This article and associated images are based on a poster originally authored by Greta Klejborowska, Łukasz Szczupak, Jan Kulczycki, Łukasz Sztukiewicz, Piotr Setny, Michał Michalski, Karolina Zakrzewska, Jarosław Walczak, Michał Komorowski, Michał Mońka, Jan Rzymkowski, Paulina Wach, Paweł Włodarczyk-Pruszyński, Piotr Byrski and Stanisław Jastrzębski and presented at ELRIG Drug Discovery 2025 in affiliation with Molecule.one and Inventro.
This poster is being hosted on this website in its raw form, without modifications. It has not undergone peer review but has been reviewed to meet AZoNetwork's editorial quality standards. The information contained is for informational purposes only and should not be considered validated by independent peer assessment.

Rapid and reliable hit generation with Direct-to-biology-SpaceM1
- Unique and highly novel molecular space of 1.05 billion compounds and still growing
- First chemical space built using deep learning models trained on proprietary HTE lab data of over 300,000 reactions
- Rapid turnaround (fastest subset from order to measured biological activity in four weeks)
- Compounds starting from < $10.
In comparative virtual screening# on 12 protein targets with ~395 randomly selected compounds from commercial reference space and D2B-SpaceM1, D2B-SpaceM1 showed, on average, higher hit rates:
Source: ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
| Target (examples) |
D2B-SpaceM1 docking hit rate** |
C-Ref* docking hit rate** |
Novel to C-Ref (Tanimoto < 0.75) |
Highly novel to C-Ref (Tanimoto < 0.5 & Different Scaffold) |
| PRMT5 |
10.4 % |
1.0 % |
60.0 % |
10.8 % |
| KRAS(G12C) |
6.6 % |
0.0 % |
48.6 % |
18.9 % |
| LRRK2 |
4.3 % |
0.3 % |
54.5 % |
21.2 % |
| mGluR5-5M |
8.1 % |
0.5 % |
43.5% |
10.1 % |
| BTK |
24.3 % |
3.6 % |
46.7 % |
15.6 % |
#Based on ligand efficiency; *C-Ref - commercial reference, **Hit rates calculated using ligand efficiency with threshold of activity set dynamically as at max (0.4, thr_chembl), where thr_chembl is the median ligand efficiency of top 10 % most active compounds stored in ChEMBL. Compounds were randomly sampled from each space.
Hit identification & confirmation from virtual screen in four weeks
D2B-SpaceM1: designed with generative deep models & 300,000+ reaction data points
- The biggest D2B space available on the market
- Highly novel compared to commercial ref.
- HTE data-driven feasibility prediction (~80 % success rate).
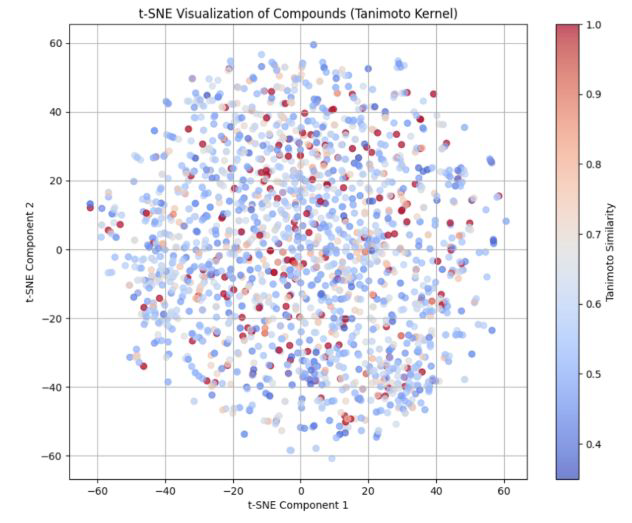
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Greta Klejborowska et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Only 4 % of SpaceM1 compounds exhibit > 0.7 Tanimoto similarity to common commercial ref.
Hit candidates selection based on INVENTRO AI Predictive Models
- Efficient exploration of 1012 cmpd spaces
- On-target activity hit rate for up to 30 %
- Cost (AI model & biological assay): ~$100 per one active
- Time: hours to days
- Multiple activities.
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Greta Klejborowska et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Direct-to-biology (D2B) plate synthesis
- D2B: parallel micro-scale synthesis in well plates followed by minimal work-up
- Molecule’s one HTE lab: on average 13,000 reactions/weekly
- Synthesis success rate ~92 % (84/ 92)
- Feasibility based on proprietary experimental data
- Cmpds delivered in 384-well plates (1–10 mM).

Image Credit: Image courtesy of Greta Klejborowska et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Rapid biological screening
- Initial 100× dilution screen in ADP-Glo → 12 compounds with CLK1 activity <10 %
- Second run at 1,000× and 10,000× dilutions
- Outcome: 11 compounds inhibited CLK1 activity >50 %; hit rate: 18 % (AI-prioritized), 12 % (full grid).
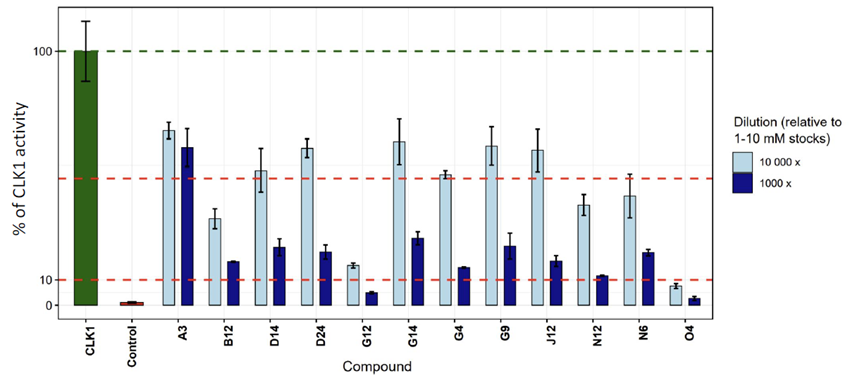
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Greta Klejborowska et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
ADP-Glo - luminescence-based, quantifies ADP as a readout of enzymatic activity; 100 % activity is defined in the absence of inhibitor, control CLK-IN-T3 at one μM.
Hit resynthesis & confirmatory assay
- Fast turnaround: hits resynthesized, purified, and delivered within one week of D2B assay results
- All purified hits confirmed active at Inventro
- Potent hits* down to sub-nM level (IC50 distribution: two at μM, two at sub-μM, two at nM, one at sub-nM).
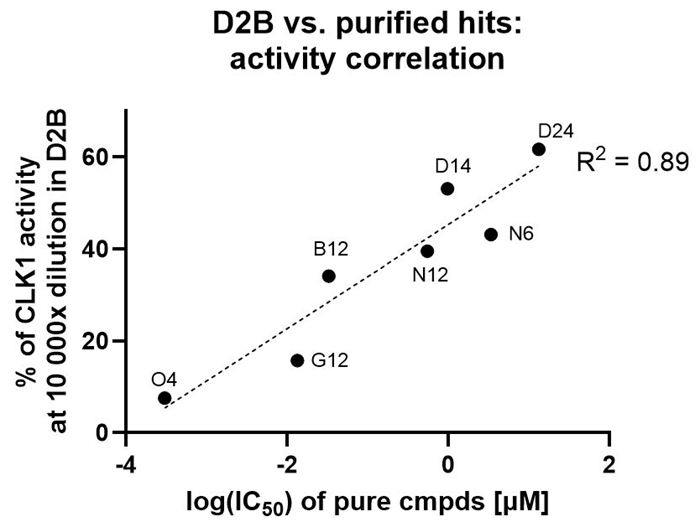
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Greta Klejborowska et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
*No prior literature reports for these structures; for O4, SciFinder similarity 85 to the closest known
Summary:
- Largest & most novel D2B space, built on extensive HTE reaction data
- Strong (0.89 R2) correlation between D2B crude activity and purified IC50 ranking
- Hit activity up to sub-nM level, hit rate 18 %
- End-to-end workflow is very rapid, enabling experimental hitID and confirmation within weeks, not months
- Workflow applicable also to hit expansion and hit2lead
About Molecule One
Molecule One is a deep-tech chemistry company that blends artificial intelligence, machine learning and high-throughput automated experimentation to solve one of the biggest bottlenecks in small-molecule R&D: how to make novel compounds reliably and at scale. Their flagship platform, “Maria™”, is a synthesis-planning engine powered by more than 300 000 microliter-scale reaction experiments, allowing it to map chemical reactivity patterns beyond classical human intuition.
About ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
The European Laboratory Research & Innovation Group (ELRIG) is a leading European not-for-profit organization that exists to provide outstanding scientific content to the life science community. The foundation of the organization is based on the use and application of automation, robotics and instrumentation in life science laboratories, but over time, we have evolved to respond to the needs of biopharma by developing scientific programmes that focus on cutting-edge research areas that have the potential to revolutionize drug discovery.
Comprised of a global community of over 12,000 life science professionals, participating in our events, whether it be at one of our scientific conferences or one of our networking meetings, will enable any of our community to exchange information, within disciplines and across academic and biopharmaceutical organizations, on an open access basis, as all our events are free-of-charge to attend!
Our values
Our values are to always ensure the highest quality of content and that content will be made readily accessible to all, and that we will always be an inclusive organization, serving a diverse scientific network. In addition, ELRIG will always be a volunteer led organization, run by and for the life sciences community, on a not-for-profit basis.
Our purpose
ELRIG is a company whose purpose is to bring the life science and drug discovery communities together to learn, share, connect, innovate and collaborate, on an open access basis. We achieve this through the provision of world class conferences, networking events, webinars and digital content.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 13, 2025