This article is based on a poster originally authored by D. Cole and N. Bevan.
3D models, including spheroids and organoids, are increasingly used to investigate disease and development. Developing, monitoring, and characterizing these models requires efficient and reliable procedures due to their complexity, cost, and resource requirements.
Creating disease models with specific markers or genetic alterations adds complexity. Creating a physiologically appropriate system through proper cell manipulation is crucial for model development.
In this study, spheroids were cultivated from individual iPSCs to develop clonal iPSC spheroids obtained from a single cell. Human iPSC-derived hepatic organoids were then chosen from Matrigel domes based on their characteristics and transferred for further culture and analysis.
This article presents a straightforward, standardized, and robust workflow that employs CellCelector Flex to discover and select 3D cell models for further development based on essential growth and morphological characteristics.
The process utilized the Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System and the iQue® HTS Cytometer to track growth and morphology over time, as well as characterize phenotypes using marker expression analysis.
This method facilitates the creation of organoids and monoclonal spheroids from iPSCs for drug discovery, development, and toxicity testing.
3D model workflows
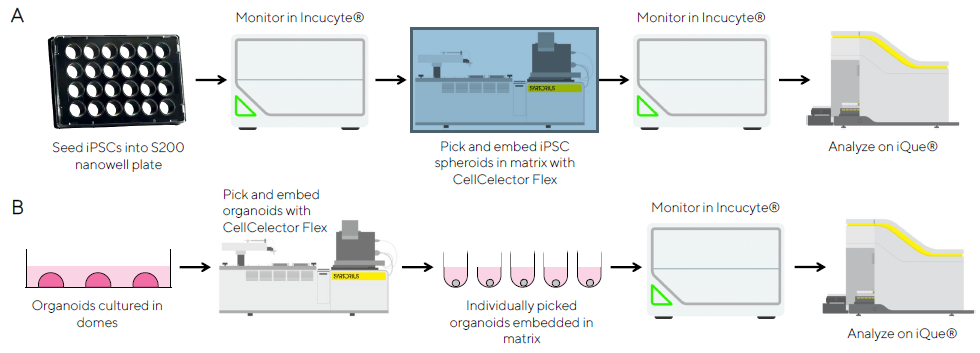
Image Credit: Sartorius
The 3D model method shows how to produce iPSC spheroids from single cells and isolate individual organoids from Matrigel® dome cultures.
For 10 days, monoclonal iPSC spheroids were cultured from individual GFP-expressing cells.
Isolating organoids based on specified properties is a valuable tool for developing 3D cell models and conducting research.
Monoclonal iPSC spheroid generation
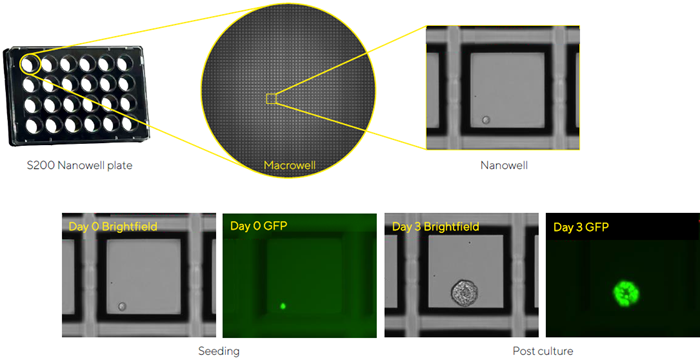
Image Credit: Sartorius
S200 nanowell plates have hundreds of nanowells per macrowell of a typical tissue culture plate.
Nuclight Green GFP-expressing iPSCs were seeded at a density to deposit a single cell into each nanowell.
After three days of culture, healthy GFP-expressing iPSC spheroids developed throughout several wells.
Picking and embedding iPSC spheroids
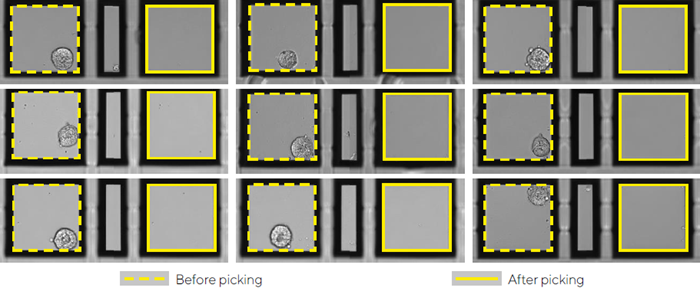
Image Credit: Sartorius
- iPSC spheroids were identified and picked using the CellCelector Flex.
- Analyzed individual wells to identify GFP-expressing spheroids from a single cell.
- Only specific spheroids were targeted for choosing.
- The CellCelector removed each spheroid from its nanowell and resuspended it in hydrogel.
- The hydrogel-embedded spheroid was seeded into a well of media in a 96-well ULA plate.
- The plates were then moved to the Incucyte® and monitored.
CellCelector Flex, Incucyte® & iQue® systems
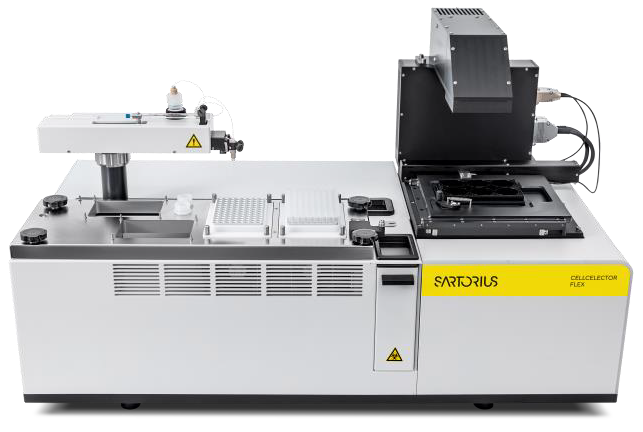
CellCelector Flex Cell Picking Platform. An automated cell selection and picking platform providing solutions to complex experimental methods such as clone development and 3D spheroid and organoid culture. Image Credit: Sartorius

Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System. A fully automated phase contrast and multi-color fluorescence system that resides within a standard cell incubator for optimal cell viability. Designed to scan plates and flasks repeatedly over time. Image Credit: Sartorius

iQue® HTS Cytometer. A high throughput screening cytometry platform with a patented sampling method allowing for rapid sample acquisition to deliver fast actionable results. Capable of handling 96 and 384 well plates. Image Credit: Sartorius
Monitoring and characterizing iPSC spheroids
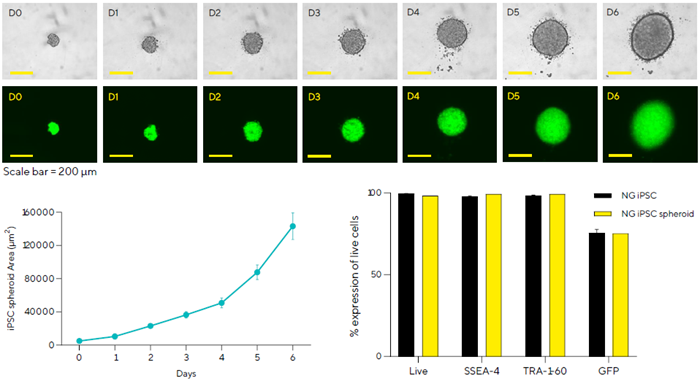
Image Credit: Sartorius
- Hydrogen-embedded Nuclight Green (NG) iPSC spheroids were tracked in the Incucyte® for six days after harvesting to evaluate growth and shape.
- Incucyte® micrographs show spheroids growing steadily and expressing GFP consistently.
- Brightfield area measurements from Incucyte® pictures show significant spheroid growth.
- Marker expression study on iQue® indicates higher viability, pluripotent marker expression, and GFP expression in iPSC spheroids compared to source iPSCs.
- CellCelector isolates and seeds healthy spheroids with consistent expression profiles.
Identification and isolation of organoids
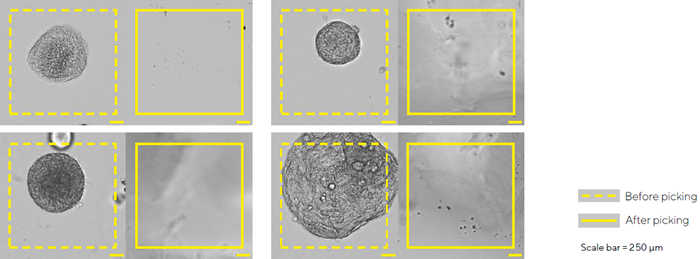
Image Credit: Sartorius
- CellCelector Flex was used to identify and select iPSC-derived hepatic organoids grown on Matrigel® domes.
- Organoids were chosen for their size and morphology, with varying sizes to assess picking accuracy and success rates.
- After picking, embed the organoids in a Matrigel® droplet and seed them on 96-well ULA plates.
- Transfer the plates to the Incucyte® to monitor growth and morphological changes.
Monitoring and characterizing organoid development
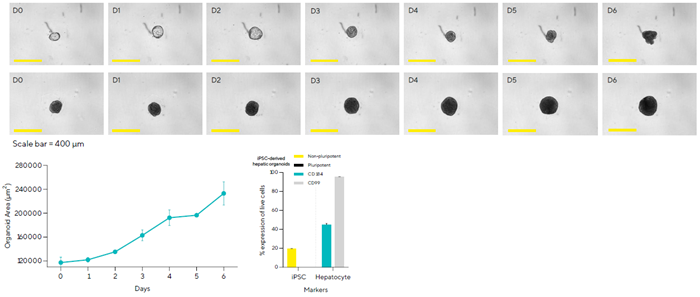
Image Credit: Sartorius
- CellCelector-selected Matrigel®-embedded hepatic organoids were scanned in the Incucyte® six days after seeding to assess growth and shape.
- Brightfield area measurements from Incucyte® pictures show significant organoid growth.
- iQue® analysis of hepatic marker expression in iPSC-derived organoids reveals significant levels of CD99 and CD184.
- CellCelector enables the selection and isolation of organoids with specified properties using an automated workflow that includes Incucyte® for morphological monitoring and iQue® for marker expression analysis.
About Sartorius
Sartorius is a leading international pharmaceutical and laboratory equipment supplier. With our innovative products and services, we are helping our customers across the entire globe to implement their complex and quality-critical biomanufacturing and laboratory processes reliably and economically.
The Group companies are united under the roof of Sartorius AG, which is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and holds the majority stake in Sartorius Stedim Biotech S.A. Quoted on the Paris Stock Exchange, this subgroup is comprised mainly of the Bioprocess Solutions Division.
Innovative technologies enable medical progress
A growing number of medications are biopharmaceuticals. These are produced using living cells in complex, lengthy and expensive procedures. The Bioprocess Solutions Division provides the essential products and technologies to accomplish this.
In fact, Sartorius has been pioneering and setting the standards for single-use products that are currently used throughout all biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Making lab life easier
Lab work is complex and demanding: Despite repetitive analytical routines, lab staff must perform each step in a highly concentrated and careful way for accurate results.
The Lab Products and Services Division helps lab personnel excel because its products, such as laboratory balances, pipettes and lab consumables, minimize human error, simplify workflows and reduce physical workloads.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 27, 2025