Sponsored Content by MerckReviewed by Emily MageeFeb 1 2024
Polyethylene glycol (PEG), also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or poly(oxyethylene) (POE), is a synthetic polyether recognized for its hydrophilic and biocompatible nature. Typically, substances with a molecular weight below 20,000 g/mol are classified as PEGs, while those with a molecular weight exceeding 20,000 g/mol are identified as PEOs.
 Image Credit: SciePro/Shutterstock.com
Image Credit: SciePro/Shutterstock.com
These polymers are not only soluble in water but also dissolve in various organic solvents, including ethanol, acetonitrile, toluene, acetone, dichloromethane, hexane, and chloroform.
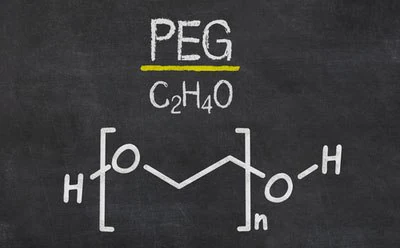
Image Credit: Merck
Applications of PEGs
PEGs are non-toxic and find widespread use in bioconjugation, surface functionalization, biomedical research, drug delivery, tissue engineering, and the food and cosmetics sectors. The process of attaching PEG polymer chains to molecules, whether through conjugation or non-covalent means, is termed PEGylation.
Employing the PEGylation technique can enhance the water compatibility, solubility, stability, and pharmacokinetic properties of therapeutics, thereby elevating their safety and efficacy in targeted diagnostics and drug delivery.
PEG hydrogels are typically employed for the controlled release of therapeutics as cell culture scaffolds in regenerative medicine, wound healing, and tissue engineering.
PEG derivatives and PEG linkers
Merck Millipore Sigma provides a diverse range of well-defined PEGs featuring varying molecular weights, end functionalities, reactivities, and polymer architectures:
- Heterobifunctional PEGs
- Homobifunctional PEGs
- Monofunctional PEGs
- PEG Dendrimers and Multi-Arm PEGS
- PEG Copolymers
- PEG Standards for GPC
- PEG and Oligo Ethylene Glycol
- Polyethylene oxide Powders
- High Oligomer Purity PEGs
About Merck
Our pursuit is progress for people everywhere. That's why we take a closer look at things, ask questions, and think ahead.
We've been around for more than 350 years, yet our majority owners are still the descendants of Friedrich Jacob Merck, the man who founded our company in Darmstadt, Germany in 1668.
From advancing gene-editing technologies and discovering unique ways to treat the most challenging diseases to enabling the intelligence of devices – the company is everywhere.
We are Merck. The only exceptions are the United States and Canada. Here we operate as EMD Serono in the Biopharma business, as MilliporeSigma in the Life Science business, and as EMD Performance Materials in the materials business.
Our life science business
We provide infinite solutions to solve the toughest problems in life science in collaboration with the global scientific community. Our tools, services, and digital platforms empower scientists and engineers at every stage, helping deliver breakthrough therapies more quickly.
Focus areas
With our three business units, we are a leading worldwide supplier of tools, high-grade chemicals, and equipment for academic labs, biotech, and biopharmaceutical manufacturers, as well as the industrial sector.
- Research Solutions provides our academic customers with the chemicals and tools needed to make scientific discovery easier and faster.
- Process Solutions provides drug manufacturers with process development expertise and technologies, such as continuous bioprocessing.
- Applied Solutions offers both testing kits and services to ensure that our food is safe to eat and our water is clean to drink.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.