Fingerprints may be more useful to us than helping us nab criminal suspects: they also improve our sense of touch. Sensory neurons in the finger can detect touch on the scale of a single fingerprint ridge, according to new research published in JNeurosci.
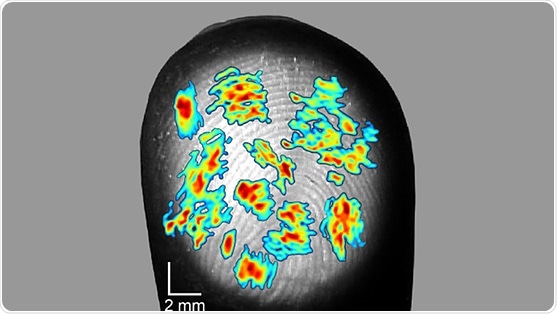
Image Credit: Society of Neuroscience
The hand contains tens of thousands of sensory neurons. Each neuron tunes in to a small surface area on the skin — a receptive field — and detects touch, vibration, pressure, and other tactile stimuli. The human hand possesses a refined sense of touch, but the exact sensitivity of a single sensory neuron has not been studied before.
To address this, Jarocka et al. measured the electrical activity of the sensory neurons in human fingertips when they stimulated with raised dots swept over the skin. The research team calculated the detection areas of the sensory neurons and mapped them onto the fingerprints. The width of the detection areas matched the width of a single fingerprint ridge. These areas stayed on the same fingerprint ridges during different scanning speeds and directions, indicating that they are anchored to the fingerprint ridges. The overlap of receptive fields with small detection areas explains how humans have such a sensitive and accurate sense of touch.
Source:
Journal reference:
Jarocka, E., et al. (2021) Human touch receptors are sensitive to spatial details on the scale of single fingerprint ridges. Journal of Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1716-20.2021.