This article and associated images are based on a poster originally authored by Kamini Magon, Alison Holiday, Iwona Ziomkiewicz, Jonathan Powell, Jon Dunn, David Tickle, David Dexter, Janusz Julagowski, and Ian Winfield, and presented at ELRIG Drug Discovery 2025 in affiliation with Domainex Ltd and Parkinson’s UK.
This poster is being hosted on this website in its raw form, without modifications. It has not undergone peer review but has been reviewed to meet AZoNetwork's editorial quality standards. The information contained is for informational purposes only and should not be considered validated by independent peer assessment.

Introduction
Elevated levels of C5a, an inflammatory peptide produced upon complement activation, initiate a feed-forward loop of inflammation via recruitment of microglia to sites of injury, leading to neuronal damage and death.
C5a exerts its effects by binding and activating the complement 5a receptor 1 (C5aR1), a G protein-coupled receptor that couples to Gαi/o, recruits β-arrestins, and modulates chemotaxis.
Preventing C5aR1 activation may reduce neuroinflammation, potentially leading to disease-modifying effects.
Here, a drug discovery program has been developed utilizing medicinal and computational chemistry, in vitro pharmacology, and ADME/PK, which successfully identified and characterized lead-like negative allosteric modulators (NAMs) of the C5aR1, with data for the most promising compound (PVB-800218) presented.
Screening cascade
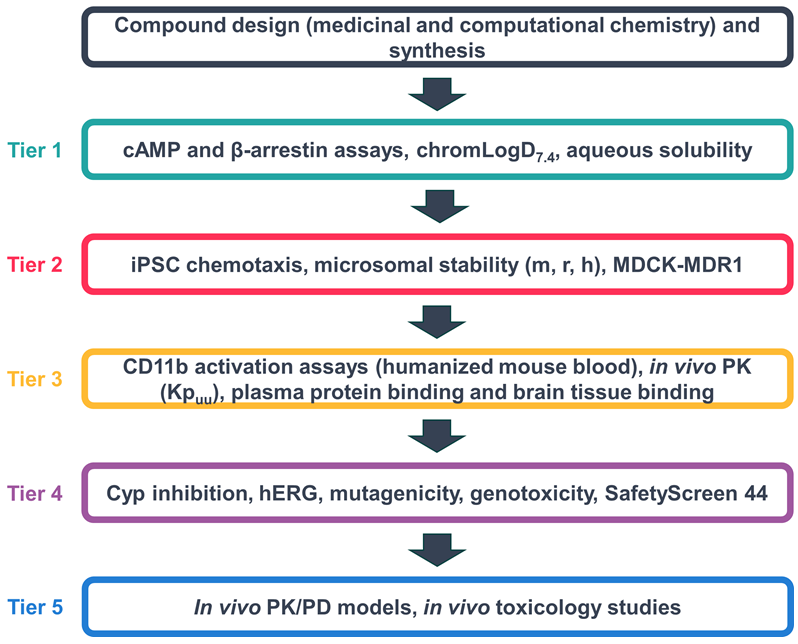
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
A five-tier screening cascade suitable for testing novel compounds has been developed. These were designed through robust SAR analysis and further validated using computational chemistry efforts, followed by pharmacological validation as C5aR1 NAMs via a series of assays utilizing a range of recombinant, hiPSC, and ex vivo models.
Tier 1 screening – Function effects
CHO-K1 cells overexpressing hC5aR1 were utilized for cAMP inhibition assays, whilst the DiscoverX PathHunter® assay was employed for investigating β-arrestin recruitment.
These assays, performed with C5a concentration-response curves tested in the presence of increasing concentrations of the test compound, were analyzed using the operational model of allosteric modulation of pharmacological agonism to confirm the allosteric nature of the test compounds.
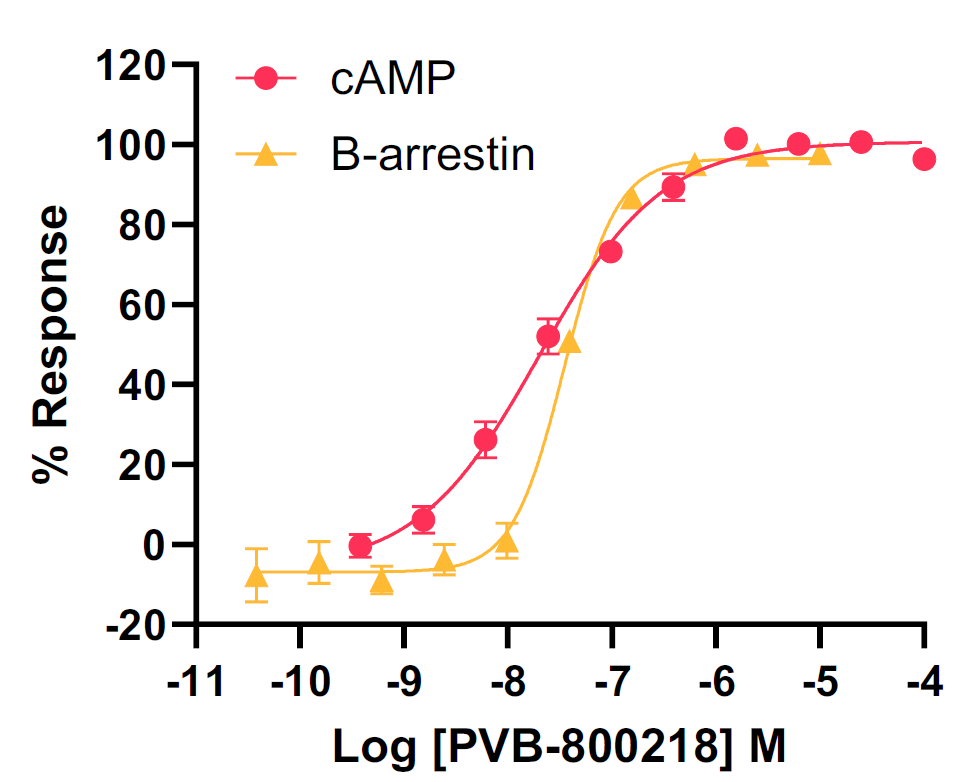
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
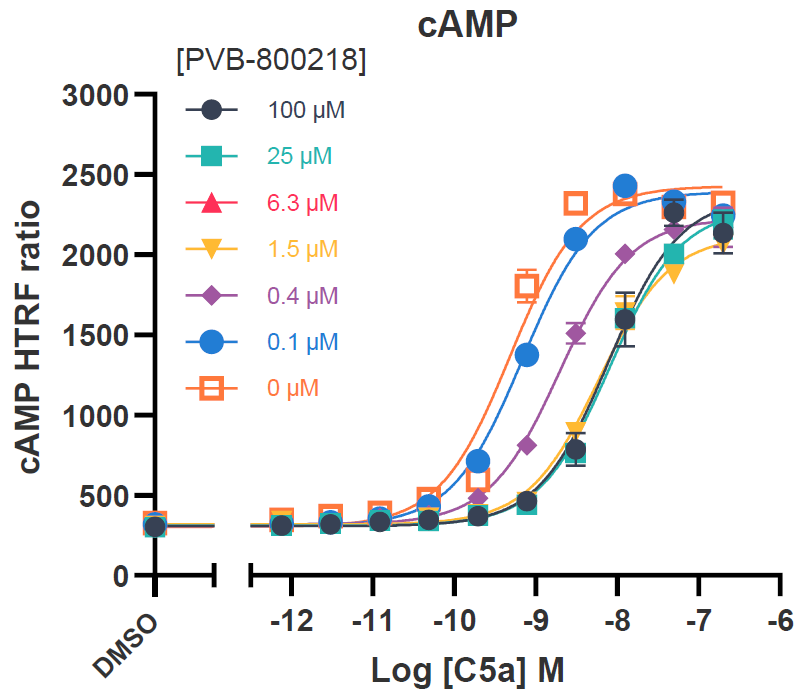
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
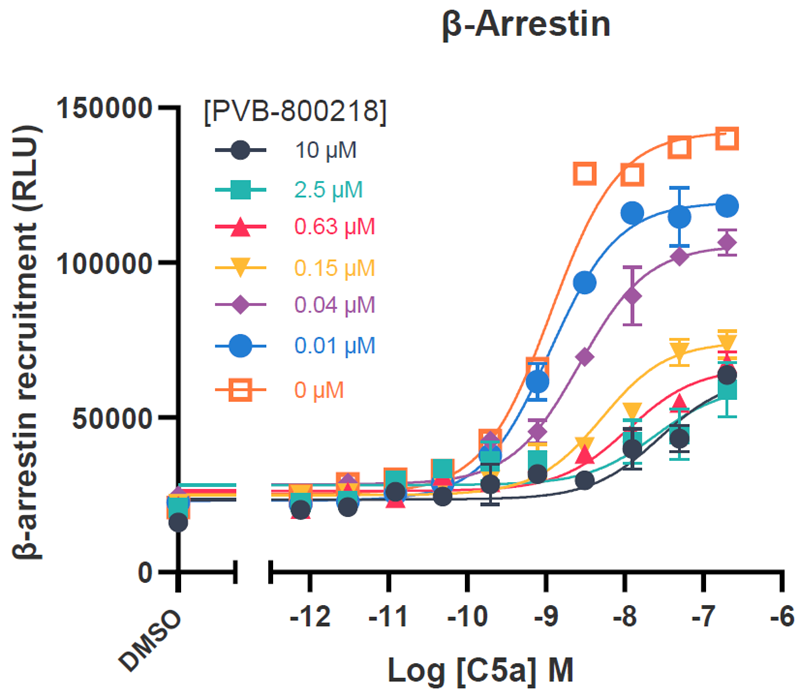
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Tier 2 screening – System effects
One of the main physiological actions of C5a is as a chemoattractant. The C5aR1 NAMs was tested in a chemotaxis assay using human iPSC microglia, investigating their ability to inhibit C5a-induced chemotaxis.
Numerous compounds tested displayed inhibitory activity in this assay, with the lead compound having an IC50 of 27 nM.
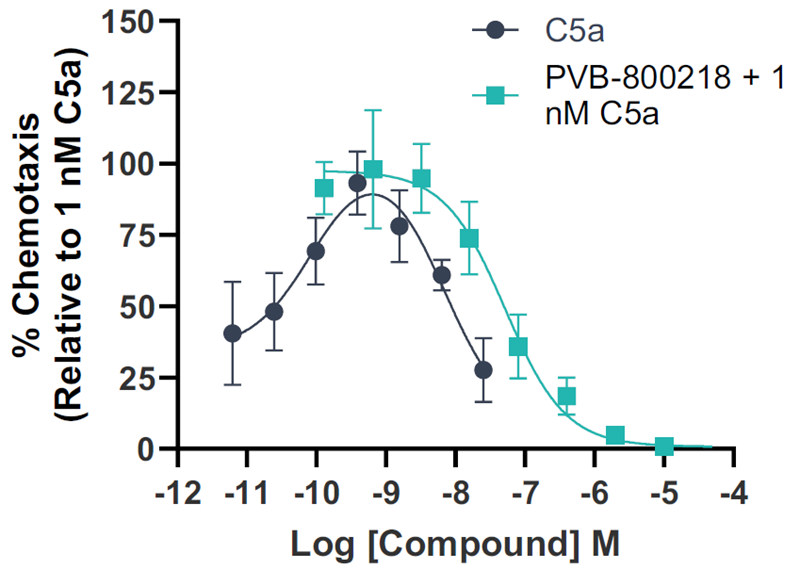
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Tier 3 mouse model validation and Ex Vivo profiling
The C5aR1 allosteric site is not present in the mouse isoform. Thus, a humanized mouse model was developed. To validate this model, initial data identified the ability of the compounds to inhibit C5a-induced neutrophil activation (reduced CD11b expression) as well as reducing the expression of Ly6G, a marker of chemotactic cells, confirming the chemotaxis data with hiPSC microglia.
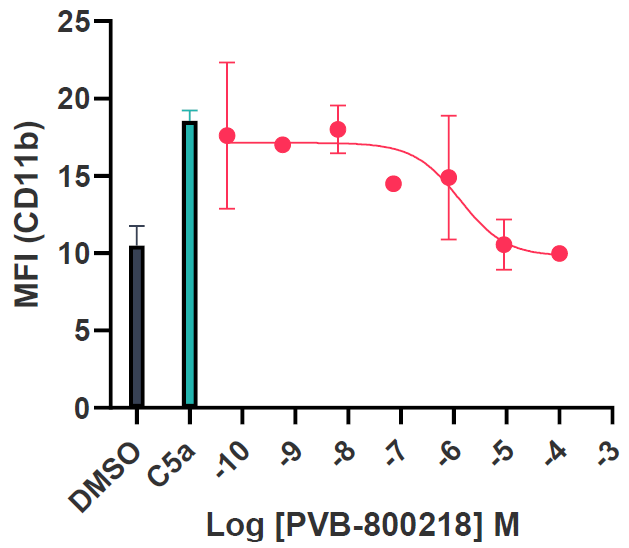
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
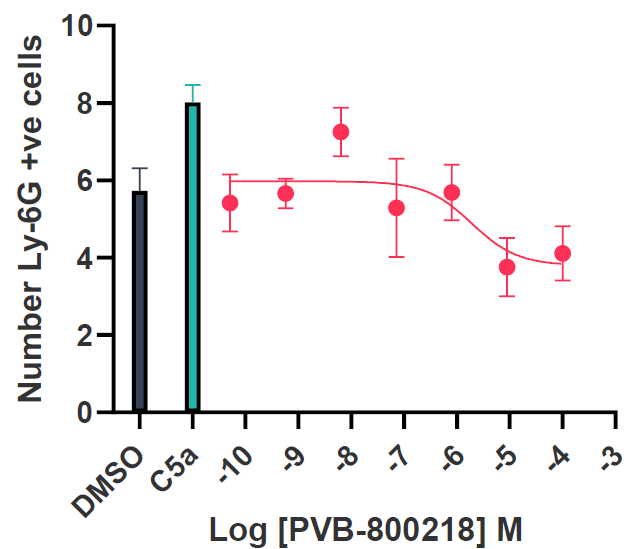
Image Credit: Image courtesy of Kamini Magon et al., in partnership with ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
Lead compound profile
The drug discovery program has enabled the development of a lead compound with nanomolar potencies in both recombinant systems and hiPSC models, as well as demonstrated effects in ex vivo blood studies using humanized mice.
Operational modelling of the data has identified the allosteric nature of our compounds with both α and β values <1.
Initial profiling has also indicated PVB-800218 is a good candidate for further development, focusing on improving metabolic stability, whilst retaining on-target potency and efficacy.
Source: ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
| Property |
PVB-800218 |
| Mwt, TPSA, MPO |
561.6, 78, 4.5 |
| β-arrestin IC50 (nM), α and β |
35, 0.11, 0.76 |
| cAMP IC50 (nM), α and β |
20, 0.13, 1.02 |
| Chemotaxis IC50 (nM) |
27 |
| CD11b IC50 (μM) |
2.2 |
| ChromLogD(7.4) |
4.7 |
| Kinetic solubility (μM, 60 mins) |
26 |
| Mouse microsomal clearance (t1/2 (mins), Clint (μL/min/mg protein) |
16, 90 |
| t1/2 (hr) |
1.6 |
| Cl (ml/min/kg) |
8.6 |
| Vd (L/Kg) |
0.9 |
| Brain: Plasma (5 min) |
0.4 |
| Time [Brain] above β-arrestin IC50 (mins) |
30 |
Conclusions
A combined team of disciplines has been utilized to deliver a fully integrated drug discovery program, successfully identifying lead-like negative allosteric modulators of the C5aR1.
The lead compound will progress through more advanced ADME/DMPK assays, selectivity screening, and in vivo studies, to further improve metabolic stability.
About Domainex
Domainex is a fully integrated drug discovery CRO based near Cambridge, UK. It serves pharmaceutical, biotechnology, academic and patient foundations globally. Domainex’s drug discovery service business was established in 2001 and since that time has continued to expand to serve a wider range of international clients including UCB, FORMA Therapeutics, St George’s University, and The Institute of Cancer Research.
About ELRIG (UK) Ltd.
The European Laboratory Research & Innovation Group (ELRIG) is a leading European not-for-profit organization that exists to provide outstanding scientific content to the life science community. The foundation of the organization is based on the use and application of automation, robotics and instrumentation in life science laboratories, but over time, we have evolved to respond to the needs of biopharma by developing scientific programs that focus on cutting-edge research areas that have the potential to revolutionize drug discovery.
Comprised of a global community of over 12,000 life science professionals, participating in our events, whether it be at one of our scientific conferences or one of our networking meetings, will enable any of our community to exchange information, within disciplines and across academic and biopharmaceutical organizations, on an open access basis, as all our events are free-of-charge to attend!
Our values
Our values are to always ensure the highest quality of content and that content will be made readily accessible to all, and that we will always be an inclusive organization, serving a diverse scientific network. In addition, ELRIG will always be a volunteer led organization, run by and for the life sciences community, on a not-for-profit basis.
Our purpose
ELRIG is a company whose purpose is to bring the life science and drug discovery communities together to learn, share, connect, innovate and collaborate, on an open access basis. We achieve this through the provision of world class conferences, networking events, webinars and digital content.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 26, 2025