In addition to routine blood and biochemical tests to check for underlying factors such as hypovitaminosis K, hypervitaminosis D, or hypercalcemia, X-rays (e.g. for the breasts) and CT scans (e.g. for the brain) may be used to detect calcifying deposits.
The two types of breasts calcifications, macro and micro calcifications look like large randomly dispersed dots and white specks on the mammogram (breast X-ray), respectively. Breast calcification tissue may be removed and biopsied in order to rule out more serious pathologies such as cancer.
Arterial calcifications, for example, in the coronary arteries, may be detected in vivo (in a living person) by methods such as electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) coronary arteriography, plain film X-rays, fluoroscopy, intravascular ultrasound, MRI, and CT scan.
EBCT and fluoroscopy are the most commonly used techniques in the blood vessel investigations, while CT scans are very sensitive for the detection as well as the localization of intracranial calcifications. Calcifications produce the appearance of high-density material on CT scans and X-rays.
Non-neoplastic dystrophic and metastatic calcifications caused by conditions such as infections, trauma, and neoplasms, appear with radiolucent centers on radiographs. Sheet-like patterns of calcifications in the skin can be seen in conditions like dermatomyositis. In the joints, peri-articular calcifications are non-specific and can be seen after trauma and extra-articular deposition of calcium is seen in the more mobile joints.
The diagnostic approach to calcifications in general may also be investigated based on the suspected cause of the calcification, whether it is hypercalcemia or due to injury and / or inflammation.
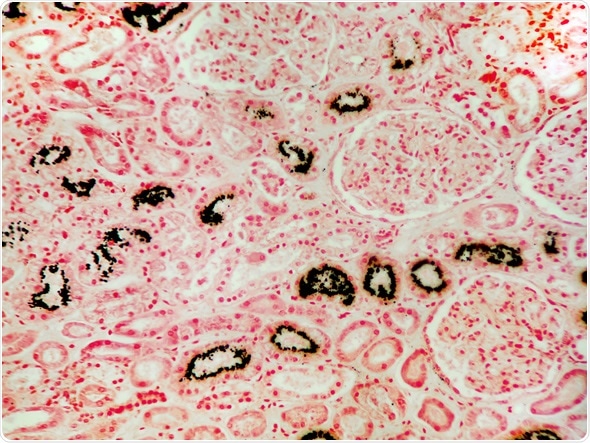
The condition of excess calcium and its resulting deposition in the kidneys. In this micrograph of kidney tissue, the calcium is shown stained black with a calcium stain. Image Copyright: Jubal Harshaw / Shutterstock
Diagnostic Approach to Hypercalcemia
If looked at from a clinical perspective, the majority of cases involving hypercalcemia are due to malignancy or primary hyperparathyroidism. Cases of hypercalcemia can be further broken down into those that are (parathyroid hormone) PTH-dependent and ones that are PTH-independent.
PTH is usually elevated in physiological conditions when there is a drop of calcium in the blood and then returns to baseline once it corrects the problem.
This is not the case, however, in hyperparathyroidism. Furthermore, PTH-related peptide (PTHrP), which is capable of acting on PTH receptors is abnormally elevated in certain cancers such as cancers of the genitourinary tract and the breast.
Taking the aforementioned biochemical markers into account, they are measured and imaging tests of parathyroid glands are also conducted to determine if there is hyper-function of the gland. If PTHrP levels are lower than normal, then measurements for vitamin D-mediated hypercalcemia must also be done as this is typical in lymphomas.
In addition to these tests, the clinician also takes into account medications such as thiazide diuretics and lithium, which have the potential to worsen hypercalcemia and thus must be discontinued.
Further Reading
Last Updated: Jan 3, 2023