Rhabdomyolysis represents a syndrome characterized by muscle necrosis and the release of intracellular muscle constituents into the circulation. The clinical manifestations and ensuing complications of rhabdomyolysis stem from muscle cell death, which can be triggered by a myriad of initiating events.
Causes of rhabdomyolysis can be broadly divided into physical (traumatic) and non-physical (non-traumatic). The most common causes are muscle overextension, muscle compression and crush injury, but there are also numerous non-traumatic etiologies. The latter group can be broadly divided into toxic, infectious and metabolic causes.
Common final pathophysiological mechanisms among all of the causes include an uncontrolled rise in free intracellular calcium and activation of calcium-dependent proteases, which lead to destruction of myofibrils and lysosomal digestion of muscle fiber contents.
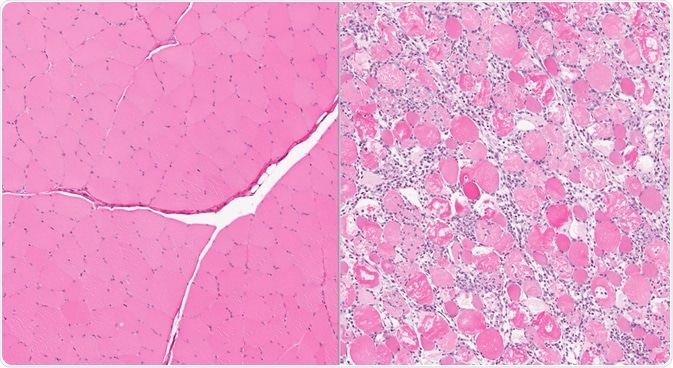 Normal skeletal muscle (left) and severe rhabdomyolysis affected muscle showing injury and inflammation (right). Image Credit: vetpathologist / Shutterstock.com
Normal skeletal muscle (left) and severe rhabdomyolysis affected muscle showing injury and inflammation (right). Image Credit: vetpathologist / Shutterstock.com
Toxic causes
Cocaine is a common cause of rhabdomyolysis, namely in urban patient populations. Prolonged vasoconstriction of intramuscular arteries result muscle ischemia and acute rhabdomyolysis, but there is also a direct toxic effect which can produce acute skeletal myofibrillar degeneration.
A large number of prescription drugs have been implicated in cases of rhabdomyolysis, including colchicine, zidovudine, isoniazid, benzodiazepines, opiates, corticosteroids, statins and fibric acid derivatives. One particular interaction that has been studied extensively and is clinically significant given the comorbidities often found in patients is the interaction between statins and fibrates.
Infectious causes
The pathogenesis of rhabdomyolysis precipitated by infections (whether bacterial, viral or fungal) is thought to be the result of direct cell invasion of striated muscle and cellular degeneration by the pathogen. Substantial morbidity (57% of cases with acute renal failure) and mortality (death in almost 40% of cases) are linked to bacterial causes of rhabdomyolysis.
In adult patients, Legionella species are most often associated with rhabdomyolysis. Other bacteria linked to rhabdomyolysis include group A β-hemolytic streptococci, Salmonella species, Francisella tularensis and Escherichia coli. Viruses such as influenza, parainfluenza, Coxsackievirus, Epstein–Barr virus, adenovirus, HIV and cytomegalovirus have also been associated also with this condition.
Rhabdomyolysis can also be observed in septic patients without direct muscle infection, when the damage is caused by a toxin, associated fever, dehydration and rigors. Physicians should be aware of the association between all aforementioned causative agents and rhabdomyolysis in order to facilitate optimal treatment of these patients.
Rhabdomyolysis - an easy overview
Metabolic causes
Electrolyte disorders, such as hyponatremia or hypernatremia, hypokalemia and hypophosphatemia can result in rhabdomyolysis, distorting the permeability and the functions of sarcelemma in the muscles. Some endocrinologic disorders (i.e. pheochromocytoma and thyreotoxicosis) are also able to potentiate rhabdomyolysis due to hypermetabolism.
Metabolic myopathies caused by genetically determined abnormality of an enzyme implicated in energy production pathways are considered as uncommon causes of rhabdomyolysis. Still, in cases where the exact etiology remains elusive, a genetic disorder should be considered – especially in pediatric patients.
References
Further Reading
Last Updated: Feb 4, 2021