Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that affects the lower digestive tract and impacts an estimated 10–15% of the population. While it's common, IBS can be deeply disruptive to daily life.
Many people living with the condition struggle with a lack of effective treatment options and often feel overlooked or dismissed by healthcare providers. This can lead to frustration, isolation, and a sense of not being taken seriously.
IBS symptoms can include:
- Stomach cramps
- Bloating
- Discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
Types of IBS:
- IBS-C: IBS characterized by constipation
- IBS-D: IBS characterized by diarrhea
- IBS-M: IBS characterized by mixed bowel habits
- Post-Infectious IBS: Often occurs following a gastrointestinal infection
Image Credit: Bedfont® Scientific Ltd
Causes of IBS
There’s no single known cause of IBS, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include gut inflammation, changes in gut motility, heightened sensitivity to certain foods, and disruptions in the gut microbiome.
Triggers for IBS symptoms can vary widely between individuals, but some of the more common ones include:
- Psychological stress
- Anxiety
- Certain foods
- Changes in routine
- Hormonal changes
Gut-brain connection
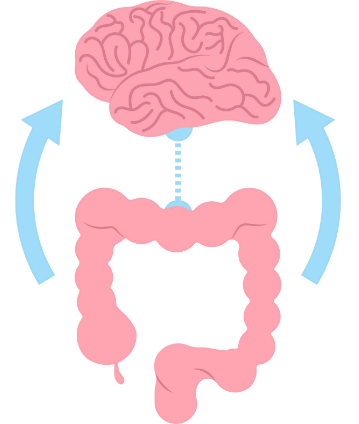
Image Credit: Bedfont® Scientific Ltd
Research has demonstrated that gut microbes produce or assist in the production of many chemical neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters act as messengers conveying information between the gut and brain, which is why the gut is commonly referred to as the “second brain.”
Examples of these messages between the gut and brain include:
- Sensation of butterflies in the stomach due to nervousness
- Sickness or nausea after receiving bad news
- Having a “gut feeling”
How IBS can impact daily life
IBS is more commonly diagnosed in women than in men, and it tends to occur most often in people between the ages of 20 and 40. That said, it can affect individuals of any age.
For those living with IBS, symptoms can be unpredictable and may include sudden urgency, making everyday activities like attending social events or eating out feel stressful or even unmanageable. This unpredictability often contributes to anxiety and can have a significant impact on overall quality of life.
However, it is important not to self-diagnose, as IBS symptoms can overlap with other gastrointestinal conditions. Seeing a healthcare professional allows for proper evaluation, which may include blood tests, stool analysis, or other investigations, rather than relying solely on over-the-counter remedies.
How an HMBT can help
While a Hydrogen and Methane Breath Test (HMBT) cannot directly diagnose IBS, it can be a valuable tool in helping to rule it out. HMBT was developed to address the challenges of accessing the small intestine and is particularly useful for detecting conditions like small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and certain types of dietary malabsorption.
Hydrogen (H2) and methane (CH4) are gases produced when undigested carbohydrates are fermented by bacteria in the gut. Elevated levels of these gases may point to disorders such as SIBO or carbohydrate malabsorption—conditions that can mimic IBS symptoms. By identifying or ruling out these underlying issues, HMBT can support a more accurate diagnosis and guide appropriate treatment.
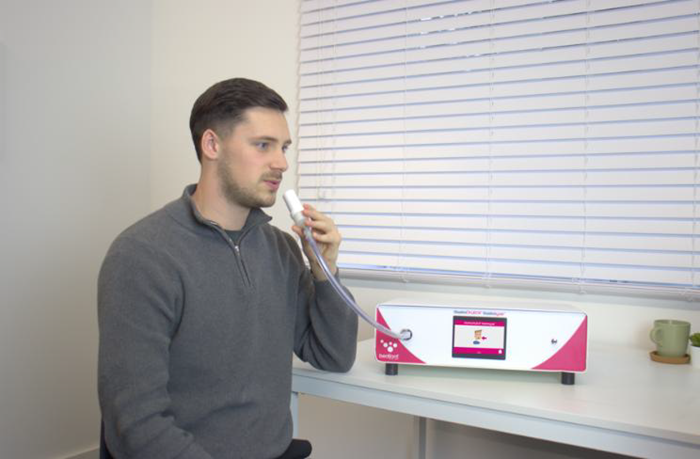

Image Credit: Bedfont® Scientific Ltd
Melissa offers an in-depth discussion on IBS, SIBO, and carbohydrate malabsorption during the webinar, including a comprehensive real-world case study.
To learn more and watch the webinar in full, click here.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Melissa Dooley.
About Bedfont® Scientific Ltd
Bedfont® Scientific has specialised in the design and manufacture of exhaled breath and gas monitoring instruments since 1976.
For medical gas monitoring, their Medi-Gas Check medical pipeline testing range verifies not only the quantity but also quality of gas administered to patients.
Bedfont's breath analysers include carbon monoxide (CO) monitors such as the Smokerlyzer®, used for smoking cessation, and the ToxCO®, used by emergency services, to diagnose CO poisoning.
The NObreath® FeNO monitor provides accurate analysis of airway inflammation for the control of asthma, and the Gastrolyzer® range aids in the detection of gastrointestinal disorders and food intolerances. Quick and non-invasive, breath analysis is the new blood test.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.