Sponsored Content by BioDlinkReviewed by Maria OsipovaDec 18 2025
Lyophilization, or freeze-drying, is essential in biopharmaceutical production but presents significant challenges, such as long timelines, high prices, and inconsistent scale-up to GMP production. Traditional trial-and-error procedures prolong development cycles.
BioDlink's BDKLyoTM digital-intelligence process calculation platform uses predictive models to expedite development and enable dependable, efficient scaling up.
This technique overcomes lyophilization inefficiencies, enabling biotech businesses and their partnered CDMOs to meet key production milestones more quickly and with greater confidence.
Existing lyophilization inefficiencies
Lyophilization is critical in biopharmaceutical production. It stabilizes sensitive biological medicines, increases their shelf life, and maintains therapeutic efficacy. Despite its importance, lyophilization is one of the most time-consuming and costly stages of drug development.
Inefficiencies plague traditional process development: trials frequently last more than two months, necessitating numerous iterative rounds with limited flexibility to modify crucial parameters. This laborious, trial-and-error technique slows progress and leaves teams dealing with poor lyophilization conditions.
When scaling up, the current approach, which relies on a one-step drying technique, creates additional risks. Differences in heat and mass transfer dynamics between laboratory and production settings frequently result in uncertain product quality, variations in drying time, and costly rework.
These problems become even more critical as biologics pipelines grow to include increasingly complicated compounds ranging from antibodies to ADCs and beyond, emphasizing the need for faster, more reliable techniques.
Digital and intelligent tools for smarter development
Enter BDKLyoTM, a digital-intelligence process calculation platform developed by BioDlink, a global leader in CDMO. Based on the Pikal model, the 'gold standard' for lyophilization, BDKLyoTM improves a classic process by incorporating predictive precision.
Benefits
- Faster development cycles: Reduced development time from two months to under one month.
- Fewer experimental runs: Only one to two validation rounds are needed to establish optimal settings, resulting in significant cost savings compared to multiple runs.
- Shorter lyophilization times: Optimized lyophilization cycles reduce energy use and manufacturing costs. Case studies show that anticipated drying periods and product temperatures closely match experimental results, with variances of less than 10 % and ±1 °C.
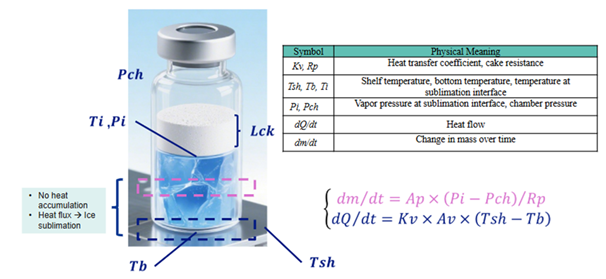
Figure 1. Pikal model and formula. Image Credit: BioDlink
The BDKLyoTM platform helps development teams through three crucial stages:
Process development phase
Traditional CDMOs often require multiple experimental rounds for lyophilization process development, with cycles lasting more than two months.
Critical factors such as primary drying temperature (Tsh), chamber pressure (Pch), and time must be modified repeatedly, resulting in imprecise and often poor outcomes.
BDKLyoTM eliminates the need for manual calculations by combining mass transfer resistance (Rp) with vial geometry, fill volume, critical product temperatures, and heat transfer coefficient (Kv) to generate main drying curves. It also conducts DOE-based full factorial simulations of shelf temperature and chamber pressure to determine the parameters that yield the highest sublimation rates and the shortest drying times while maintaining product quality.
As a result, users only need 1-2 development and validation runs on a lab-scale lyophilizer to define efficient transfer parameters, resulting in development timescales of less than one month.
BDKLyoTM has continuously demonstrated great accuracy, with simulated drying durations deviating from experimental findings by less than 10 % and anticipated product temperatures within ±1 °C.
Process scale-up phase
During the process scale-up phase, the industry typically uses PATs (e.g., Pirani gauge, pressure rise) to calculate production duration while maintaining the same primary drying temperature as in lab research. However, this procedure involves significant risks.
First, changes in cleanliness between lab and production conditions could affect mass transfer resistance, elevating product temperatures and influencing cake appearance and drying time.
Second, differences in heat transfer coefficients between lab- and production-scale dryers can result in significant differences in lyophilization times, rendering lab-derived references unreliable.
BDKLyoTM addresses these issues by combining mathematical modeling with various scale-up tactics, including maintaining consistent shelf temperature, product temperature, and sublimation rate across different scales. Using existing parameters and user requirements, it determines the best method for adjusting processes and achieving a dependable and efficient scale-up.
Process characterization phase:
During the process characterization phase, BDKLyoTM utilizes historical parameters and the maximum sublimation rate curve from the production-scale lyophilizer to define the design space.
Users can utilize this to assess lyophilization risks, define the Process Acceptance Range (PAR) and Normal Operating Range (NOR) for each parameter, and develop management strategies.
Implications for innovative biotech companies
For innovative biotech startups, the risks are very high. Every month saved in development reduces the time to clinical proof of concept, accelerates fundraising milestones, and boosts competitiveness in congested therapeutic areas.
Biotech inventors can benefit from predictive modeling, simplified development, and risk-free scale-up by collaborating with CDMOs that use digital-intelligence lyophilization platforms such as BDKLyoTM.
In short, digital intelligence lyophilization does more than merely enhance operations; it allows biotech companies to meet commercial and clinical goals faster and with greater assurance.
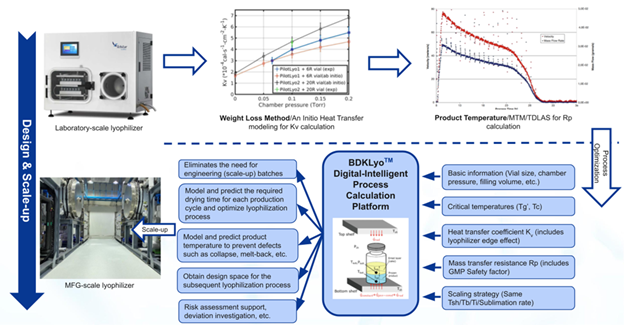
Figure 2. Flowchart and Interface of BDKLyoTM Digital-Intelligence Process Calculation Platform. Image Credit: BioDlink
Case studies: Real-world impact
Case study A – Optimizing lyophilization time
This case study investigated the lyophilization process. The initial cycle was carried out at a shelf temperature of -25 °C, chamber pressure of 20 Pa, and primary drying time of 56 hours.
To lower the cycle time, additional optimization was required. The mass transfer resistance equation was derived by fitting the lyophilization curve to the BDKLyoTM digital intelligence process computation platform:
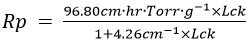
With this resistance value, the lyophilization curve was recalculated, and the shelf temperature was raised to -20 °C. Predictions suggested that primary drying time might be reduced to 36.4 hours (as shown in Table 1).
The experimental validation revealed an actual time of 39.4 hours, with product temperatures roughly matching forecasts (see figure below). This scenario highlights the BDKLyoTM platform's strong predictive accuracy, with modeling findings that are within 10 % of experimental outcomes while maintaining product integrity.
Table 1. Table of lyophilization duration and product temperature of Case A. Source: BioDlink
| Pressure (Pa) |
Plate temperature (℃) |
Prediction |
Experiment |
| Primary drying product temperature (℃) |
Primary drying time (hr) |
Primary drying product temperature (℃) |
Primary drying time (hr) |
| 20 |
-25 |
- 30.1 |
57.6 |
- 30.2 |
56.0 |
| 20 |
-20 |
-27.3 |
36.4 |
- 27.7 |
39.4 |
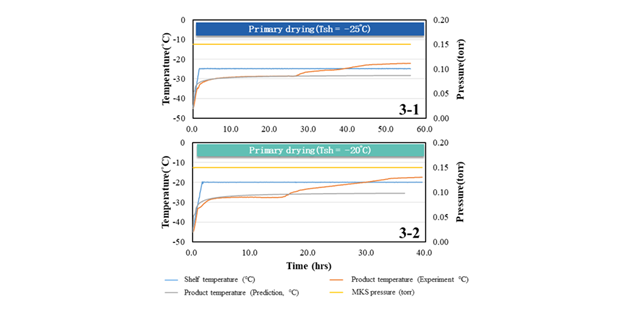
Figure 3. Lyophilization process curve of Case A. Image Credit: BioDlink
Case study B – Optimizing large-volume fills
This case study involved 10 mL fills in 20R vials, which represents a significant product volume. Under conservative lyophilization parameters, the process was expected to take a long time.
During the development phase, the initial shelf temperature was set to -18°C, resulting in an actual drying time of 75 hours. The mass transfer resistance equation was derived by fitting the product temperature data to the BDKLyoTM digital-intelligence process computation platform.
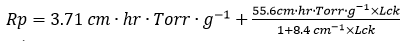
Based on this equation, BDKLyoTM projected a drying time of 73.5 hours at -18 °C, which closely matched the experimental outcome of 75 hours. The actual product temperature curve closely matched the calculated values (Figure 4).
Further optimization increased the shelf temperature to -15 °C, with BDKLyoTM estimating a primary drying time of 64.9 hours. Experimental validation confirmed 66 hours, proving the platform's high prediction accuracy.
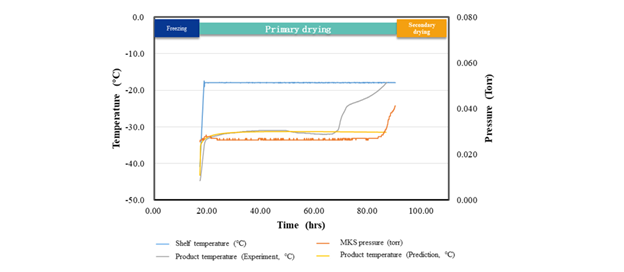
Figure 4. Lyophilization process curve of Case B. Image Credit: BioDlink
Looking ahead: A smarter path to market
These case studies demonstrate the ability of the BDKLyoTM digital-intelligence process calculation platform to accelerate lyophilization process development and scale-up.
With BDKLyoTM, IND-stage projects can be completed in 1-2 experimental rounds, saving time and money during the CMC phase. This platform also creates critical facts and models, which serve as a solid foundation for subsequent process characterization.
About BioDlink
BioDlink (1875.HK) is a leading global CDMO specializing in biologics and bioconjugates (ADCs/XDCs). Headquartered in Suzhou with centers in Shanghai and Beijing, the company provides fully integrated, end-to-end services spanning early R&D through commercial manufacturing.
With its one-base integrated platform and proprietary technologies - such as BDKcell® for rapid cell line development and GL-DisacLink® for site-specific conjugation - BioDlink helps partners accelerate development, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
The company operates four commercial manufacturing lines with large-scale sterile fill-finish capabilities, backed by a global GMP-aligned quality system that has earned PMDA accreditation in Japan and supported product approvals across China, Indonesia, Nigeria, Pakistan, Colombia and Bolivian.
Guided by the philosophy of “Quality First, Innovation Driven, Success Together,” BioDlink is committed to advancing global access to next-generation biologics and building trusted partnerships worldwide.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.