Studies have identified cardiac symptoms, including intolerance to exercise, tachycardia, and atypical chest pain, as late-stage complications of COVID-19. In addition, studies have also documented subtle myocardial inflammatory changes, non-ischemic myocardial scarring, and pericarditis in young athletic individuals shortly after the initial severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. However, the underlying pathophysiology leading to long-term cardiac symptoms in individuals with mild initial COVID-19 and no history of cardiac diseases remains unclear.
 Study: Long-term cardiac pathology in individuals with mild initial COVID-19 illness. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
Study: Long-term cardiac pathology in individuals with mild initial COVID-19 illness. Image Credit: Kateryna Kon / Shutterstock
About the study
In the present study, researchers evaluated individuals with SARS-CoV-2 infection and a possible subclinical cardiac involvement but no clinical indication for CMR imaging. They hypothesized that individuals with persistent cardiac symptoms after COVID-19 have different imaging and biomarker parameters than those without symptoms or controls without previous infection. The control group had similar age, gender, and cardiovascular risk factors distribution. Also, these biomarker parameters improved at follow-up and were predictable from the baseline parameters.
Trained clinical research personnel used a standardized questionnaire to systemically screen all the participants before enrollment, following which they underwent a baseline CMR imaging study.
Each eligible study participant did a baseline visit between April 2020 and October 2021, i.e., after four weeks from diagnosis of the acute COVID-19 illness. Of these, only 346 participants completed a follow-up visit scheduled after four months after the baseline visit. The researchers ensured that all the participants were evaluated at each visit to provide demographic data and underwent CMR imaging. Additionally, they assessed their cardiac symptoms, risk factors, resting blood pressure, heart rate, and blood parameters.
At the baseline visit, the researchers performed the acquisition of cardiac function, volumes, mass, myocardial mapping, and scar imaging. Follow-up scans included cardiac function, volumes, mass, and myocardial mapping.
Study findings
The average age of the study cohort was 43.3 years, and the average time between the COVID-19 diagnosis and the baseline analysis was 109 days. At baseline, 73% of participants reported new onset of cardiac symptoms, but these symptoms were mild among 38% of them. The most common cardiac symptom among all the study participants was exertional dyspnea (62%), followed by palpitations (28%), chest pain (27%), and syncope (3%).
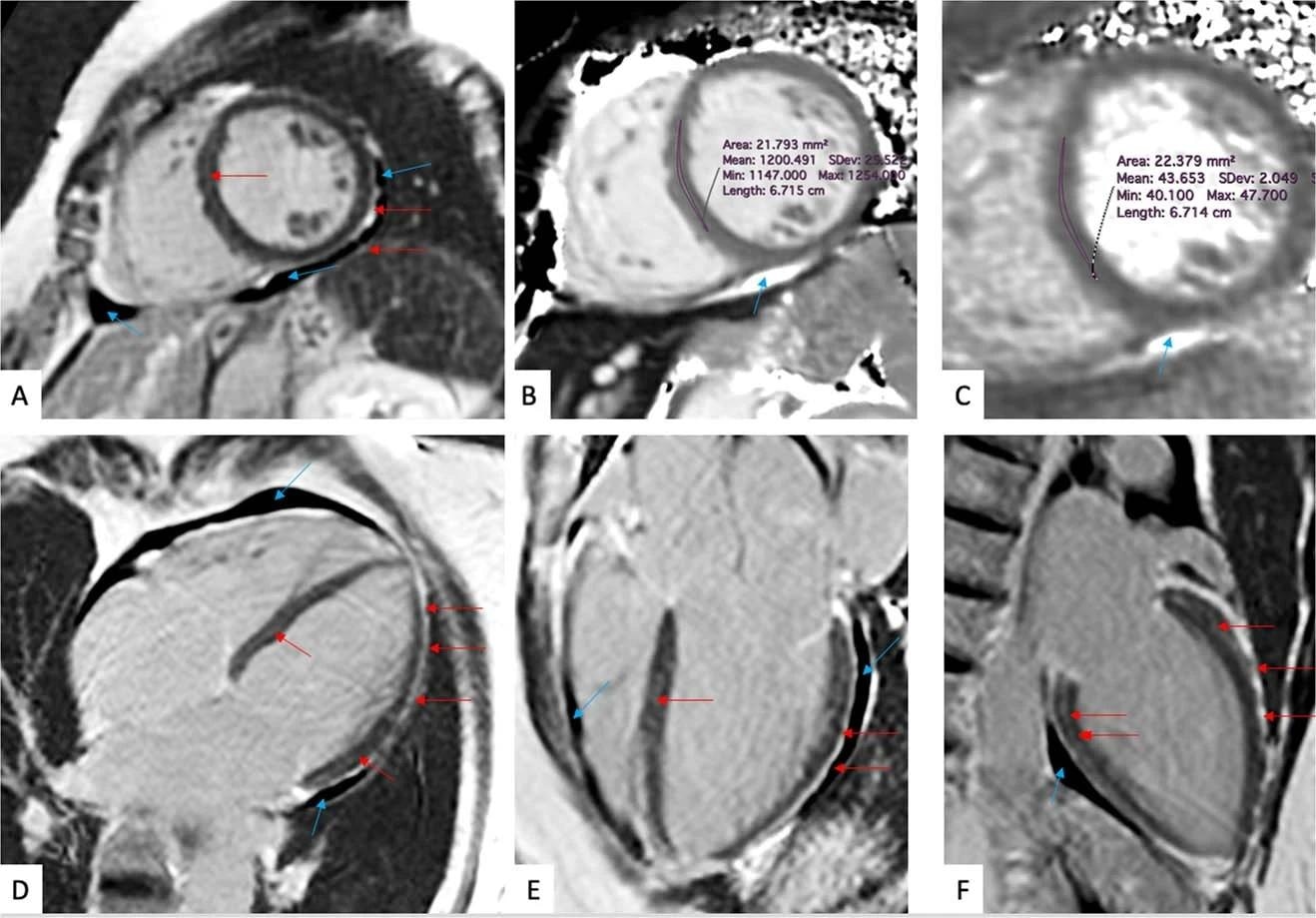 (a-f) Late gadolinium enhancement imaging (A, D-F) and Native T1 (B) and T2 (C) mapping measurements of a 57-year-old woman evaluated 201 days after COVID-19 infection. This individual reported dyspnea, palpitations, and chest pain, worsening on minimal exertion. Late gadolinium enhancement imaging allows to visualize regional accumulation of the gadolinium-based contrast agent along the outer rim of the myocardial free wall (red arrows), as well as within the thickened pericardial layers, separated by small amounts of pericardial effusion (blue arrows).
(a-f) Late gadolinium enhancement imaging (A, D-F) and Native T1 (B) and T2 (C) mapping measurements of a 57-year-old woman evaluated 201 days after COVID-19 infection. This individual reported dyspnea, palpitations, and chest pain, worsening on minimal exertion. Late gadolinium enhancement imaging allows to visualize regional accumulation of the gadolinium-based contrast agent along the outer rim of the myocardial free wall (red arrows), as well as within the thickened pericardial layers, separated by small amounts of pericardial effusion (blue arrows).
During the follow-up visits, 198 participants had cardiac symptoms, which persisted in 182 participants. Of previously asymptomatic participants, 16 developed new symptoms, 78 remained asymptomatic, and 70 became asymptomatic. More women than men (67% vs. 46%) continued to experience cardiac symptoms.
CMR imaging techniques can detect diffused inflammatory myocardial involvement (a non-specific measure of abnormal myocardium) by T1 mapping and myocardial water content by T2 mapping. The late gadolinium enhancement (LGE) denoted regional myocardial injury. On the other hand, the accumulation of gadolinium contrast agents helped visualize thickened pericardial layers.
Participants with cardiac symptoms also had markedly higher myocardial native T1 mapping values. However, they had similar blood biomarkers, including C-reactive protein (CRP) and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Furthermore, the authors noted that 64% of participants had detectable troponin. Only a few participants had structural heart diseases. Overall, CMR imaging indicated inflammatory cardiac involvement after COVID-19 as a pathophysiological commonality, irrespective of the expression of cardiac symptoms. However, since overall troponin levels were low and unrelated to the presence of cardiac symptoms, it suggested that cardiac symptoms manifested as increased myocardial wall stress and not necrosis.
Conclusions
Since the authors excluded individuals hospitalized after COVID-19 and those with abnormal lung function tests, they did not mix the effects of severe disease and its accruing pathophysiology. Hence, the current study provided a direct insight into post-SARS-CoV-2 sequelae, its spectrum, and the subsequent evolution of cardiac symptoms after COVID-19.
Exertional dyspnea emerged as the most frequently experienced cardiac symptom. The participants who experienced it found it difficult to regain a previous fitness level, limiting physical aspects of their everyday life. Most importantly, the study results defied the classical definitions of viral myocarditis and established that profound myocardial injury or structural heart disease was not a prerequisite for the presence of cardiac symptoms. However, since subclinical cardiovascular inflammation is considered a risk factor in chronic autoimmune diseases, further research is needed to establish long-term sequelae of post-COVID-19.