Their results indicate significant associations between VDR, the mode of detection, and the size of invasive tumors, suggesting a promising avenue for further study.
 Study: The Vitamin D Receptor as a Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer—A Cohort Study. Image Credit: Peddalanka Ramesh Babu / Shutterstock
Study: The Vitamin D Receptor as a Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer—A Cohort Study. Image Credit: Peddalanka Ramesh Babu / Shutterstock
Background
People with breast cancer often show lower serum levels of vitamin D compared to healthy individuals; some studies have also found links between low vitamin D levels and the probability of an adverse prognosis, while others suggest that supplementation could reduce the risk of developing advanced cancer.
Calcitriol, an active metabolite of vitamin D, binds to the VDR before it translocates into the nucleus, modifying regulatory genes that control cell signaling, apoptosis, and cell growth.
This could be a mechanism that underlies the association between VDR and favorable breast cancer prognoses, but further research is needed to understand its potential role as a biomarker for the progression of tumors.
About the study
In this study, researchers attempted to validate prior work that found positive associations between breast cancer prognoses and nuclear VDR presence. They additionally explored if prognostic information can be refined by VDR subcellular localization.
The dataset included tumor samples obtained from individuals who received a diagnosis of primary breast cancer between October 2002 and June 2012. The samples were utilized for tissue microarray (TMA) construction after excluding people who had received a prior diagnosis of any cancer in the previous 10 years.
During preoperative visits, patients were asked to complete questionnaires that included information on reproductive factors, lifestyles, and medication and supplements consumed during the previous week. Vitamin D consumption was calculated from the product information for supplements.
Nurses measured hip and waist circumference, height, weight, and breast volume. Pathology reports were used to obtain characteristics of tumors, including size, histologic type, grade, involvement of axillary lymph nodes, and status of progesterone receptors (PR) and estrogen receptors (ER).
Pathological assessment of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status and TMA were assessed jointly using microscopic methods after blinding. In multiple subcellular locations of invasive tumor cells, VDR staining was examined in the nuclear membrane (VDRnum), cytoplasm (VDRcyt), and nucleus (VDRnuc).
During the final follow-up in 2019, medical records, pathology reports, and national registries for population and tumors were used to calculate the breast cancer-free interval (BCFI) and calculate endpoints (death or last follow-up) for survival analyses.
Findings
On average, patients were 61 years old, and VDR was obtained for 878 tumors; cytoplasmic intensity evaluations showed that 7% were VDR-negative, while VDRnum was positive in 25% of patients. Tumors included in the analysis were, on average, large, of a higher grade, and more likely to be lymph node-negative than those that were excluded.
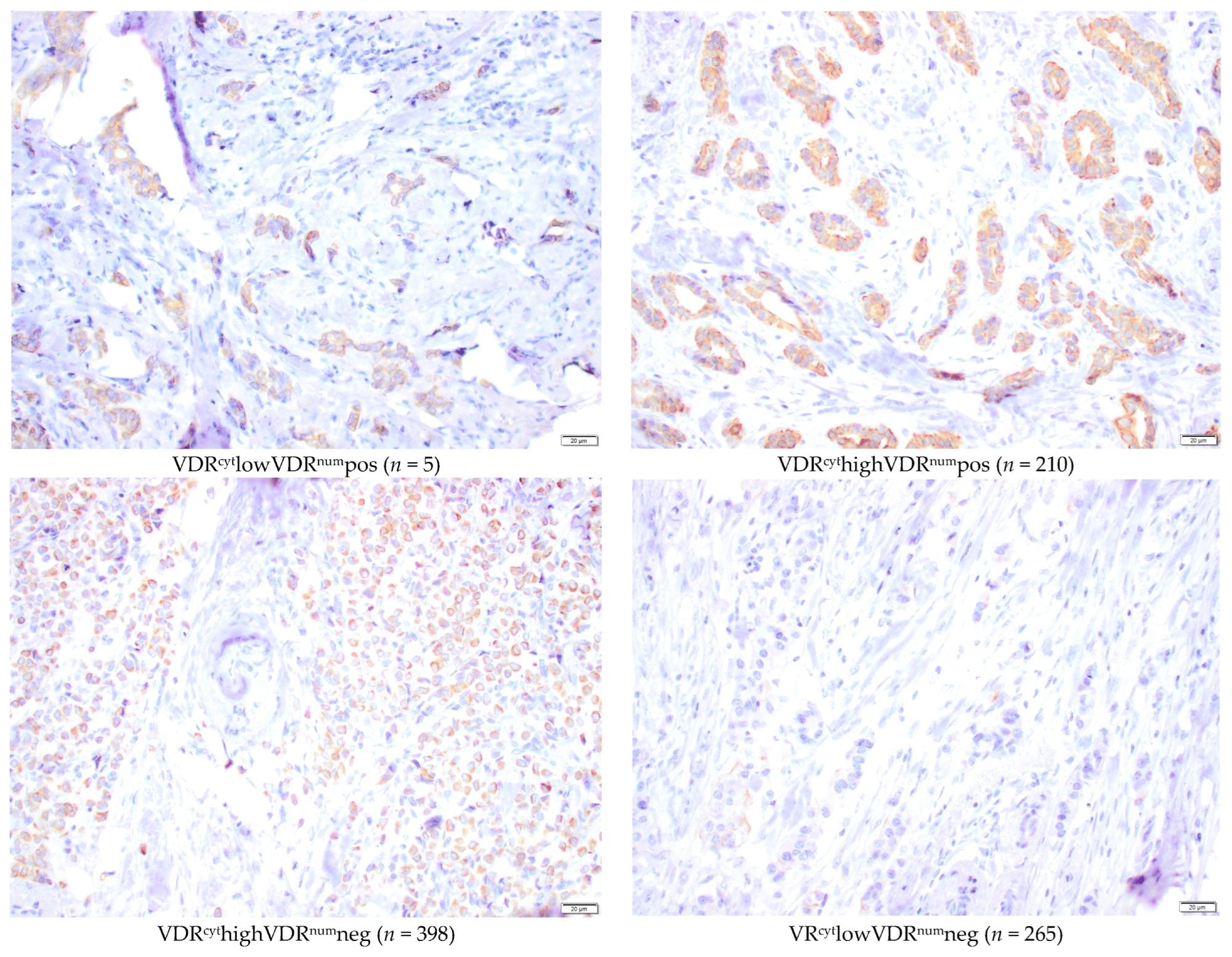 Microscopic representative images of immunohistochemical staining intensities of nuclear membrane and cytoplasmic VDR (40×) in the TMA. Bar represents 20 µm.
Microscopic representative images of immunohistochemical staining intensities of nuclear membrane and cytoplasmic VDR (40×) in the TMA. Bar represents 20 µm.
Patients with VDRnum-positive tumors had smaller waist circumferences and breast volumes on average and were more likely to have screening-detected tumors. VDRnum-positive tumors were linked with lower tumor grade, positive hormone receptors, and the absence of HER2 amplification.
After surgery, more VDRnum-negative patients received chemotherapy and trastuzumab, while VDRnum-positive patients received further endocrine therapy. In terms of prognosis, patients with VDRnum-positive tumors had better outcomes in both BCFI and overall survival (OS) in univariable analysis. This effect persisted after adjusting for various factors.
When VDR localization was considered, VDRnum-positive tumors showed the best prognosis regardless of VDRcyt. Patients with both ER-positive and VDRnum-positive tumors had the best prognosis, while those with ER-negative and VDRnum-negative tumors had the worst. Even among ER-positive tumors, VDRnum-positive tumors were associated with lower tumor grade and longer OS.
Interaction analyses suggested that VDRnum interacts with the mode of detection and size of tumors in the case of BCFI. Larger VDRnum-positive tumors (>20 mm) were associated with significantly fewer breast cancer events than small ones. Clinically detected VDRnum-positive tumors showed better BCFI than screening-detected ones.
Conclusions
This study highlights significant correlations between positive VDR staining in the nuclear membranes of breast cancer cells and favorable characteristics of tumors, OS, and longer BCFI.
Results indicate that evaluating nuclear membrane VDR levels may be a better prognosis predictor compared to cytoplasmic levels. VDRnum status could refine luminal breast cancer selection with favorable prognoses, especially when considering interactions with tumor size and detection mode.
VDR expression inversely correlates with aggressiveness, particularly in triple-negative and HER2-amplified cancers, possibly due to mutations in the tumor protein p53. Further research is needed to standardize VDR evaluation methods and explore associations with vitamin D levels.
The study suggests potential clinical relevance for VDR as a prognostic marker and underscores the need for understanding the interplay between vitamin D, VDR, and breast cancer outcomes. Since most participants in the study were of European descent, heterogeneous populations should be included in future studies to ensure the generalizability of findings.
Journal reference:
- The vitamin D receptor as a prognostic marker in breast cancer – a cohort study. Huss, L., Gulz-Haake, I., Nilsson, E., Tryggvadottir, H., Nilsson, L., Nodin, B., Jirström, K., Isaksson, K., Jernström, H. Nutrients (2024). 10.3390/nu16070931, https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/7/931