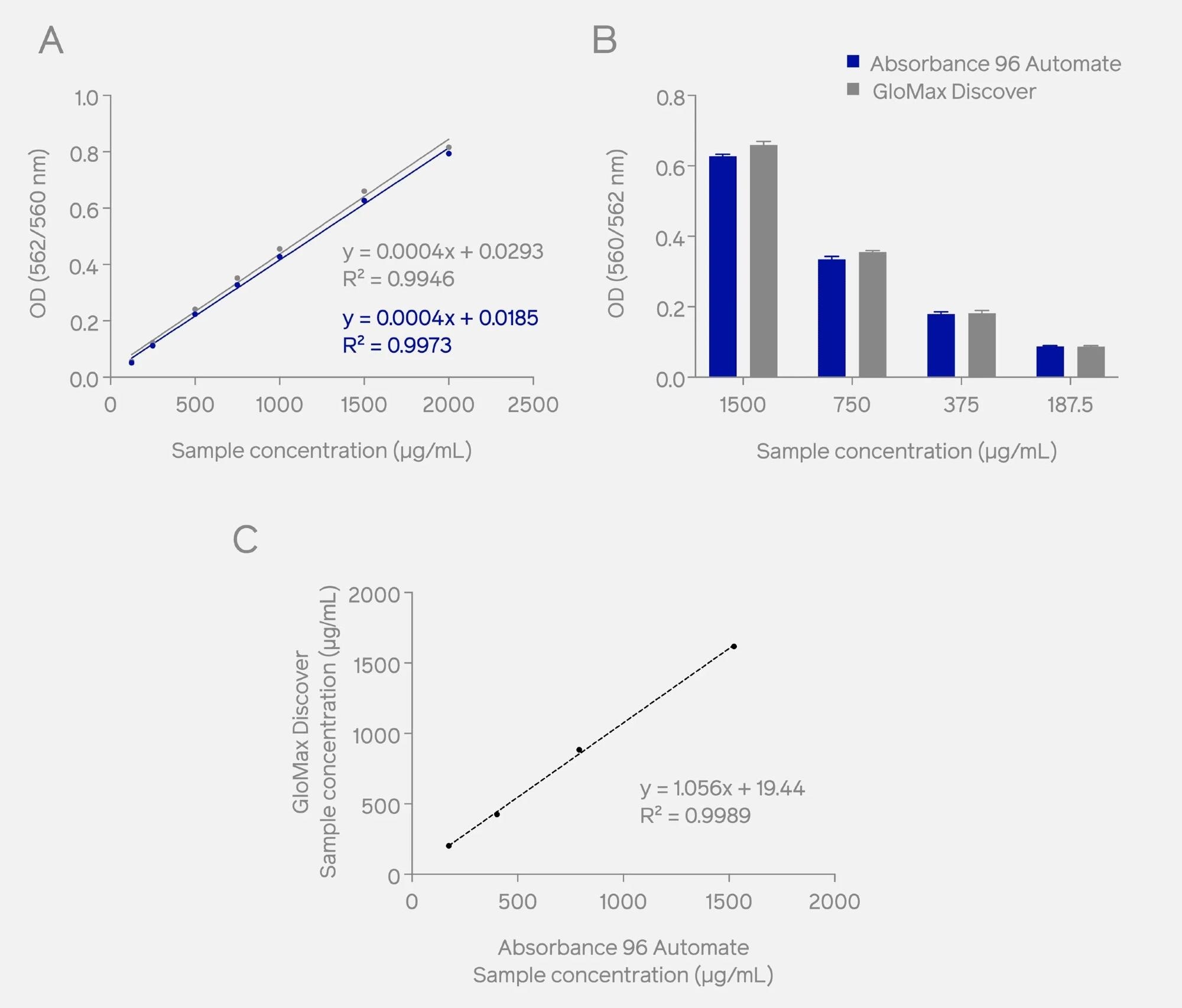
Figure 1. Comparative analysis utilizing Pierce™ Microplate BCA Protein Assay Kit demonstrates similar OD values (A) for the BSA standard curve and unknown protein samples (B) for the Absorbance 96 Automate (OD measured at 562 nm) and the GloMax® Discover (OD measured at 560 nm). A significant correlation of the sample concentration was observed using both devices (C). Image Credit: Byonoy GmbH
It is important to emphasize that the Absorbance 96 Automate had a shorter readout time than the GloMax Discover® (2 seconds compared to 52 seconds), emphasizing its efficiency for rapid data acquisition.
To examine further the benefits of an automated workflow for a BCA assay, a comparative analysis was undertaken by comparing both automated and manual methods. Results demonstrate a substantial correlation of the sample concentration between the two methods (Figure 2), validating the efficient performance of the automated approach in comparison to the manual workflow.
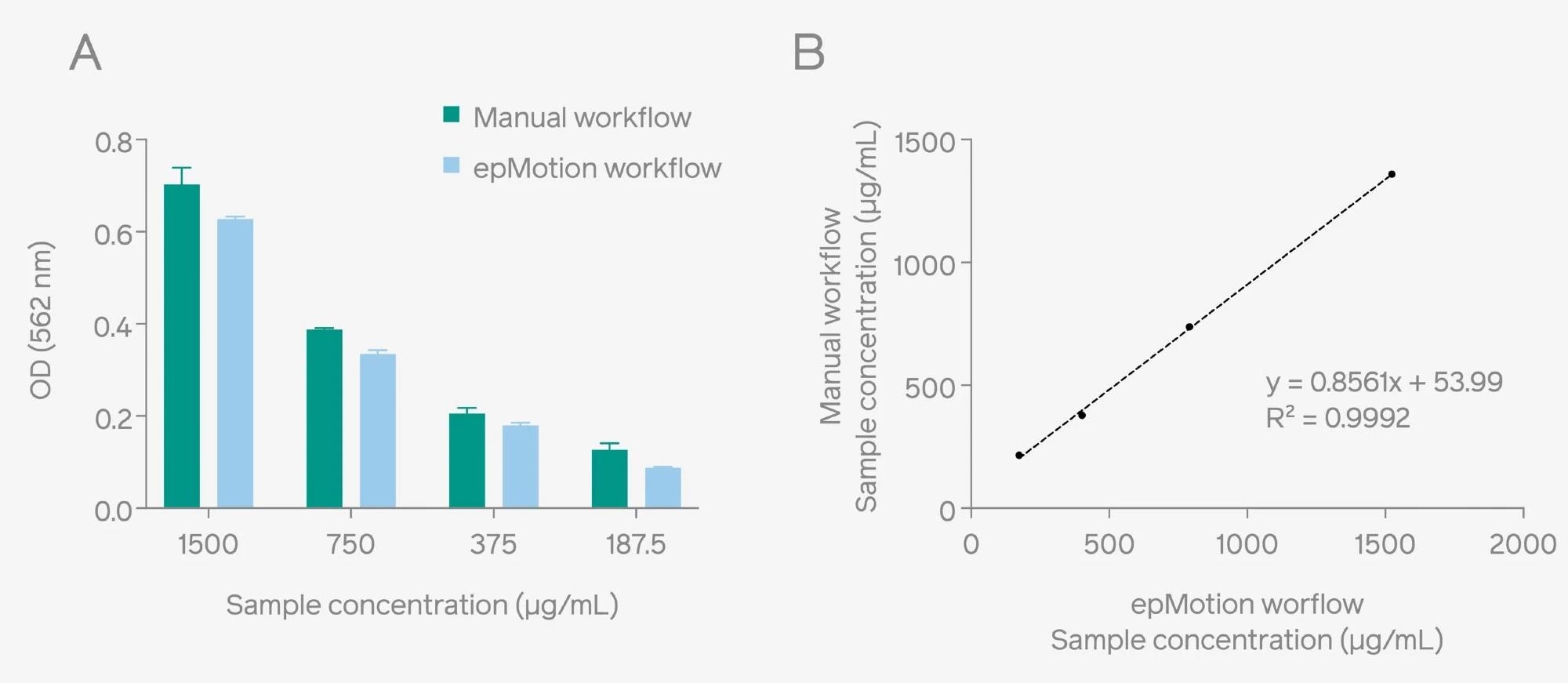
Figure 2. OD readouts of unknown protein samples obtained through the epMotion® and manual workflow using Pierce™ Microplate BCA Protein Assay Kit (A). A comparison shows a strong correlation of the sample concentration between both methods (B). Image Credit: Byonoy GmbH
When comparing the manual to the automated workflow, a significant decrease in the total analysis time was observed (90 compared to 71 minutes). The automated system also enabled direct plate reading without intervention, optimizing and saving user time during execution.
Video Credit: Byonoy GmbH
Conclusion
The results derived from the study highlight the efficacy of the Absorbance 96 Automate in conducting a BCA assay, demonstrating comparable readout sensitivity, linearity, and reproducibility like other benchtop microplate readers.
By integrating the Absorbance 96 Automate with the epMotion® LHS, the automated workflow solution facilitates a higher throughput in protein analysis characterized by increased precision and speed than a manual system.
References
- Noble, J. E., and Bailey, M. J. A. (2019) Quantitation of Protein, Methods in Enzymology, 463(C), pp.73–95.
- Brady, P. N., and Macnaughtan, M. A. (2015) Evaluation of Colorimetric Assays for Analyzing Reductively Methylated Proteins: Biases and Mechanistic Insights, Analytical Biochemistry, 491, p.43.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Abhiyan Viplav and Rucha Datar from Eppendorf SE. Check out the original article here.
About Byonoy
The Byonoy GmbH was founded in 2015 as a spin-off from the University of Kiel and is situated in Hamburg. Our core competence is to develop innovative microplate readers based on photometric measurements for laboratory use.
Our aim is to facilitate the research and development process, to give researchers new opportunities, and to make the advantages of advanced biotechnological methods accessible to a broad range of laboratories.
For the realization of a successful innovation process, our network is a crucial factor. Our partners help us to realize our ideas and we are glad to share our expertise with them.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.