This article is based on a poster originally authored by Rachel Daniels, Yu Chen, Spencer Chiang, Tianfu Zhang and Yuehchun Hsieh.
Gene and cell therapies rely heavily on culturing immune cells in vitro, a step that remains critical to their development.
Due to the specialized and diverse nature of immune cells, such as T, NK, and macrophages, as well as subpopulations like γδT cells, each cell type requires its own customized media.
Conventional, one-size-fits-all media are unable to effectively support the development of these therapies because each immune cell population has distinct metabolic requirements, cytokine dependencies, and activation pathways.
In addition, specialized media for cell sub-populations are also not amenable when exploring different cell types.
Lengthy optimization processes in cell culturing are often required to achieve changes to target immune cell types, for example, the modification of CAR-T therapies to CAR-NK ones.
A recent study by ACROBiosystems has led to the development of a two-part medium comprising a universal basal medium alongside custom-formulated supplements that have been optimized and tailored for specified immune cell subpopulations.
This novel approach allows the creation of adaptable, fine-tuned media tailored to accommodate the specific functional and biological needs of each cell type. This is enabled by systematically adjusting critical media components, including nutrients, growth factors, cytokines, and serum alternatives.
Two different supplements have been developed to be paired with a universal basal medium: NK cells and γδT cells. The NK cell and γδT cell supplements demonstrate a 1,000- and 17,600-fold increase, respectively, at a purity of 97 % and 93 %.
Each developed cell media is highly customizable, allowing researchers to adopt and implement highly specific cell media for different cell subpopulations with ease. This customizability resulted in improved efficiency within a range of cell types as part of immune cell therapy research.
Adaptable cell culture supplement scheme
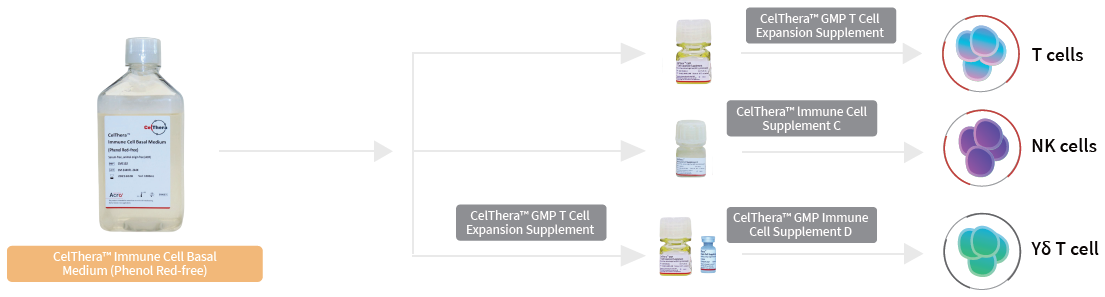
Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
NK cell media formulation for culturing
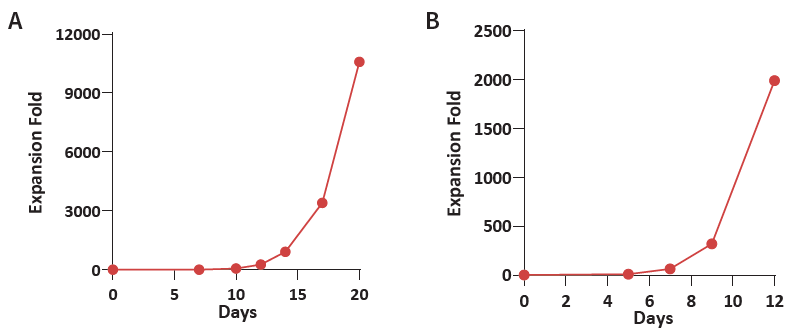
Figure 1. (A) Donor 1 and (B) Donor 2 human CBMCs were cultured using the Immune Cell Basal Medium with CelThera™ Immune Cell Supplement C. The resulting expansion fold exceeds 1,000 on Day 11 and can reach 10,000 on Day 19. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
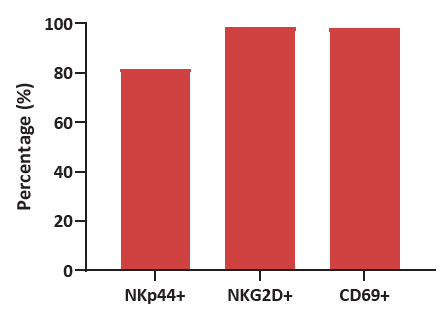
Figure 2. Human CBMCs were cultured for 2 weeks using Immune Cell Basal Medium with CelThera™ Immune Cell Supplement C. Varying ratios of NKp44/NKG2D/CD69, all markers of activation, reveal significant levels of activation after the culturing process. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
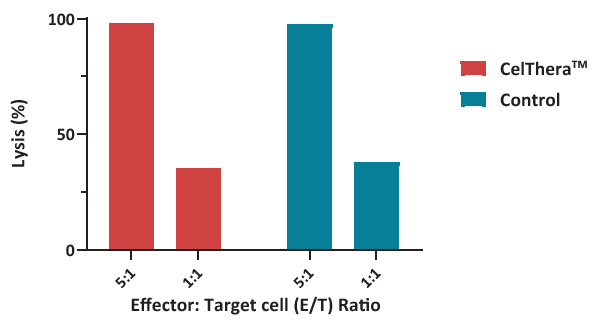
Figure 3. Measurement of remaining target cells was performed after 7-AAD/CFSE staining and analyzed via ELISA. NK cells were used to evaluate cytotoxicity at several E:T ratios, revealing that more than 30 % of target cells were lysed at the lowest ratio, similar to control NK cells. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
γδT media formulation
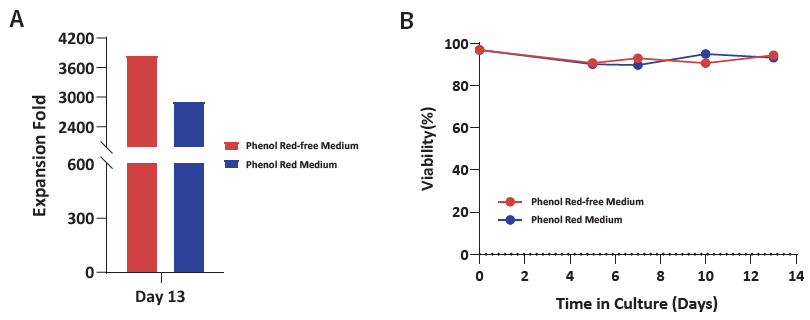
Figure 4. (A) Expansion fold and (B) viability of γδT cells were evaluated from PBMCs cultured with Basal Medium, T cell Expansion Supplement, and GMP Immune Cell Supplement D. Expansion fold exceeds 3,600 with a viability of more than 90 % across the culture period. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
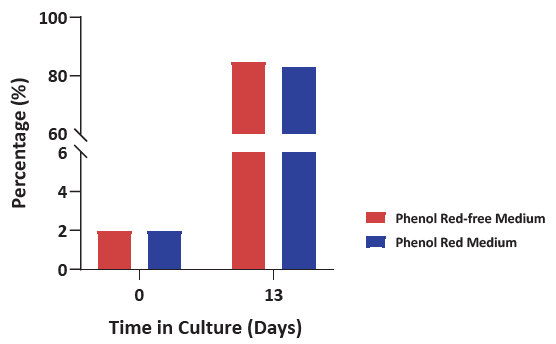
Figure 5. Cell population percentage of γδ2T after culturing using either phenol red or phenol red-free medium resulted in more than 80 %. After two weeks, a high percentage of γδ2T was achieved, using the addition of several supplements alongside the traditional basal medium, revealing the capability to tailor media to a specific subpopulation. Image Credit: ACROBiosystems
Conclusion
The development of this universal basal medium paired with custom supplements represents an efficient and versatile solution for culturing diverse immune cell subpopulations.
The approach described here supports the distinct biological and physiological requirements of each cell type by allowing the precise adjustment of nutrients, growth factors, cytokines, and serum alternatives.
The method presented here has been shown to be highly effective, enabling the successful expansion of NK cells and γδT cells, resulting in 1,000- and 17,600-fold increases at high purity.
This customizable media also streamlined the transition between different immune cell targets, lowering required optimization time and improving the scalability of gene and cell therapy research.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Rachel Daniels, Yu Chen, Spencer Chiang, Tianfu Zhang, and Yuehchun Hsieh from ACROBiosystems.
About ACROBiosystems
ACROBiosystems is a cornerstone enterprise of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. Their mission is to help overcome challenges with innovative tools and solutions from discovery to the clinic. They supply life science tools designed to be used in discovery research and scalable to the clinical phase and beyond. By consistently adapting to new regulatory challenges and guidelines, ACROBiosystems delivers solutions, whether it comes through recombinant proteins, antibodies, assay kits, GMP-grade reagents, or custom services. ACROBiosystems empower scientists and engineers dedicated towards innovation to simplify and accelerate the development of new, better, and more affordable medicine.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.net, which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices, and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 26, 2025