Broad toxicological screening in forensic toxicology laboratories is increasingly achieved using high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), with these advanced techniques able to detect a wide range of toxicants in highly complex biological matrices.
Figure 1. ACQUITY UPLC I-Class with the Xevo G3 QTof. Image Credit: Waters Corporation - Forensics
Waters™ has provided and supported a comprehensive portfolio of ready-to-implement toxicology screening solutions for over 15 years. These solutions have been applied to various HRMS systems, including the Xevo™ G2-XS QTof and, more recently, the Xevo™ G3 QTof.
The HRMS Screening Solution features dedicated chromatographic methods that offer maximum sensitivity for positive and negative ionizing analytes. Results can be compared against comprehensive, data-rich libraries generated through data-independent analysis (DIA) using MSE, comprised of accurate precursor mass, reference retention time (RT), and fragment ion information.
The study presented here involved analyzing system test solutions and a selection of authentic urine samples from a drug cohort, with the goal of evaluating the suitability of the Forensic Toxicology HRMS Screening Solution for use with the Xevo™ G3 QTof mass spectrometer.
Experimental
Materials
Testing was performed using two different test solutions:
Test Solution 1 is a commercially available standard, comprised of 10 compounds. This solution was acquired from Waters, UK (Forensic Tox Installation Standards Kit p/n: 186007361) and is regularly analyzed in order to act as a daily system suitability check.1
Test Solution 2 is an in-house sample comprising six compounds prepared from Certified Reference Material acquired from Merck (Dorset, UK). Table 1 features the compounds in Test Solutions 1 and 2.
A total of 20 authentic urine samples were randomly selected from a drug cohort. These samples were already characterized using the ACQUITY™ UPLC™ I-Class (FTN) with the Xevo™ G2-XS QTof with the Forensic Toxicology Screening Solutions (ESI positive and ESI negative modes).2
Table 1. List of compounds in Test Solution 1 and 2, used for the evaluation of the Forensic Toxicology HRMS Screening Solution. Source: Waters Corporation - Forensics
| System test solution 1 |
System test solution 2 |
| Buflomedil |
Amiloride |
| Clozapine |
Chlorthalidone |
| Milnacipran |
Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Nicotine |
Metolazone |
| Perphenazine |
Tolvaptan |
| Scopolamine |
Xipamide |
| Tianeptine |
|
| Tiapride |
|
| Trazodone |
|
| Triprolidine |
|
Sample preparation
Test Solution 1 (ESI positive): This 500 ng/mL 10-compound mixture was diluted 20-fold using 5 mM ammonium formate, pH 3.0 (mobile phase A1), to achieve a 25 ng/mL concentration.
Test Solution 2 (ESI negative): This 2500 ng/mL stock solution comprises six compounds. It was prepared in methanol before being diluted 100-fold using 0.001% formic acid in water (mobile phase A2) in order to achieve a concentration of 25 ng/mL.
Authentic urine samples were prepared for positive ionization analysis via a 5-fold dilution using mobile phase A1 and prepared for negative ionization analysis via a 5-fold dilution using mobile phase A2. All samples were vortex mixed before being analyzed.
Data acquisition
Data was acquired using the ACQUITY™ UPLC™ I-Class (FTN) system working in conjunction with the Xevo™ G3 QTof.
Data was collected based on established techniques, with sample information processed via the waters_connect™ informatics package before comparison with the Waters forensic toxicology database. This database has been prepared under identical conditions and contains more than 2,000 drugs and metabolites.
Samples were screened using dedicated positive (ESI positive) and negative (ESI negative) ionization methods,3,4 with analysis completed in 15 minutes (ESI positive) and 7.5 minutes (ESI negative) via their respective mobile phases and established toxicology screening gradients.2
The Xevo™ G3 QTof mass spectrometer was used in MSE acquisition mode, facilitating the collection of full MS spectra.
This technique involves rapid alternations between two collision-cell voltages. The first is acquired at a low voltage, delivering an accurate mass of the precursor ion, while the second is a ramped voltage (10-40 eV) that delivers an accurate mass of the fragment ions. This latter voltage is used for additional confirmatory purposes.
Results and discussion
Acceptance criteria for identifying each analyte were specified in both ESI positive and ESI negative modes. These were:
- Three-dimensional (3D) low-energy ion count intensity greater than 250
- Retention time within 0.35 minutes of the reference retention time
- Observed precursor mass within 5 ppm of expected exact mass
A minimum of one diagnostic fragment ion in the high-energy function must be detected as an additional confirmation step. Identifying all 10 compounds (25 ng/mL) was possible. Figure 2 shows Test Solution 1 (ESI positive) results for clozapine in the waters_connect™ Review Tab.
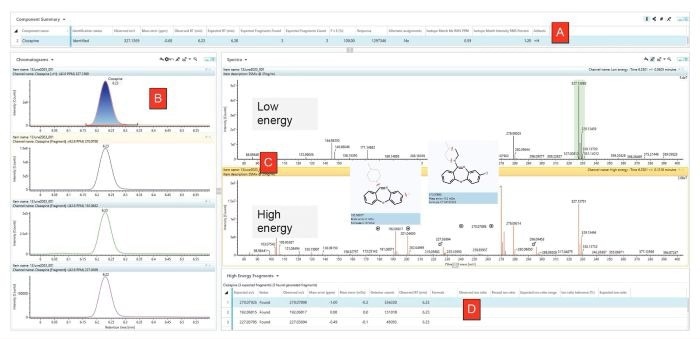
Figure 2. Detection of Clozapine identified in Test Solution 1 (System Suitability Mix), acquired in ESI positive. In this figure the upper table (A) details the results of the comparison of acquired data against the reference information contained in the Toxicology Library. Panel B displays the extracted ion chromatograms for the targeted precursor and the 3 diagnostic fragment ions and demonstrates that all ions are time-aligned at 6.23 minutes. The low and high energy spectra are shown in Panel C, and details of the fragment ions are listed in the lower table, Panel D. Image Credit: Waters Corporation - Forensics
Using the acceptance criteria, detecting 27 parent drugs and/or their metabolites in the 20 urine samples for the ESI positive analysis was possible. Detected drugs could be broadly divided into several key drug classes:
- Amphetamines
- Antidepressant
- Antihypertensive
- Antimalarial
- Opiate/opioid
- Prescription/over-the-counter (OTC) medication
- Sedatives
Figure 3 shows the distributions of these drug classes. It was observed that the data demonstrated excellent concordance with previously characterized data on the Xevo™ G2-XS QTof.
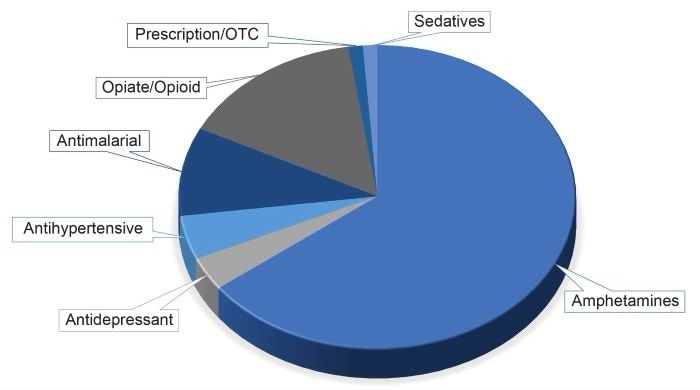
Figure 3. Results summary following the analysis of 20 authentic urine samples. Image Credit: Waters Corporation - Forensics
The ESI negative method correctly detected and assigned the six target compounds within Test Solution 2 (25 ng/mL). It was also noted that results acquired for the urine samples via this method were comparable with results previously acquired using the Xevo™ G2-XS QTof.
These results included the presence of ethyl-sulfate, ethyl-glucuronide, furosemide, naproxen, salicylic acid, and carboxy-THC. Figure 4 shows the results for carboxy-THC in the Review Tab .
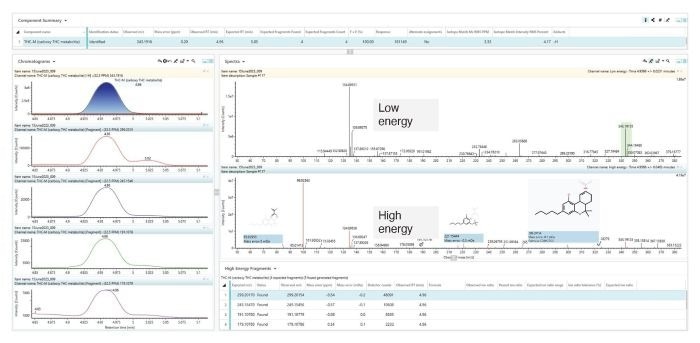
Figure 4. Detection of carboxy-THC identified in an authentic urine sample (ESI negative). Identified with a mass error of 0.20 ppm, within 0.09 min of the reference retention time, and with all expected fragment ions detected. Image Credit: Waters Corporation - Forensics
Conclusion
The confident identification of analytes in complex biological matrix samples remains a key analytical challenge in toxicology laboratories. The study presented here showcased the successful implementation of the Forensic Toxicology HRMS Screening Solution with the Xevo™ G3 QTof and the waters_connect™ informatics platform.
This ready-to-use HRMS Screening Solution boasts more than 2,000 library entries and has been shown to be compatible via the analysis of a system suitability mix featuring known compounds.
Its effectiveness was also shown via the consistent detection of various compounds in authentic urine samples, which had previously been characterized using the Xevo™ G2-XS QTof.
References and further reading
- Care and Use Manual; Forensic Toxicology Installation Standards Kit, Waters User Manual 715004381 Available at: Forensic Toxicology Installation Standards Kit Care and Use Manual | Waters (Accessed 29 Apr. 2025)
- HRMS Forensic Toxicology Screening solution media available by "Digital Delivery" on the Waters Platform.
- Waters (2022). The Utility of MSE for Toxicological Screening. [online] Available at: https://www.waters.com/nextgen/in/en/library/application-notes/2014/utility-of-mse-toxicological-screening.html?srsltid=AfmBOorg2U814xM03bf1lZBCCI-iK9Tcb8lMHIFdFJxNJJrIbnRav1xJ (Accessed 23 Apr. 2025).
- Waters (2015). No Compromise! Improved Sensitivity for Negatively-Ionizing Substances. (online) Available at: https://www.waters.com/nextgen/in/en/library/application-notes/2015/no-compromise-improved-sensitivity-for-negatively-ionizing-substances.html?srsltid=AfmBOop2k6RTL5NJJG1bzXEb4e3No91EDkrSplKmXmQ2RnxMZA8CENet (Accessed 23 Apr. 2025).
Acknowledgments
Produced from materials originally authored by Nayan S. Mistry, Lisa J. Calton, and Jane Cooper from Waters Corporation.
About Waters Corporation - Forensics
Address the constantly evolving challenges faced by forensic and toxicology labs with Waters LC-MS systems and informatics, proven LC-MS solutions that deliver data you can trust in forensic labs.
You have a challenging job to do, whether that’s identifying seized drugs or new psychoactive substances, presenting reliable forensic data in court, monitoring illicit drug use, or analyzing prohibited substances in a sports doping investigation.
With Waters as your partner, you’re never alone in overcoming those challenges. Get the critical data you need with our powerful forensic solutions portfolio, including industry-leading liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, informatics, chemistries, and comprehensive support. At Waters, we’re committed to advancing science in partnership with our customers, and we love to prove it.
For forensic toxicology use only.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.