This article is based on a poster originally authored by Mohamed Nsaibia, Spundana Malla, Daniel Mongeluzi, Silvia Pires Lourenco, Rabi Mishra, Vibhor Gupta, Jane Fisher and Mark Semanick.
Background
OTC deficiency is a rare genetic condition and the most prevalent urea cycle disorder.
Newborns with neonatal onset OTC deficiency exhibit hyperammonemia symptoms shortly after birth, including lethargy, difficulty sucking, and vomiting, which, if left untreated, can swiftly progress to seizures, brain damage, coma, and death. In severe cases, liver transplantation is the only known treatment option.
Unlike previous AAV therapies, ECUR-506 consists of two AAV vectors: ECUR-506A, which expresses ARCUS®* nuclease to target the PCSK9 region, and ECUR-506D, which is intended to integrate the functional OTC transgene into the genome.
In collaboration with iECURE, the Pharmaron team is creating two complementary in vitro cell-based tests to evaluate the efficacy of ECUR-506.
(1) A PCR-based technique to confirm the effective integration of the OTC transgene at the PCSK9 locus; and
(2) a functional potency assay to assess OTC enzyme activity.
*iECURE has licensed Precision BioSciences' ARCUS® nuclease.
Methods
Ornitine transcarbamylase (OTC) is an enzyme that transforms ornithine to citrulline in the urea cycle.
Huh7 cells were transduced with a mixture of ECUR-506A and ECUR-506D at different multiplicity of infection (MOI).
Genomic DNA was taken from both untransduced (UTD) and transduced cells for OTC transgene integration study, and integration was assessed using PCSK9/OTCspecific primers using qPCR.
PCR amplification and Sanger sequencing confirmed OTC transgene insertion at the PCSK9 locus.
To demonstrate functionality, the conversion rate of d7-ornithine to d7-citrulline was measured by LC-MS/MS to determine quantitative OTC enzyme activity.
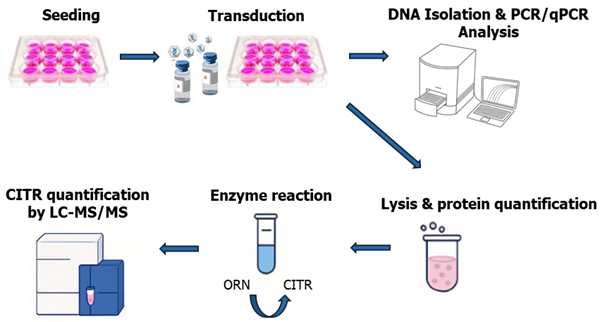
Figure 1. in vitro potency assay workflow to assess OTC transgene integration by PCR/qPCR and OTC enzyme activity by LC-MS/MS. Image Credit: Pharmaron
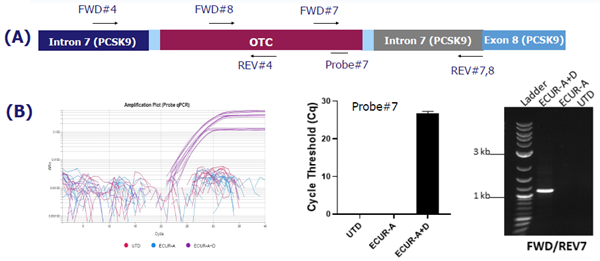
Figure 2. OTC gene integration into the PCSK9 locus in ECUR-506A+D co-transduced cells. (A) schematic, (B) probe-based qPCR specific amplification plot and cycle threshold quantification, (C) agarose gel image of qPCR products. Image Credit: Pharmaron
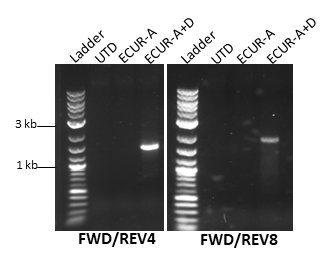
Figure 3. Agarose gel electrophoresis of PCR products submitted for Sanger sequencing. Sequencing confirmed accurate integration of the OTC transgene, showing consensus sequences identical to the reference. Image Credit: Pharmaron
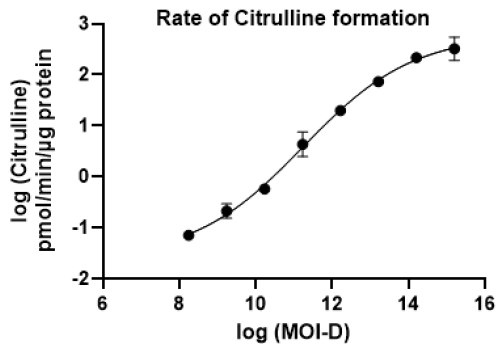
Figure 4. Citrulline formation rate as a function of AAV dose in the in vitro functional potency assay. The rate of citrulline formation (pmol/min/μg protein) was quantified by LC-MS/MS and plotted against log-transformed MOI values. Data represent mean ± SEM (n=2). Image Credit: Pharmaron
Conclusion
- Control samples revealed no amplification, indicating effective site-specific OTC transgene integration into the PCSK9 locus.
- Sanger sequencing demonstrated accurate integration of the OTC transgene, with consensus sequences matching the reference.
- Increasing AAV MOI resulted in a dose-dependent rise in OTC enzyme activity, indicating functional activity.
About Pharmaron
Pharmaron (Stock Code: 300759.SZ/3759.HK) is a premier R&D service provider for the life sciences industry. Founded in 2004, Pharmaron has invested in its people and facilities, and established a broad spectrum of research, development and manufacturing service capabilities throughout the entire drug discovery, preclinical and clinical development process across multiple therapeutic modalities, including small molecules, biologics and CGT products. With over 17,000 employees, and operations in China, the U.S., and the U.K., Pharmaron has an excellent track record in the delivery of R&D solutions to its partners in North America, Europe, Japan and China.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Jan 9, 2026