A radial arm maze features a circular center element from which eight equally spaced arms extend. Each arm is an elongated column of equal distance, with the far end of an arm potentially containing a reward such as food that cannot be seen from the center compartment.
Principles of the radial arm maze test
This test involves placing rodents in the center area of the radial arm maze and allowing them freedom to explore the maze in search of the reward. The animal must remember the arms it has previously visited to avoid repeatedly re-entering arms that do not contain a food reward.
The maze is designed to require the animal to return to the center after each arm visit, presenting the animal with the same eight options each time. This means that the animal must remember which arm it has already chosen, allowing the measurement of both reference memory and working memory.
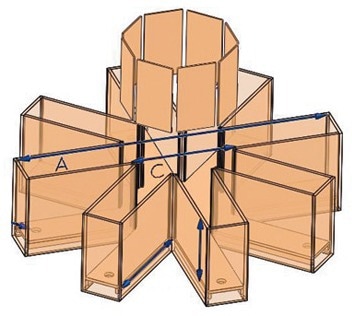
Image Credit: San Diego Instruments, Inc.
History of the radial arm maze test
Drs. Olton and Samuelson created initial designs for the radial arm maze in 1976 in order to evaluate reference and working memory in rodents. The test was designed to model serial learning, enabling an assessment of the way that lists are recalled.
Understanding reference memory
Radial arm maze tests monitor reference memory, which can be understood as the capacity to recall information in relation to the situation of spatial tasks. Animals in a radial arm maze must, therefore, recall their findings in each of the maze’s arms.
Understanding working memory
Working memory refers to the temporary storage of information related to spatial tasks. Unlike long-term memory, working memory involves limited information storage for use in tasks such as the radial arm maze.
Testing in the radial arm maze is done in either a single session or several sessions in rapid succession, making it useful for assessing both reference and working memory.
The radial arm maze has seen widespread use in memory testing due to a diverse array of factors and conditions. For example, it has been used to assess the effect of psychoactive drugs and medications as well as neurological conditions such as brain injuries and autism spectrum disorder. The radial arm maze has also been employed to characterize the basic functions of various areas of the brain.
San Diego Instruments’ radial arm maze
San Diego Instruments offers an eight-arm radial maze that is ideally suited for investigations into spatial learning and memory tasks with rodents.
This simple-to-use and intuitive maze is available in a range of different colors and features manual entry doors, allowing researchers to close off particular arms as required.
SDI’s radial maze is available in both mouse and rat models and is fully compatible with the company’s ANY-maze video tracking system, allowing easy integration where required.
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by San Diego Instruments.
About San Diego Instruments, Inc.
For more than 30 years, San Diego Instruments has served the scientific community as a comprehensive resource for the design, manufacture and distribution of behavioral neuroscience research instruments used in human and animal studies. Utilized in laboratories and cited in research papers worldwide, SDI systems have come to represent the industry standard for quality and longevity. Our premier SR-LAB™ is the world’s most widely used startle response system. At SDI, our commitment to developing quality products that stand the test of time is matched only our dedication to excellent customer service. We take pride in our ever-growing core of loyal clientele.
SDI behavioral neuroscience research systems afford you the utmost in quality and performance, giving you the edge in an industry where Power, Flexibility and Ease of Use are everything.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.