This article is based on a poster originally authored by Jing Lai; Huimin Chen; Qi Cheng; Danxi Li and Mandy Xu.
Introduction
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a key obstacle to central nervous system (CNS) drug development, with over 98 % of small-molecule medicines failing to reach therapeutic brain exposure due to low BBB permeability.1
Traditional in vitro models (e.g., MDCK-MDR1 monolayers) frequently lack important physiological characteristics such as functioning transporters, receptors, and endothelium indicators.
To address this, the researchers created a co-culture BBB model using primary rat brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), pericytes (PCs), and astrocytes (ACs) on Transwell inserts to create a physiologically appropriate screening platform.
Methods
- BMECs, pericytes, and astrocytes were seeded and grown in a 24-well HTS Transwell® system for five to seven days to create a tight barrier. A variety of combinations of sowing procedures were used.
- TEER readings and lucifer yellow leakage were used to identify the ideal culture setup.
- Detecting receptor-mediated transcytosis receptors and transporters in BMECs/Pericytes using immunofluorescence and qPCR.
- Used rat BMEC and pericytes co-culture models, as well as in vivo Kp,uu,CSF, and Kp,uu, brain data, to conduct drug permeability tests and IVIVE analyses.
Establishment of a rat BBB tri-culture system
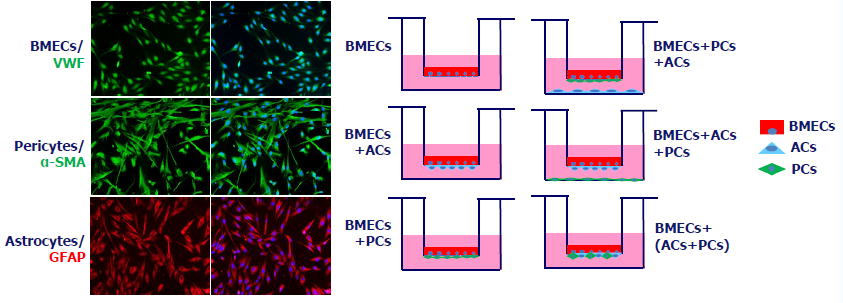
Image Credit: Pharmaron
Schematic diagram of tri-culture system: Immunofluorescence showed the high purity (>90 %) of BMECs (VWF+), pericytes (α-SMA+), and astrocytes (GFAP+).
Create various tri-culture systems by combining ACs and PCs or seeding them individually on the back of the PET membrane or the bottom of the plate.
Co-culture of BMECs with pericytes alone demonstrated optimal barrier integrity
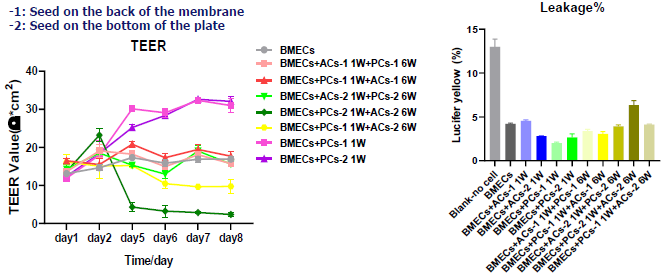
Image Credit: Pharmaron
Barrier integrity of different co-culture systems: The BMECs/Pericytes co-culture system had the highest TEER value compared to the other systems. Lucifer yellow leakage in BMECs/Pericytes co-culture is the lowest, at around 2.07 %.
The model retained functional RMT receptor expression, confirming key BBB features
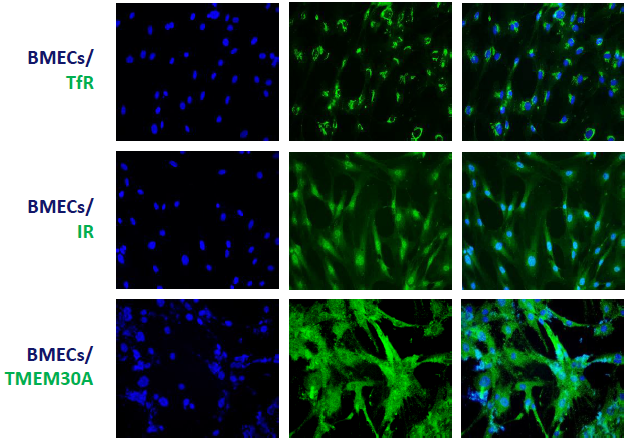
Image Credit: Pharmaron
Immunofluorescence of RMT markers: Transferrin receptor (TfR), insulin receptor (IR), and transmembrane protein 30A (TMEM30A) are all highly expressed in BMEC cells.
The BMECs/Pericytes co-culture system showed the highest expression of transporters mRNA expression
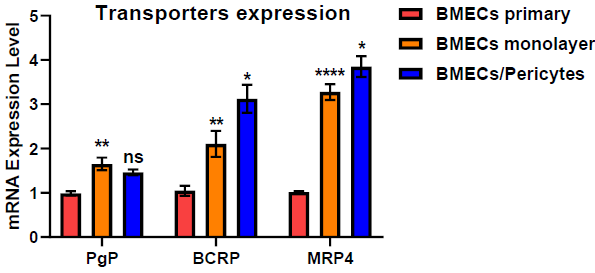
Image Credit: Pharmaron
QPCR of transporters mRNA expression: BMECs creating a barrier on the transwell boost the expression of transporters Pgp, BCRP, and MRP4, and co-culture of BMECs and Pericytes promotes the expression of BCRP and MRP4 even more. There was no substantial change in PgP expression between the BMEC monolayers.
BMECs/Pericytes co-culture showed strong correlation with in vivo rat Kp,uu CSF and Kp,uu
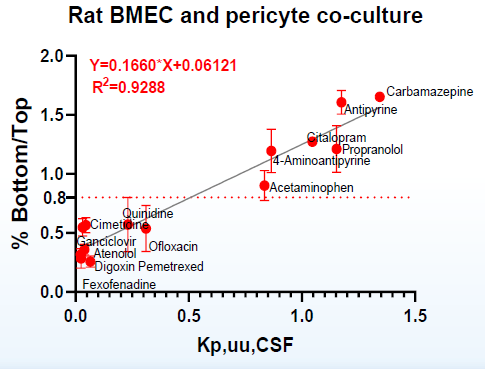
Image Credit: Pharmaron
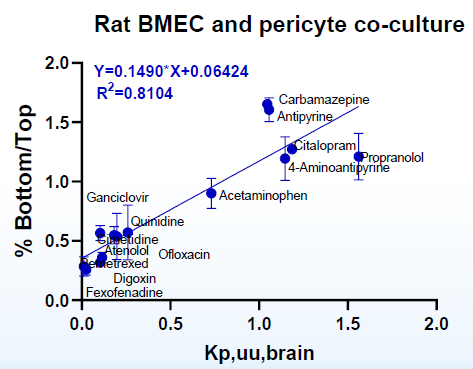
Image Credit: Pharmaron
Conclusion
IVIVE study demonstrated that BMECs/Pericytes cultivated on transwell plates were consistent with in vivo results. The reproducible, high throughput approach provides:
- A cost-effective method for early CNS drug screening, with established in vivo correlation.
- New insights into pericyte-dominated barrier modulation, challenging the need for astrocytes in some assays.
- Consistent with preclinical Kpuu results, indicating direct application to pharmaceutical procedures.
Reference
- Wu, D., et al. (2023). The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 8(1), pp.1–27. DOI: 10.1038/s41392-023-01481-w. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-023-01481-w.
About Pharmaron
Pharmaron (Stock Code: 300759.SZ/3759.HK) is a premier R&D service provider for the life sciences industry. Founded in 2004, Pharmaron has invested in its people and facilities, and established a broad spectrum of research, development and manufacturing service capabilities throughout the entire drug discovery, preclinical and clinical development process across multiple therapeutic modalities, including small molecules, biologics and CGT products. With over 17,000 employees, and operations in China, the U.S., and the U.K., Pharmaron has an excellent track record in the delivery of R&D solutions to its partners in North America, Europe, Japan and China.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Jan 9, 2026