Over the past decade, the introduction of drug-eluting stents (DES) has revolutionized the field of interventional cardiology. To massively decrease stent restenosis, the DES-type of stent is coated with a thin layer of drug eluting material. This stops vessel revascularization in most instances.
Typically, DES is made up of three main components:
- A drug carrier, normally polymer-based, that is utilized as a coating for the metallic stent which contains and delivers the drug to the artery over time.
- A drug which is embedded in the polymer-based coating, that prevents excess tissue forming.
- A metallic stent structure, the stent platform, typically made from metallic alloys such as cobalt-chromium or stainless steel.
Together with various coating processes, manufacturing methods for DES are made up of different types of materials (polymers and drugs). Most of the coating techniques usually consist of spraying the drug-eluting coating over the metallic stent structure, despite the variations.
With thicknesses that are usually between 5 and 15 µm, the characterization of coating uniformity has undeniably become crucial in order to decrease therapeutic risks, but this part is also an effective control of the coating process and its stability.
Yet, due in part to the requirement to carry out non-destructive and high-throughput measurements on structures possessing extremely complex morphologies, the characterization of these coatings is still a challenging application.
In recent years, it has been common in the industry to test equipment like Chromatic Confocal Distance Sensors (CCDS), Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM), Total Coating Mass or Spectroscopic Reflectometry as non-destructive methods for coating characterization.
When employed for coating characterization on DES, the three aforementioned methods each possess different limitations, e.g. point vs. areal measurements, low working distance, and low light efficiency. Although Total Mass Coating is the most used method to streamline stent production, it does depend on a qualitative assumption, i.e. on the homogeneity of the coating.
Partly due to the fact that they need a different measurement platform to characterize coatings than the one utilized to examine the rest of the stent, none of these technologies has proven to be ideal for a reliable and quick characterization of DES coatings at the production rate needed.

Insertion, balloon inflation, stent in position, in-stent restenosis (from left)
Coating Characterization Using the Q Six
For the characterization of coating uniformity and thickness on DES, Q six utilizes Vertical Scanning Interferometry (VSI) as an embedded technology. This technology generates a thickness map of the stent surface with a vertical resolution of 2 nm and a lateral resolution of 0.5 µm.
The main benefit supplied by Q six is that the coating characterization is carried out in only a few seconds and on the same platform where dimensional and visual inspection of the stent is carried out. This permits utilization of the same platform for inspection of all critical characteristics of the stent in production.
Q six carries out a vertical scan that locates the best contrast of an interferometry signal at each point in the field-of-view (FOV) gathered through an appropriate objective to acquire a three-dimensional map of a surface. The maximum contrast position establishes the exact height of each point on the surface within the FOV.
Two interference signals are gathered in the case of coating measurements:
- One corresponding to the air/coating interface
- A second signal corresponding to the coating/stent interface
By using the correction models based on the index of refraction of the coating, a thickness map of the coating with nanometer accuracy is generated, simply by subtracting one interface plane from another.
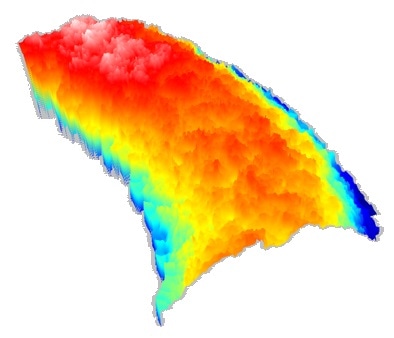
Coating measurement on a DES
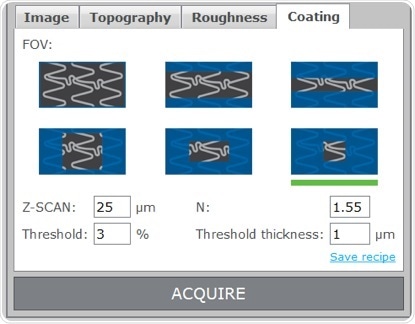
Using the Q six to characterize coatings on DES is as simple as focusing on the strut surface, choosing the area size to be mapped and entering the index of refraction of the coating material into the coating panel of the SensoINSPECT User Interface. SensoINSPECT will show the thickness map of the coating inside the selected area on screen seconds after beginning the acquisition.
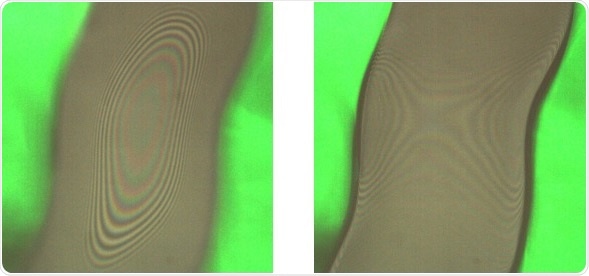
Interference patterns for the upper (left) and lower (right) interfaces of the coating
A set of profile parameters and surface parameters to qualitatively complete the set of information is always displayed, in addition to the quantitative results (3D thickness map and selected profile). The average value gives the user useful information for thickness characterization, whilst the minimum, maximum, and standard deviation values supply the information which is required for coating uniformity characterization.
Conclusion
In a production environment, a number of gains are possible by employing the embedded technology in the Q six stent inspection system:
- Quantitative and reliable values for coating thickness are gathered within just a few seconds with nanometer repeatability and accuracy.
- Coating characterization in production can be carried out by using the same measurement platform employed during the device prototyping and development.
- Coating measurements are carried out optically with no contact with the sample to guarantee no sample manipulation.
- The same platform can be utilized for dimensional measurements, coating characterization and visual inspection.
- Coating integrity assessment and coating characterization can be done within a single measurement routine, for streamlining of the process.
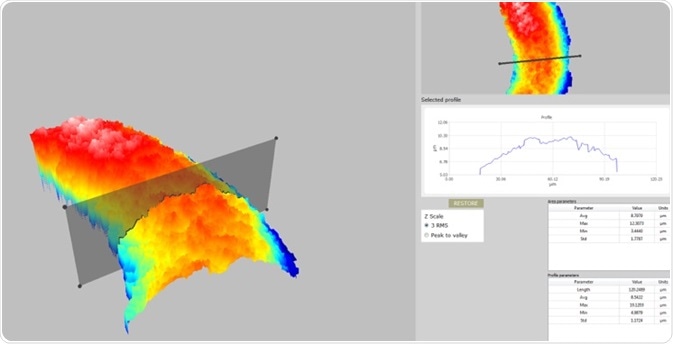
The results are shown as a 3D map of the coating thickness. The user can analyze any transversal section (profle) of the thickness map by simply manipulating the profle handles shown on screen with the mouse. It is also possible to evaluate the coating thickness of the selected profle, which provides a highly intuitive and quantitative characterization of coating thickness and uniformity.
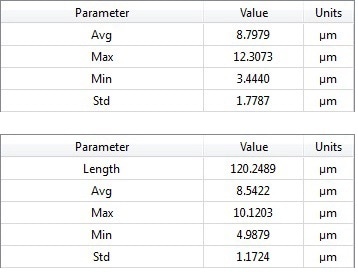
Area (top) and profle (bottom) parameter tables
Parameters panel in SensoINSPECT

About Sensofar Metrology
Sensofar Metrology provides state-of-the-art systems – such as the Q six – for the inspection of implantable medical devices and components, as well as supplying leading-edge solutions for R&D worldwide. Each system is designed to incorporate the highest quality standards within the field.
Sensofar is headquartered in Barcelona, the technological heart of Spain, is represented in over 20 countries through a global network of partners and has its own offices in Asia, Japan and the United States.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.