This article is based on a poster originally authored by N. Lewis, D. Cole, A. Ward, J. Trigg and N. Bevan.
Researchers are increasingly using 3D models, such as organoids, to generate species-specific and physiologically appropriate systems for studying disease and development.
Producing biologically accurate tissue models can be costly and time-consuming, so efficient and reliable methods for development, monitoring, and characterization are necessary.
Stem cells have been shown to be useful in laboratory and clinical research for a variety of diseases and therapeutic development.
To differentiate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) into somatic tissues, various conditions are required based on the target tissue type.
In this workflow, human iPSCs were differentiated into hepatocytes utilizing three separate medium types, each with its own cytokine and growth factor supplementation during critical stages of differentiation, resulting in a very straightforward way for creating mature hepatic cells.
The generation of human hepatic organoids from these donor cells demonstrates a reliable method for infinite organoid development.
This article introduces a simple, standardized, and robust workflow for phenotypic characterization and growth monitoring using Sartorius RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines, the Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System, and the iQue® HTS Cytometer.
This method facilitates the creation of functional liver cells and organoids from iPSCs for drug discovery, development, and toxicity testing.
Differentiation workflow
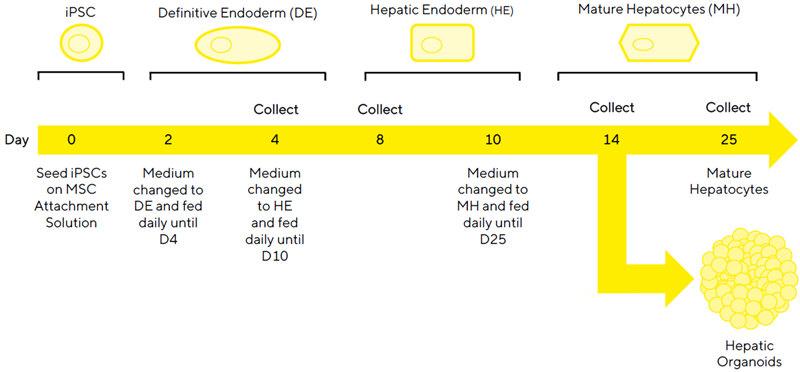
Image Credit: Sartorius
- The differentiation workflow guides the creation of mature hepatocytes and organoids from iPSCs.
- For 25 days, iPSCs were cultured in three media formulations with Sartorius RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines.
- On day 14, cells can be expanded to mature hepatocytes or extracted and cultured in a 3D matrix to create hepatic organoids. Collection timestamps are marked for characterisation analysis.
Monitoring iPSC to hepatocyte differentiation
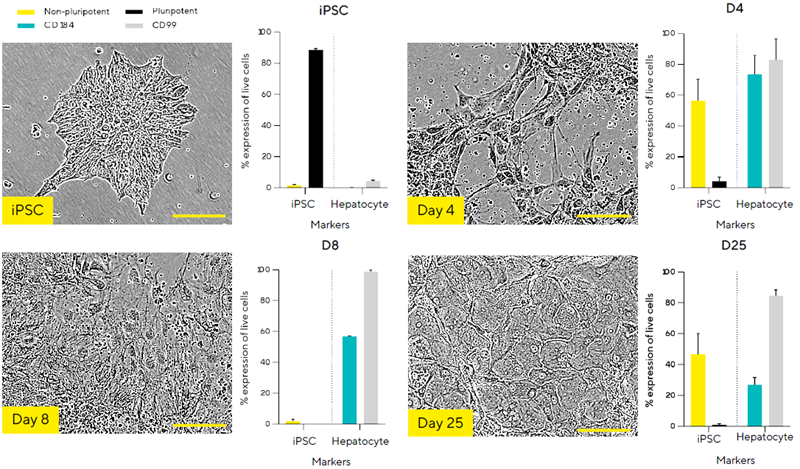
Image Credit: Sartorius
- Monitoring iPSC differentiation into hepatocytes with the Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System and iQue® HTS Cytometer.
- At Day 25, iPSCs treated with differentiation media have a hepatocyte-like shape, with big polygonal structures and round nuclei with conspicuous nucleoli, rather than the normal colony formation.
- Surface marker analysis confirms that pluripotency markers decrease while non-pluripotency markers and hepatocyte markers (CD184 and CD99) increase throughout differentiation.
Characterizing expression and functional activity of iPSC-derived hepatocytes
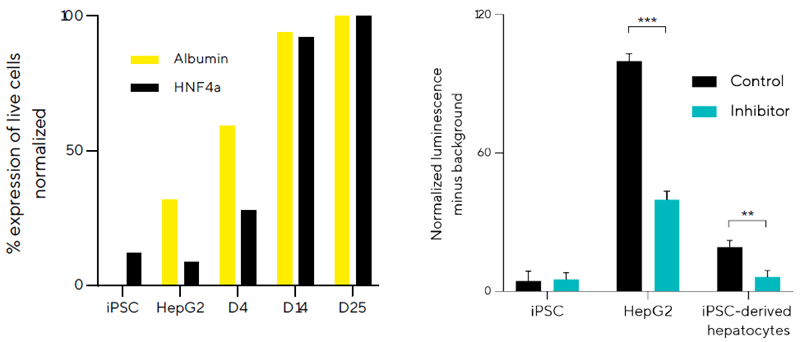
Image Credit: Sartorius
- Hepatocytes produced from iPSCs were further characterized using intracellular marker expression.
- High levels of Albumin and HNF4a were found during hepatocyte differentiation.
- Higher expression levels compared to iPSC and HepG2 control cell lines.
- The Cytochrome P450 inhibition experiment assessed the functioning of iPSC-derived hepatocytes.
- α-napthoflavone significantly inhibits CYP1A2 enzyme activity in iPSC-derived hepatocytes.
RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines, Incucyte® & iQue® Systems
Sartorius RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines. Sartorius provides a broad range of high quality RUO growth factors and cytokines which are produced using recombinant DNA technology and do not contain any animal-derived components or contaminants. Image Credit: Sartorius

Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System. A fully automated phase contrast and multi-color fluorescence system that resides within a standard cell incubator for optimal cell viability. Designed to scan plates and flasks repeatedly over time. Image Credit: Sartorius

iQue® HTS Cytometer. A high throughput screening cytometry platform with a patented sampling method allowing for rapid sample acquisition to deliver fast actionable results. Capable of handling 96 and 384 well plates. Image Credit: Sartorius
Monitoring iPSC-derived hepatic organoid development
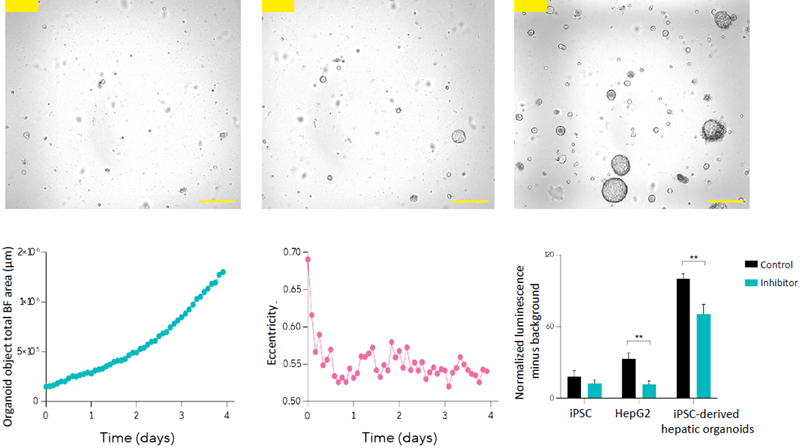
Image Credit: Sartorius
- On day 14, iPSC-derived hepatocytes were grown in a 3D matrix for seven days, resulting in hepatic organoids.
- The Incucyte® Live-Cell Analysis System assessed the morphological state of the organoids.
- iPSC-derived hepatic organoids grew quickly, reaching a diameter of 600 µm on day 5.
- Quantification of organoid growth revealed a continuous rise in organoid object area over time.
- Early-stage growth showed reduced organoid eccentricity, which plateaued by day 2 and indicated a stable homogenous phenotype.
- Verapamil hydrochloride significantly inhibited CYP3A4 activity in iPSC-derived hepatic organoids (Cytochrome P450 inhibition assay).
Characterizing iPSC-derived hepatic organoids
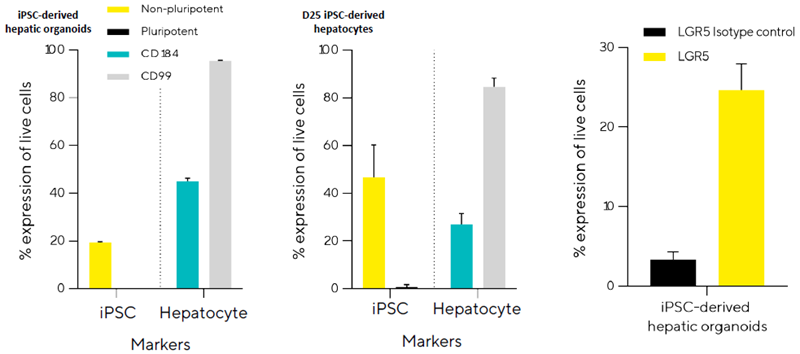
Image Credit: Sartorius
- Used iQue® HTS Cytometer to analyze surface marker expression in iPSC-derived hepatic organoids.
- iPSC-derived hepatic organoids exhibit similar expression profiles to iPSC-derived hepatocytes, including high levels of hepatic marker CD99 and expression of CD184.
- Nonpluripotency markers indicate a differentiated phenotype, but pluripotency markers are undetectable in both cell types.
- In iPSC-derived hepatic organoids, 25% of cells express LGR5, indicating a significant proportion of component stem cells with proliferative capacity.
RUO growth factors and cytokines for organoid culture
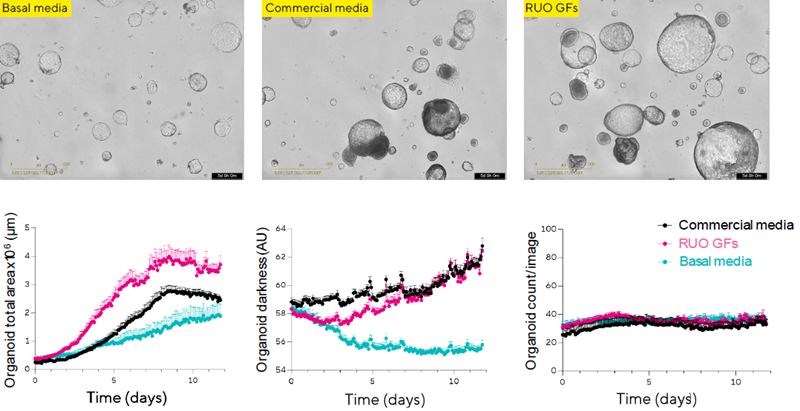
Image Credit: Sartorius
- Various media formulations were explored to assess the impact of Sartorius RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines on iPSC-derived hepatic organoids.
- Hepatic organoids cultivated in basal media without growth factors were significantly smaller than in other settings.
- Media containing Sartorius RUO Growth Factors and Cytokines (RUO GFs) resulted in faster growth of organoids compared to basal or commercial media.
- Organoids cultivated in RUO GFs showed comparable organoid darkness values to commercial media, but with lower beginning darkness. Organoid numbers remained consistent across media types.
About Sartorius
Sartorius is a leading international pharmaceutical and laboratory equipment supplier. With our innovative products and services, we are helping our customers across the entire globe to implement their complex and quality-critical biomanufacturing and laboratory processes reliably and economically.
The Group companies are united under the roof of Sartorius AG, which is listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and holds the majority stake in Sartorius Stedim Biotech S.A. Quoted on the Paris Stock Exchange, this subgroup is comprised mainly of the Bioprocess Solutions Division.
Innovative technologies enable medical progress
A growing number of medications are biopharmaceuticals. These are produced using living cells in complex, lengthy and expensive procedures. The Bioprocess Solutions Division provides the essential products and technologies to accomplish this.
In fact, Sartorius has been pioneering and setting the standards for single-use products that are currently used throughout all biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Making lab life easier
Lab work is complex and demanding: Despite repetitive analytical routines, lab staff must perform each step in a highly concentrated and careful way for accurate results.
The Lab Products and Services Division helps lab personnel excel because its products, such as laboratory balances, pipettes and lab consumables, minimize human error, simplify workflows and reduce physical workloads.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.
Last Updated: Nov 27, 2025