Blocking dopamine receptors in different regions of the amygdala reduces drug seeking and taking behavior with varying longevity, according to research in rats published in eNeuro.
The amygdala contains receptors for dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in reward seeking, and has been shown to influence cocaine reward behaviors, making it a target for addiction treatment research.
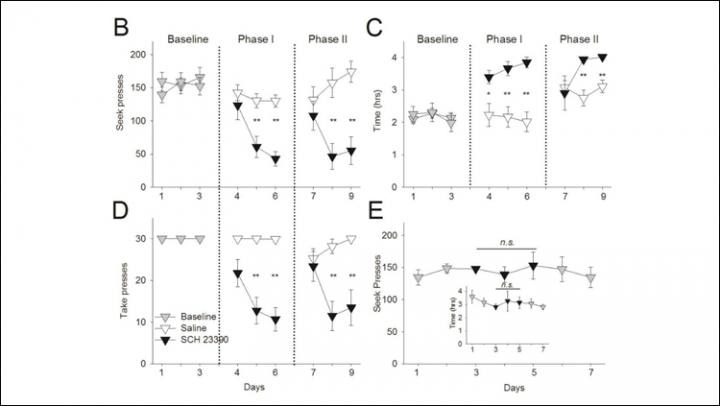
Matthew Lattal and Earnest Kim at Oregon Health & Science University blocked dopamine receptors in the amygdala of rats that were self-administering cocaine. The rats were trained to push a lever that caused another lever to appear, which modeled drug-seeking behavior, and to press the second lever to receive a dose of cocaine, which was the actual drug-taking behavior.
Blocking dopamine receptors in the basolateral amygdala gradually decreased drug seeking and taking behaviors, even when the rats were placed in a new environment. In the central amygdala, blocking dopamine caused a rapid decrease in drug seeking and taking. The effect was reversed when the rats entered a new environment.
These findings clarify the unique roles of the basolateral and central amygdala and reveal that blocking dopamine during cocaine use weakens the effects of the drug. This offers insight into potential therapies for drug addiction and relapse.
Source:
Journal reference:
Kim, E. et al. (2019) Context-dependent and -independent effects of D1 receptor antagonism in the basolateral and central amygdala during cocaine self-administration. eNeuro. doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0203-19.2019.