Process development is key to identifying the optimal parameters used for synthesis, manufacturing, and stability testing. It is also key to generating the data required for the filing processes of many pharmaceutical regulatory bodies.
NMR is widely used in the structural characterization of impurities, intermediates, and final products. Cryogen-free benchtop NMR spectroscopy can also be used to explore chemical pathways and better optimize the synthesis process to accommodate the drug target molecule.
Small molecule pharmaceuticals’ synthesis processes typically involve multi-step organic chemical reactions. In circumstances where the structure of a target intermediate or the location of a characteristic NMR peak is known, there is no longer any need to completely elucidate the structure.
The simple detection and identification of characteristic peaks can quickly determine the presence of expected intermediates and products in these intermediate process reactions, saving users time, work, and money.
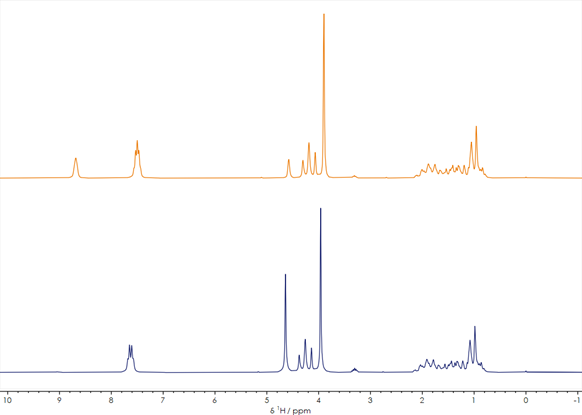
Figure 1. One-dimensional 1H stacked spectra of a reaction mixture before and after reaction. Image Credit: Oxford Instruments
Two one-dimensional 1H spectra of a compound prior to (orange spectrum) and following (blue spectrum) the synthesis process is shown in Figure 1. These spectra were each acquired with an approximately one-minute acquisition time, clearly demonstrating sufficient signal-to-noise to make key decisions about the synthesis process.
It is noteworthy that the two 1H spectra’s overall peak shapes are very similar, particularly in the 0-5 ppm region. Differing chemical shifts and splitting patterns shown in the characteristic peaks in the 7-9 ppm region confirm that the chemical reaction has altered the compound, however.
It would be possible to determine whether the product in this example is an expected intermediate or a different compound by leveraging further spectral analysis via database matching or comparison with predicted spectra. This could be done by also evaluating information about the relevant reactant structures, reaction mechanism, and process flow.
For example, fluorine is a high-sensitivity NMR active nucleus frequently found to be more powerful for reaction monitoring than the more widely used hydrogen. Thanks to the less complex fluorine NMR spectra and the wider chemical shift dispersion, straightforward resolution of reactant and product signals is possible.
It is possible to use 19F NMR in this instance to provide key information for a diverse array of pharmaceuticals, including a number of new APIs containing fluorine. Two stacked 19F spectra acquired prior to (orange spectrum) and following (blue spectrum) a synthetic process are displayed in Figure 2.
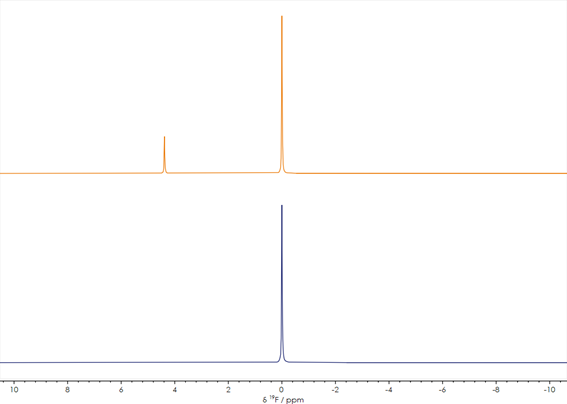
Figure 2. One-dimensional ¹⁹F NMR spectra acquired before (lower) and after completion of (upper) a reaction (spectra unreferenced). Image Credit: Oxford Instruments
The change is clear in this example. A new peak appears in the spectrum following the reaction, highlighting the addition of another type of fluorinated group to the molecule. The X-Pulse can quickly provide screening results in any standard laboratory, due to its capacity to offer these straightforward one-dimensional spectra.
Knowing the identities of reactants and products is essential in drug development and production, as is understanding the reaction process and kinetics.
A benchtop X-Pulse NMR can be equipped to study and monitor reactions using a flow chemistry module directly connected to an external reaction vessel. This setup allows the reaction mixture to be continuously pumped through the flow cell, allowing chemical reactions to be monitored online and in real time.
The pharmaceutical industry widely uses 3-nitrobenzaldehyde, an important intermediate in the synthesis of Nitrendipine, Nimodipine, and Nicardipine.
Using a sodium borohydride catalyst, 3-nitrobenzaldehyde can be reduced to 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol. The flow rate can be continuously pumped into the X-Pulse NMR flow cell every 20 seconds, and a 1H spectrum can be recorded.
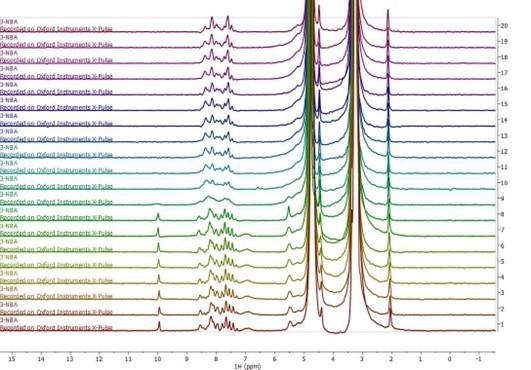
Figure 3. Stacked series of one-dimensional 1H NMR spectra acquired during online monitoring of the reduction of 3-nitrobenzaldehyde to 3-nitrobenzyl alcohol. Image Credit: Oxford Instruments
Results of online chemical reaction monitoring using a one-dimensional 1H spectrum are shown in Figure 3. The reaction mixture in this example was pumped continuously through the flow cell at a rate of 1 ml/minute, and a spectrum was collected every 20 seconds.
The aldehyde group of the reactant (located at around 10 ppm) was found to entirely disappear in the tenth spectrum. This spectrum was acquired approximately 200 seconds after the reaction had been initiated, confirming the rapidity of the reaction process.
It was also noted that the resolution of the benzene ring region located between around 7-9 ppm was found to suddenly deteriorate in the ninth spectrum. This is likely due to the formation of an intermediate product with a medium rate of exchange on the NMR timescale.
Later spectra continued to lack the aldehyde peak while exhibiting a higher-resolution benzene ring region. This likely indicates that the reaction had been completed.
Benchtop NMR is used to monitor chemical reactions online. This allows the concentration curves of reactants and products to be obtained over time. Using this data, the order and rate constant of the chemical reaction can be determined.
Acquiring chemical reaction rate constants under various temperature conditions enables the calculation of enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs free energy changes, as well as other kinetic reaction parameters.
This data is especially valuable for improving reaction efficiency, optimizing reaction conditions, controlling the reaction process, and better designing reactors.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Oxford Instruments.
About Oxford Instruments
Oxford Instruments is a leading provider of high-technology tools and systems for research and industry, dedicated to accelerating breakthroughs that create a brighter future for our world. With a global presence, we are committed to innovation and excellence, offering cutting-edge solutions that enable researchers and industry professionals to achieve breakthroughs in their fields. Our advanced technologies deliver numerous benefits through unparalleled precision and reliability, allowing users to obtain accurate and reproducible results. By utilising Oxford Instruments' innovative solutions, research is accelerated, productivity is enhanced, and innovation is achieved in various fields, including materials analysis, life sciences, semiconductors, physics, chemistry, and food sciences. We take pride in being a trusted partner for those aiming to push the boundaries of scientific and industrial advancements, providing the tools and support necessary to realise their visions.
Atomic force microscopy: These advanced instruments are utilised for high-resolution imaging and precise measurement of surface properties at the nanoscale level. They offer detailed topographical information and enable accurate measurements of features such as height, roughness, and mechanical properties.
Light microscopy: Our solutions encompass a comprehensive range of advanced imaging systems that utilise visible light for examining samples at the microscale. Equipped with high-quality lenses, cameras, and illumination systems, these optical microscopes deliver detailed images with exceptional clarity and resolution. They find applications in fields such as biology, materials science, and forensics.
Deposition and etching: Our advanced tools are specifically designed for the precise fabrication and modification of materials at the nanoscale. They include a variety of deposition techniques like physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapour deposition (CVD), and atomic layer deposition (ALD), as well as etching processes, such as plasma etching and reactive ion etching (RIE). These tools empower users to create customised materials and devices with exceptional control and precision.
Electron microscopy analysis: Our high-performance tools are tailored for materials characterisation, particle analysis, and sample manipulation at the nanometre scale. Techniques such as Backscatter Electron and X-ray (BEX), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS), and Electron Backscatter Diffraction (EBSD) enable imaging, chemical analysis, and crystallographic characterisation of materials at atomic and nanoscale levels.
Optical imaging and spectroscopy: Our optical imaging solutions comprise a range of advanced technologies and systems for capturing and analysing images using light. From state-of-the-art optical microscopes to spectroscopy systems and imaging software, these solutions provide high-quality images and data for applications such as materials characterisation, biological research, and semiconductor analysis.
Nanoindentation: Our high-resolution, MEMS-based nanoindenters are designed to measure the mechanical properties of materials, including hardness, elastic modulus, stiffness, and creep behaviour. These instruments offer superior fabrication tolerances, enhancing sensitivity, resolution, and repeatability beyond conventional technology limits.
Nuclear magnetic resonance: We offer a variety of benchtop Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) instruments for research, industrial quality assurance/control, and rock core analysis. These instruments provide advanced capabilities for chemical analysis, materials characterisation, and more.
Raman microscopy: Our advanced imaging systems are tailored for high-resolution microscopy and analysis, offering cutting-edge technology and precision optics for detailed insights into samples at the micro- and nanoscales. Trusted by researchers and scientists in fields such as materials science, life sciences, and nanotechnology, these systems are available in various models to suit different applications.
X-ray technologies: Our technologies encompass a range of advanced systems and solutions for materials analysis and characterisation. With cutting-edge capabilities and high sensitivity, Oxford Instruments X-ray technologies are widely used in various industries and research academic institutions for applications such as material identification, quality control, and research in fields like geology, metallurgy, and semiconductor manufacturing.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.