Both liposomes and micelles are effective carriers for hydrophobic molecules within hydrophilic environments, but they have distinct differences.

An amphibian and amphiphilic molecules forming a micelle. Image Credit: Genizer
Both structures comprise amphiphilic molecules with hydrophilic (water-attracting) and hydrophobic (water-repelling) components. This dual nature allows them to interact with water and lipids.

Amphibians live in and out of water, like amphiphilic molecules. Image Credit: Genizer
When amphiphilic molecules are present in sufficient quantities in a solution, their hydrophobic parts cluster together, forming a spherical structure. The key distinction lies in their architecture: micelles consist of a single-layer sphere, while liposomes have a bilayer structure. This bilayer configuration is similar to the lipid bilayer that forms the cell membranes of human cells.
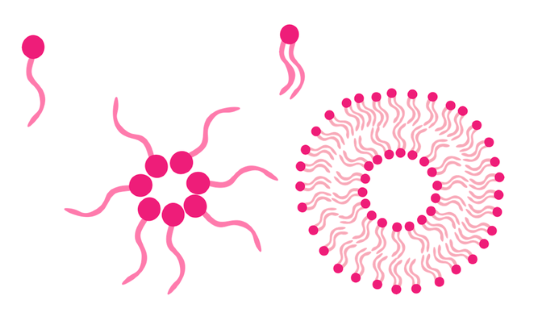
A single chain amphiphilic molecule and micelle on the left, dual chain amphiphilic molecule and liposome on the right. Image Credit: Genizer
The type of amphiphilic molecules involved influences the formation of monolayers versus bilayers. Typically, single-chain amphiphiles form monolayers, whereas double-chain amphiphiles lead to bilayers.
Both micelles and liposomes are valuable for creating emulsions or suspending insoluble molecules in solutions. In these structures, the hydrophobic molecules can be encapsulated within the micelle, liposome, or even within the center of the liposomal bilayer.
Liposomes are particularly beneficial in pharmaceutical applications due to their resemblance to cell membranes, which enhances their biocompatibility. This liposomal encapsulation can help minimize side effects and prolong the circulation time of therapeutic agents.
References
- Cancer. NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (online) Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/micelle#.
- Cancer. (2025). NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (online) Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/liposome.
- Cancer. NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms. (online) Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/exosome.
- Biology LibreTexts. (2018). 10.2: Lipids Aggregates in Water - Micelles and Liposomes. (online) Available at: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Biochemistry/Fundamentals_of_Biochemistry_(Jakubowski_and_Flatt)/01%3A_Unit_I_Structure_and_Catalysis/10%3A_Lipids/10.02%3A_Lipids_Aggregates_in_Water_-_Micelles_and_Liposomes.
About Genizer
Genizer™, located in Technology Link in Greater Los Angeles, is dedicated to advancing homogenizer nanotechnology.
The company provides high-pressure homogenizers, liposome extruders, sanitary heat exchangers, diamond interaction chambers, and high-pressure gauges compatible with other brands of high-pressure homogenizers, pumps, and microfluidizers.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.