Two components of imagination — constructing and evaluating imagined scenarios — rely on separate subnetworks in the default mode network, according to research recently published in JNeurosci.
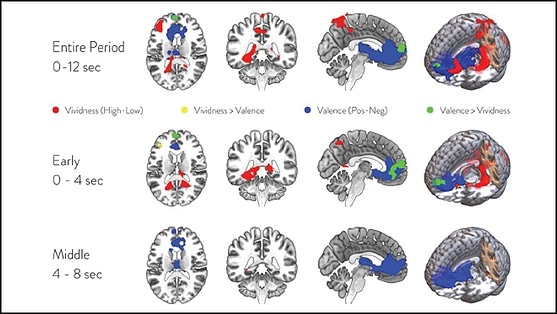
Image Credit: Society of Neuroscience
Even when you aren’t doing anything, your brain is hard at work. The default mode network (DMN) activates during the brain’s resting state and has been linked to daydreaming, planning, and imagining the future. In previous studies, scientists noticed the DMN could be divided into two subnetworks, ventral and dorsal, but their different roles were debated
Lee et al. used fMRI to measure participants’ brain activity while they imagined scenarios listed on prompts, like “Imagine you win the lottery.” The scenarios varied in vividness and valence — some were positive, others negative. Only the vividness of a scenario influenced the activity of the ventral default mode network. Conversely, only the positive or negative quality of the imagined scenario affected the activity of the dorsal default mode network. The results indicate the default mode network is divided into separate subsystems for constructing and evaluating imagined scenarios. Understanding this division allows for future, more detailed studies on the neural mechanisms underlying imagination.
Source:
Journal reference:
Lee, S., et al. (2021) The ventral and dorsal default mode networks are dissociably modulated by the vividness and valence of imagined events. Journal of Neuroscience. doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1273-20.2021.