This article and associated images are based on a poster originally authored by Rose Bigley, James Craswell, Michael Carter, Philip Fallon, and Nicholas Bland, and presented at ELRIG Drug Discovery 2025 in affiliation with Domainex Ltd.
This poster is being hosted on this website in its raw form, without modifications. It has not undergone peer review but has been reviewed to meet AZoNetwork's editorial quality standards. The information contained is for informational purposes only and should not be considered validated by independent peer assessment.

RNA as a drug target
Drug discovery is evolving beyond the traditional paradigm of binary interactions between small molecules and protein targets. Among the most challenging targets are those considered "undruggable" at the protein level.
An attractive approach to targeting such proteins is to hit them at the RNA stage. Targeting RNA, before it is translated into deleterious proteins, represents a promising new frontier in therapeutic development.
Domainex is pioneering a platform for RNA-targeted drug discovery, aiming to intercept disease at its earliest molecular stages.
Traditionally, RNA-directed therapeutics were typically antisense oligonucleotides or siRNAs. Small molecules have become increasingly important in the field of RNA drug discovery.
One of the most famous small molecules that targets RNA is Evrysdi (ridisplam), a treatment for 5q Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
As the field progresses, new molecules are constantly being identified, such as neomycin-S, which can bind human premiRNA.
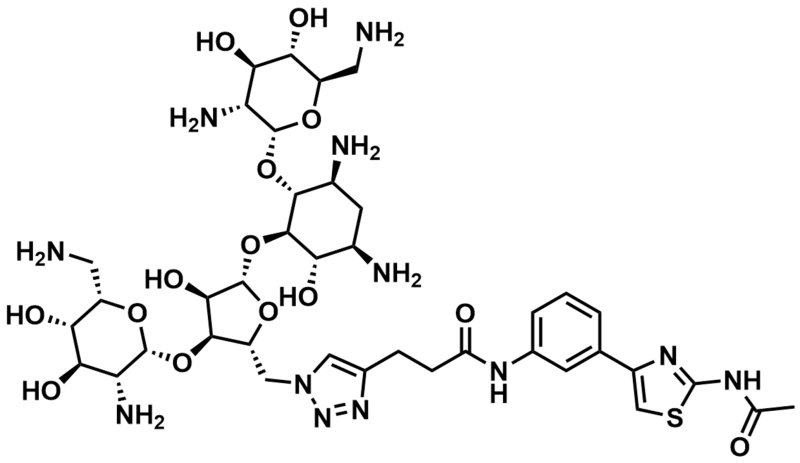
Neomycin-S Inhibitor pre-miRNA 372/373. Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
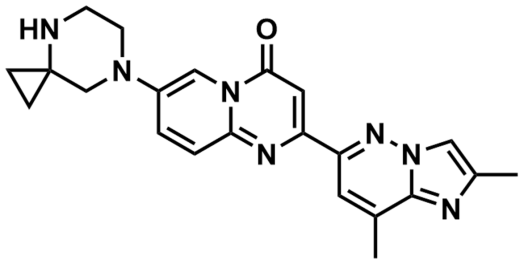
Evrysdi (ridisplam) FDA-approved drug treatment for SMA. Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Biophysical assays for small-molecule RNA binders
Riboswitches are structured RNA molecules that are essential for regulating bacterial metabolism, making them attractive targets for novel antibiotics.
Domainex utilized its suite of cutting-edge biophysical technologies to measure the binding of small molecules to the riboswitch SAM-VI.
SAM-VI’s endogenous ligands are S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM) and SAdenosylhomocysteine (SAH).
Assays were developed using the NanoTemper Dianthus and Grating-Coupled Interferometry (GCI).
Both methods showed excellent recapitulation of published values, providing an excellent platform for any RNA-targeted drug discovery program.
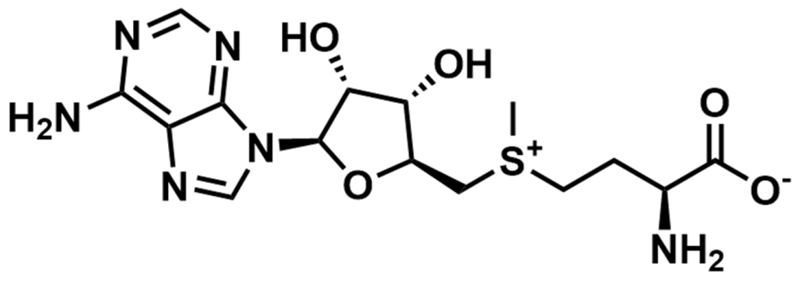
S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM). Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
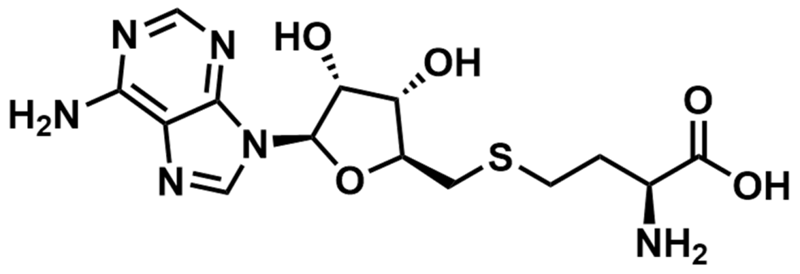
S-Adenosylhomocysteine (SAH). Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
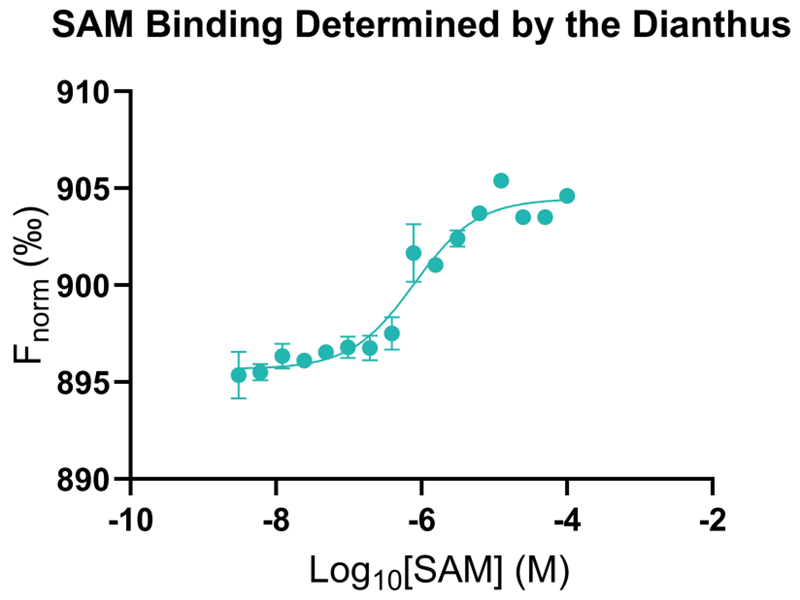
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
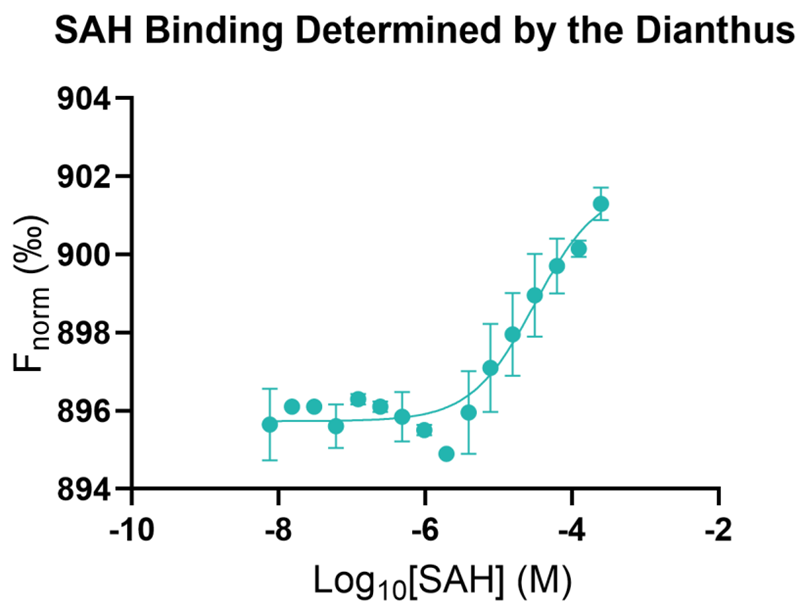
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
GCI
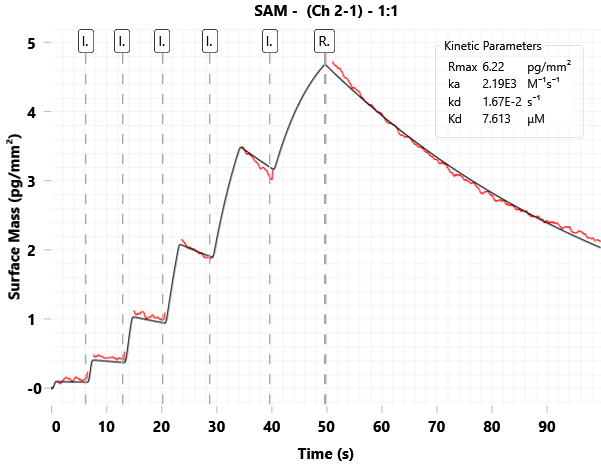
Image Credit: Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
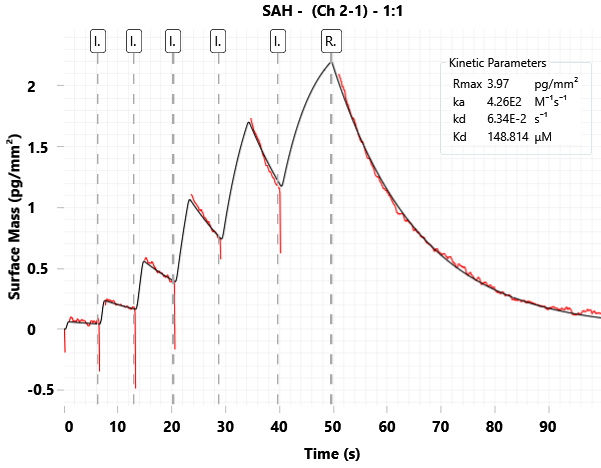
Image Credit: Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Source: ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
| SAM |
ka (M-1s-1) |
kd (s-1) |
KD (μM) |
| Literature* |
2.98E+03 |
9.8E-03 |
3.72 |
| Domainex |
2.19E+03 |
1.67E-02 |
7.61 |
Source: ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
| SAH |
ka (M-1s-1) |
kd (s-1) |
KD (μM) |
| Literature* |
3.88E+02 |
5.4E-02 |
150 |
| Domainex |
4.26E+02 |
6.34E-02 |
149 |
*Almena Rodriguez et al., J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 8, 8659–8678
Computational approaches to identify RNA-binding fragments
- Virtual Screening of Domainex's proprietary fragment library
- Developed Ligand-Based Drug Design (LBDD) models to identify small molecules targeting SAM-VI RNA
- Constructed Shape and Electrostatic similarity models using Phase (Schrödinger) to capture key physicochemical complementarity to known SAM-VI RNA binders
- Built Pharmacophore models using Phase (Schrödinger) to define essential interaction features and guide virtual screening
- LBDD models enabled rapid scoring of Domainex's fragment library using prior structural and ligand information
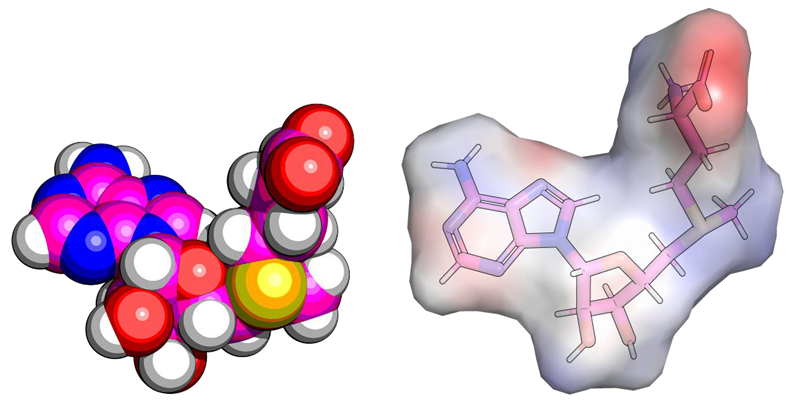
SAM Shape and Electrostatic models. Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
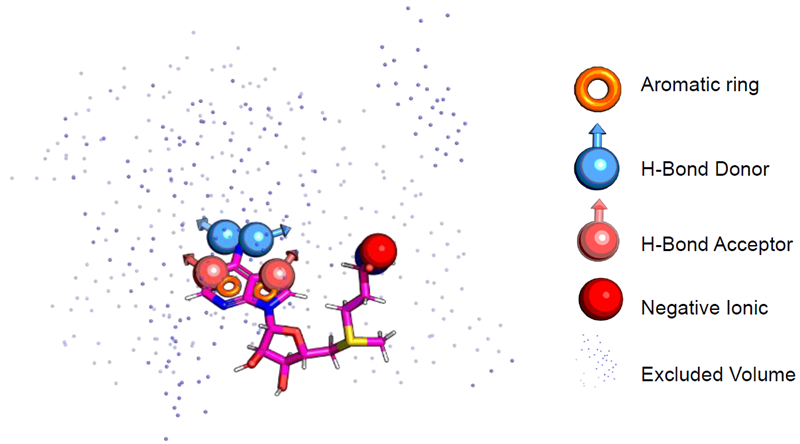
SAM Pharmacophore model. Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
- Implemented Structure-Based Drug Design (SBDD) workflows leveraging Glide (Schrödinger) for high-precision SAM-VI RNA–ligand docking
- Integrated RNAmigos2, a deep graph learning algorithm trained to predict RNA–ligand binding probabilities based on 3D RNA binding sites using 2.5D graph-based binding site features
- Combined physics-based docking scores with AI/ML-derived interaction likelihoods to enhance confidence in hit prioritization
- Established a hybrid LBDD/SBDD virtual screening workflow that used both physics-based and AI/ML scoring functions to score and rank Domainex’s fragment library
- Utilized Pareto ranking to identify fragments on the Pareto frontier across all Virtual Screening models, selecting 100 fragments for experimental screening
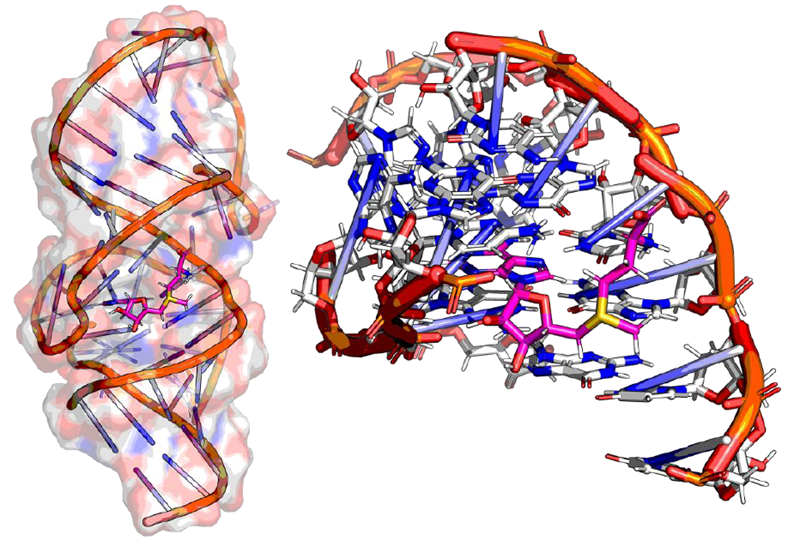
SAM-VI Docking Model (PDB:6LAS). Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
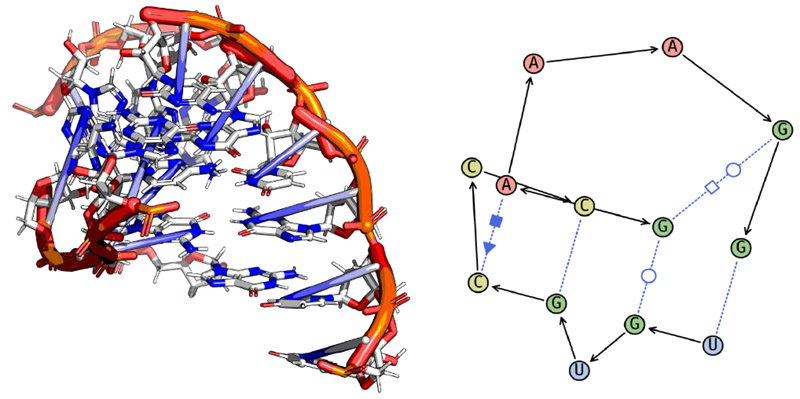
SAM-VI 3D Binding Site – RNAmigos2 2.5D Graph. Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Screening of computationally selected fragments
- Spectral shift is an attractive technology for screening RNA
- RNA requires a simple modification – addition of Cy5
- The 384-well-based format allows for rapid turnaround of screening data
- 100 fragments were screened at 500 μM with both SAM and SAH controls
- Compounds were automatically classified into six categories, allowing for easier classification and interpretation
- Only a small number of compounds cause interference by autofluorescence - an advantage of using a far-red dye
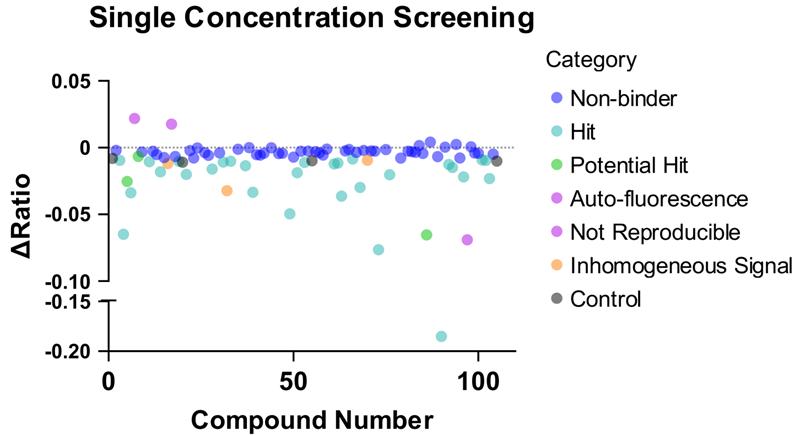
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
- One third of the compounds screened were confirmed as binders of the SAM-VI riboswitch.
- Approximately 20 % of compounds were excluded due to assay interference.
- Almost half of the compounds did not return a significant Δratio and were classified as non-binders.
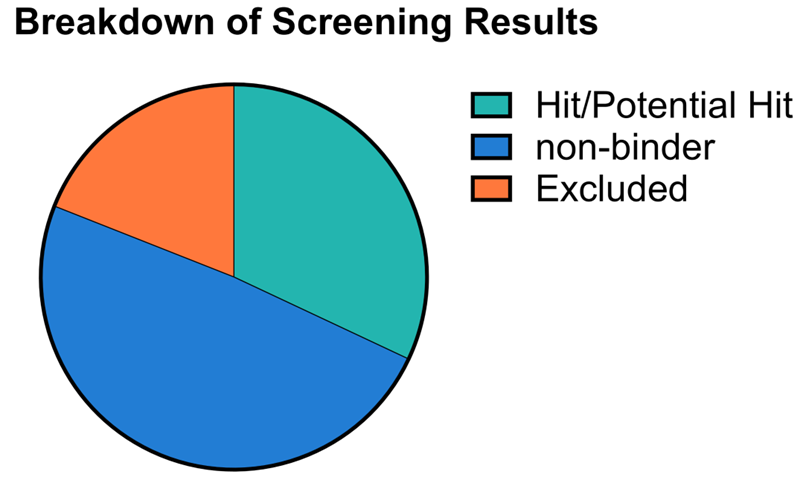
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Rose Bigley et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Summary
- Small-molecule binding to RNA is an exciting new modality in drug discovery.
- Domainex’s suite of computational and biophysical techniques provides a powerful platform for exploring the exciting new frontier of RNA-directed small molecule therapies.
About Domainex
Domainex is a fully integrated drug discovery CRO based near Cambridge, UK. It serves pharmaceutical, biotechnology, academic and patient foundations globally. Domainex’s drug discovery service business was established in 2001 and since that time has continued to expand to serve a wider range of international clients including UCB, FORMA Therapeutics, St George’s University, and The Institute of Cancer Research.
About ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
The European Laboratory Research & Innovation Group (ELRIG) is a leading European not-for-profit organization that exists to provide outstanding scientific content to the life science community. The foundation of the organization is based on the use and application of automation, robotics and instrumentation in life science laboratories, but over time, we have evolved to respond to the needs of biopharma by developing scientific programs that focus on cutting-edge research areas that have the potential to revolutionize drug discovery.
Comprised of a global community of over 12,000 life science professionals, participating in our events, whether it be at one of our scientific conferences or one of our networking meetings, will enable any of our community to exchange information, within disciplines and across academic and biopharmaceutical organizations, on an open access basis, as all our events are free-of-charge to attend!
Our values
Our values are to always ensure the highest quality of content and that content will be made readily accessible to all, and that we will always be an inclusive organization, serving a diverse scientific network. In addition, ELRIG will always be a volunteer led organization, run by and for the life sciences community, on a not-for-profit basis.
Our purpose
ELRIG is a company whose purpose is to bring the life science and drug discovery communities together to learn, share, connect, innovate and collaborate, on an open access basis. We achieve this through the provision of world class conferences, networking events, webinars and digital content.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 25, 2025