Sponsored Content by PromoCellReviewed by Alex SmithJul 20 2022
As the mesenchymal stem cells’ potential for use in cancer therapy grows, it is essential to understand the biology behind them as this can help inform and inspire novel cancer therapies. The efficiency and usability of these in-demand cells can be increased by the use of high-quality media and culture kits.
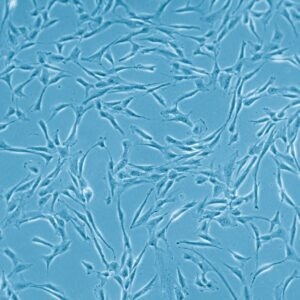
Image Credit: PromoCell
The forefront of biomedical research is characterized by the continuous innovation of cancer therapies. The approach of targeting the immune system and harnessing biological mechanisms in order to strengthen its response to cancer has huge potential for therapeutics.
MSCs, or mesenchymal stem cells, are a specialized type of multipotent cell that can be divided into different types of tissue, as well as participate in the regeneration and repair of tissues.1
In addition, mesenchymal stem cells have immunomodulatory functions, which have led to them gaining a lot of attention as a new, promising approach for the advancement of gene and cell therapies. For instance, depending on what is required for tissue repair, MSCs can regulate the inflammatory and immune response in the body by stimulating specialized immune cells.1
However, as a biological instrument, mesenchymal stem cells are dual-edged. The cells can also contribute to the creation of tumors by supporting tumor microenvironments, contributing to the growth of tumors, and suppressing antitumor immune responses, even though they can be of benefit to the body during tissue regeneration.1
Thus, understanding the mechanisms and relationships of mesenchymal stem cells in cancer is essential for developing effective therapeutics for the disease due to their pleiotropic nature.
In this article, the role of mesenchymal stem cells in oncology is explored by highlighting a number of aspects of their existence, including how they communicate, their role within the tumor microenvironment and cancer stem cells, and how they can be harnessed within cancer treatments for cell and gene therapy.
It is also important to recognize how the clinical usability of mesenchymal stem cells in biomedicine can be amplified by innovative products and procedures.
Mesenchymal stem cells: How do they communicate?
Human MSCs isolated from bone marrow
Within regenerative medicine, MSCs are the most commonly used cells. Mesenchymal stem cells must have the ability to communicate on an intercellular level to fulfill their regulatory role.
Through the use of signaling with proteins like cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors, mesenchymal stem cells can directly modify the microenvironment. Through the release of extracellular vesicles (EVs),2 mesenchymal stem cells can also influence the functions of the microenvironment.
In recent years, the medical and scientific communities have shifted their focus toward extracellular vesicles (EVs) as crucial mediators in MSC cell-to-cell communication. The biological functions of cells can be influenced by the array of molecules such as RNA and proteins within EVs that can influence the biological functions of cells.2
Molecules in extracellular vesicles secreted by mesenchymal stem cells can be suppressive or supportive of tumors. For instance, certain microRNAs have tumor-suppressive functions, while some tissue inhibitors of metalloproteases like (TIMP)-1 and -2 actively encourage tumors.2
Therefore, new avenues of hitherto-unexplored disease treatments could be opened by the mechanism of communication by mesenchymal stem cells, which presents an encouraging target for cancer therapeutics.
The tumor microenvironment (TME) and mesenchymal stem cells, cancer stem cells (CSC)
Within the tumor microenvironment, mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles are a significant player because they can be harnessed by cancer stem cells and tumor cells to communicate and induce changes affecting the function of the cells involved.1
When MSCs arrive at a tumor, for instance, they can affect the motility of cancer cells. This is done by supporting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, wherein cells gain migratory and invasive characteristics, which are often present in metastatic cancers, a more dangerous and severe character of the disease.3
The tumor microenvironment can be manipulated by the mesenchymal stem cells by promoting angiogenesis, the name given to the process of generating the blood vessels that tumors need to survive and grow, ultimately enhancing tumor progression.3
Fibrosarcoma cells and their tumorsphere culture
To investigate cancer stem cells and their interaction within the tumor microenvironment, tumorsphere formation can be used. Cancer stem cells form and modify the tumor microenvironment, which activates mesenchymal stem cells to support tumor growth and cancer stem cell proliferation.4
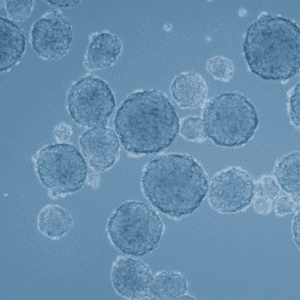
Image Credit: PromoCell
Tumor supporting factors that alter the gene expression of mesenchymal stem cells can be secreted by cancer stem cells, which are key players in tumor development, growth, resistance, and metastasis. This shifts their functions to be more conducive to cancer promotion.4
The communication between mesenchymal stem cells and cancer stem cells as a result of this relationship provides a keen treatment focus for clinicians and cancer researchers.
3D cell cultures, also called tumorspheres, can be used by scientists who investigate the interaction between mesenchymal stem cells and cancer stem cells to create a more representative model of a tumor microenvironment that has the potential to offer very valuable insights into cancer biology.5
Cutting-edge platforms, coupled with a deeper understanding of the biological processes underpinning cancer, can broaden the impact of this research, both improving existing cell and gene therapy options as well as contributing to the formulation of new ones.
Oncology: Cell and gene therapy options with mesenchymal stem cells
Cancer researchers can refine and enhance cell and gene therapy options to create personalized medical solutions through the immunomodulatory functions of mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer drug and therapy creators can influence the cells’ functioning to favor cancer suppression by harnessing the ability of mesenchymal stem cells to modulate the tumor microenvironment.
For instance, mesenchymal stem cells pose an avenue through which anti-cancer drugs could be delivered to tumor sites, thanks to their propensity to migrate to tumors.6
Additionally, through the use of antibody therapy, investigators can manipulate mesenchymal stem cells and affect the process of angiogenesis that tumors hinge upon to survive. The basis for immunotherapies can be presented by the immunological properties of mesenchymal stem cells, giving scientists a valuable tool in the fight against cancer.
Immune system cells, such as macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells that can regulate and suppress cancerous cells, can be induced by mesenchymal stem cells if engineered correctly.7
Mesenchymal stem cells can be used in CAR-T cell therapy development, as they can activate T cells – potentially a more effective cellular treatment for cancer. The ability of mesenchymal stem cells to specifically identify and migrate to tumor sites offers the potential to enhance the activity of CAR-immune cells, designed to eliminate cancer via engineered T cells.8
Mesenchymal stem cells can be utilized as an efficient solution in gene therapies against cancer in addition to cell therapies. MSCs can deliver genes in addition to being used as a vehicle to deliver drugs to the site of tumors.
A transfer of genetic material intended to alter the characteristics or function of live tumor cells into the mesenchymal stem cells can take place, which will then recognize and migrate to tumor sites and deliver the therapy.9 In addition, MSCs can be genetically modified to secrete specific proteins which are targeted to the control of cancer.9
To treat cancer, the relationship between mesenchymal stem cells and other cells – namely cancer cells – in the tumor microenvironment can be used. Cancer stem cell populations can be potentially decreased by inhibiting the intercellular communication between the two types of cells, which can also lower resistance to drugs and lessen the ability of tumors to metastasize and/or grow.4
In order to do this and destroy cancer stem cells, scientists can utilize exosomes – a type of extracellular vesicle that is used by mesenchymal stem cells and cancer stem cells to communicate with one other.4
Finally, mesenchymal stem cells’ potential to treat cancer does not stop at prevention. Mesenchymal stem cells can also be utilized within regenerative medicine to build tissue to reconstruct bones damaged by tumors and tumor removal surgeries.10
Clinical applications: Innovating the use of mesenchymal stem cells
The science surrounding mesenchymal stem cells and cancer, as well as their clinical relevance, has been outlined in this article. Products and processes centered around the manufacturing and proper use of the cells are needed in order to move forward and develop impactful cell and gene therapies.
Mesenchymal stem cells are currently in increasingly high demand, which poses a supply challenge to laboratories.11 Medical and scientific experts can, however, continue to innovate therapeutics through the exploration of various methods, media, and processes to design more standardized protocols that can sufficiently maximize the advantages of mesenchymal stem cells in disease research.
Researchers or clinical scientists working in industry or academia with mesenchymal stem cells and cancer stem cells in cancer studies and/or cell and gene therapy development can learn more about how to harness the role of mesenchymal and cancer stem cells in oncology by reaching out to the professionals at PromoCell, who will be more than happy to help.
References
- Galland, S., & Stamenkovic, I. (2019). Mesenchymal stromal cells in cancer: a review of their immunomodulatory functions and dual effects on tumor progression. The Journal of Pathology, 250(5), 555–572.
- Casson, J., et al. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles may promote breast cancer cell dormancy. Journal of Tissue Engineering, 9, 204173141881009.
- AHN, S. Y. (2020). The Role of MSCs in the Tumor Microenvironment and Tumor Progression. Anticancer Research, 40(6), 3039–3047.
- Jing, Y., et al. (2022). The Role of Mesenchymal stem cells in the Induction of Cancer-Stem Cell Phenotype. Frontiers in Oncology, 12.
- A Home for Cancer Stem Cells: 3D Tumorspheres. (2018, April 17). PromoCell.
- Aravindhan, S., et al. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells and cancer therapy: insights into targeting the tumour vasculature. Cancer Cell International, 21(1).
- Almeida-Porada, G., et al. (2020). Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Immunotherapy and for Gene and Drug Delivery. Molecular Therapy – Methods & Clinical Development, 16, 204–224.
- Chan, L. Y., et al. (2022). CAR-T Cells/-NK Cells in Cancer Immunotherapy and the Potential of MSC to Enhance Its Efficacy: A Review. Biomedicines, 10(4), 804.
- Attia, N., et al. (2021). Mesenchymal stem cells as a Gene Delivery Tool: Promise, Problems, and Prospects. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 843.
- Using mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. (2019, November 25). PromoCell.
- Mesenchymal stem cells: why optimizing manufacturing processes is key for a successful application. (2020, July 31). PromoCell.
About PromoCell
At PromoCell, we help scientists do better research with a world-class portfolio of human primary, stem and blood cells as well as optimized cell culture media. With over 30 years of expertise, we are recognized globally for supplying scientists with the tools and support they need to do groundbreaking research.
All our products comply with European biomedical conventions, ensuring human rights and donor privacy are always protected. Our ISO certifications demonstrate our absolute commitment to quality and our EXCiPACT™ GMP certification enables us to produce our cell culture media and reagents according to GMP standards as a manufacturer of pharmaceutical excipients.
Each year 600 peer-reviewed publications feature PromoCell products. We operate in over 40 countries around the world, helping scientists with all of their research needs.
Learn more about PromoCell on our website, or connect with us on Facebook, YouTube, Twitter or LinkedIn.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.