Sponsored Content by TissueGnosticsReviewed by Maria OsipovaJul 3 2025
Researchers have used TissueGnostics' advanced imaging and analysis tools to detect and quantify two cell types: the PD-1+ regulatory T cells (Treg)/PD-1+CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL) ratio and tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS) that are found in tumor tissue.
Stomach cancer remains a serious global health concern, despite significant breakthroughs in treatment. In fact, in 2022 alone, stomach cancer accounted for an estimated 660,000 fatalities, making it the fifth most deadly disease in the world.1
Studying the tumor microenvironment, which influences the body's ability to fight and/or support cancer, has made several advances in cancer treatment. Understanding the complexities of its responses to cancer may allow for better predictions of patient outcomes and the development of more effective treatment options.
In one study, researchers used TissueGnostics' advanced imaging and analysis tools to detect and quantify two cell types, the PD-1+ regulatory T cells (Treg)/PD-1+CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (CTL) ratio and the presence of tertiary lymphoid structure (TLS) in tumor tissue, as indicators of patient outcomes.2
Case study: The role of tertiary lymphoid structures (TLS)
TLS are well-organized immunological structures, thought of as "immune hubs". They emerge outside of secondary lymphoid tissues in response to persistent inflammation, as an autoimmune response, and as the immunological response to tumors.3
TLS enables the flow of immune cells into the tumor site, boosting the body's immunological response. It’s because of this ability to enhance immune cell access to the tumor site that they have become a primary focus in cancer treatment research.4
Research has found that the presence of TLS in tumors has been linked to improved immune response and treatment outcomes for gastric cancer.2
The role of PD-1+ Tregs and PD-1+ CTLs
In this study, the team looked at the ratio of PD-1+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) and PD-1+CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Tregs are a subset of T cells and are designed to suppress immunological responses.
While Tregs serve an important role in preventing autoimmunity, higher Treg levels in cancer patients indicate the potential inhibition of anti-tumor responses. In contrast, CTLs attack cancer cells directly, and a high number of CTLs indicates the body is actively working to remove the tumor.
PD-1 (programmed death 1) is a protein expressed by both Tregs and CTLs that regulates immune responses. By examining PD-1 expression in these two types of immune cells, the researchers were able to determine whether the immune system was being suppressed or activated in response to treatment.
Recent findings in advanced gastric cancer
The study examined how TLS and the ratio of PD-1+ regulatory T cell (Treg) / PD-1+CD8+ cytotoxic T cell (CTL) populations might impact treatment results for advanced gastric cancer patients.
Tumor samples were collected from ten gastric cancer patients before and after undergoing pre-operative conversion treatment. Using multiplex immunofluorescence (mIF), the researchers stained the samples for several immunological markers such as CD20, CD3, CD8, PD-1, and FOXP3, which allowed them to track the presence of various immune cells, including Tregs and CTLs.
A TissueFAXS SL scanner generated high-resolution images of the slides, allowing the researchers to identify and quantify the cells in the sample. The images were then analyzed using StrataQuest software, which calculated cell density across various immune cell types, including Tregs and CTLs, and detected the presence of TLS in the tumor tissue.
The results showed a substantial increase in survival among gastric cancer patients with high levels of TLS and CTL, which indicates a more active immune response and suggests that these patients may benefit more from neoadjuvant treatment.
This research reveals another positive step forward in cancer research, increasing therapy and prognosis for gastric cancer. It also emphasizes the importance of whole-slide imaging and image processing in medical advancement.
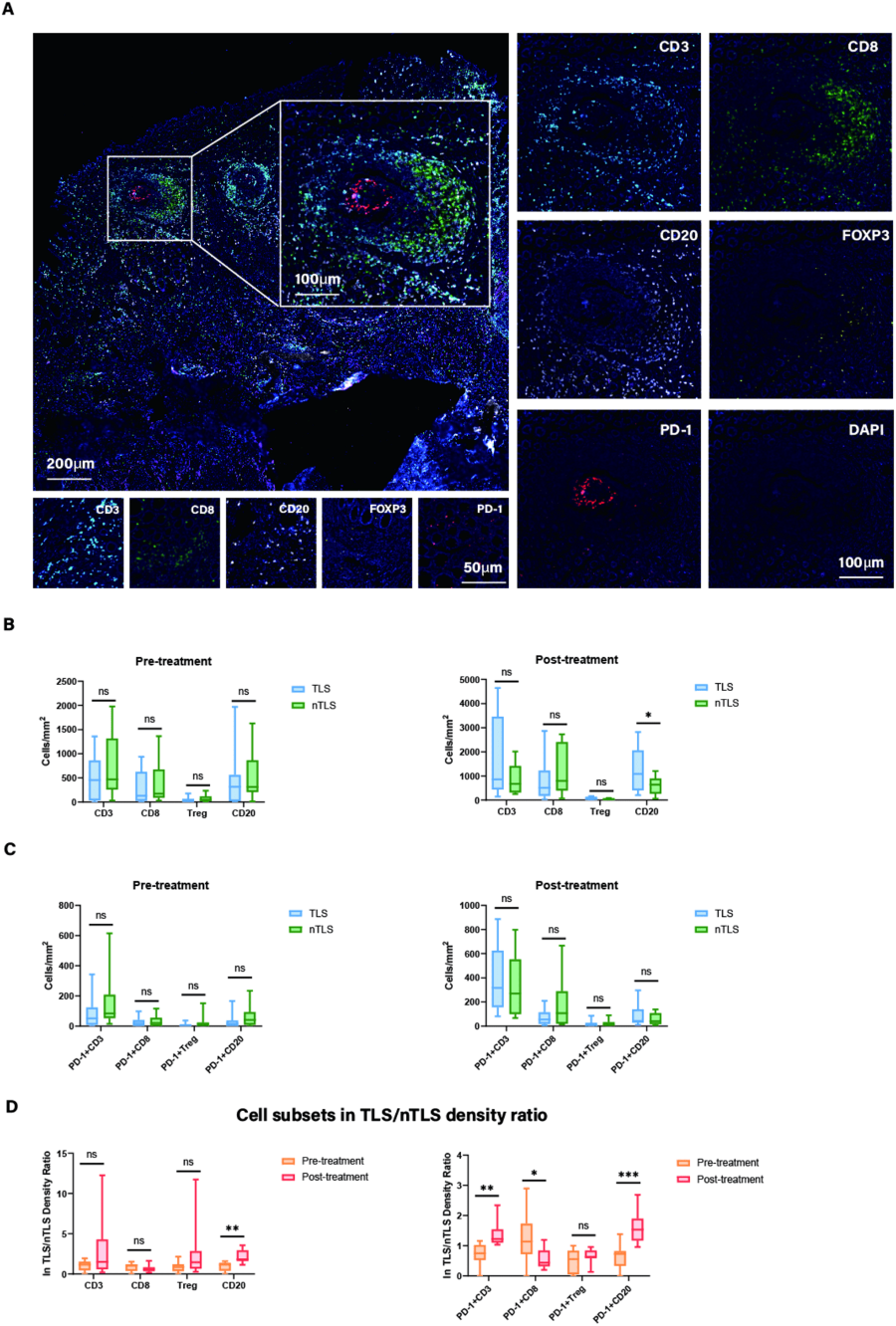
From Figure 5. Image Credit: Liu X, Xu D, Zhou C, Zhong Y, Geng H, Huang C, Shen Y, Xia X, Wang C, Zhu C, Cao H. Association of PD-1 + Treg/PD-1 + CD8 ratio and tertiary lymphoid structures with prognosis and response in advanced gastric cancer patients receiving preoperative treatment.
Advanced imaging and analysis tools in cancer research
Using cutting-edge imaging and processing techniques has enabled scientists to collect accurate and reliable data from the tissue microenvironment. TissueFAXS SL and StrataQuest software have helped researchers around the world to understand and improve cancer treatments.
TissueGnostics offers cutting-edge tools and software to support medical research, allowing scientists to build personalized treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes.
TissueFAXS SL
The researchers in this study used the TissueFAXS SL scanning device to automatically scan whole slides.
The device is completely automated with a high-throughput slide scanner, which scans up to 120 standard slides in a single run and delivers accurate and reproducible results.5
The equipment can also be updated with a multispectral or confocal mode to further improve imaging capabilities.
StrataQuest
The team used StrataQuest software to analyze cell density data for CD8+, CD3+, FOXP3+, CD20+, PD1+, PD-1+, PD-1+CD8+, PD-1+FOXP3+, and PD-1+CD20+ cells.
They detected TLS automatically by using B- and T-cell markers such as CD20 and CD3/CD8, whether within the tumor or in direct contact with tumor cells at the tumor's margins. As a variable for the follow-up analysis, they also measured the distance between the TLS and the tumor.
TissueGnostics' StrataQuest is an advanced imaging solution that integrates data mining, spatial analysis, and phenotyping techniques to analyze tissues and cells from a variety of scientific disciplines, including cancer research.
Within StrataQuest, AI techniques enable the classification of structures observed within tissues, significantly lowering analysis times.
With the latest edition of the software, users can examine and visualize complicated datasets using integrated tools such as t-SNE and UMAP, providing even more insights into immune response and related topics.
The future of cancer research
Within cancer research and treatment, understanding the tumor microenvironment will continue to be critical in advancements in the field. Treatments and therapies will be fine-tuned by examining immune response components such as TLS and immune cell interactions, resulting in reduced patient mortality.
This study is just one example of how TissueGnostics' imaging methods can produce solid, accurate data that improves our understanding of cancer.
TissueFAXS SL and StrataQuest technologies will continue to play a key role in cancer research and patient care, paving the way for more successful treatments in the future.
References
- Bray, F., et al. (2024). Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 74(3), pp.229–263. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21834.
- Liu, X., et al. (2024). Association of PD-1+ Treg/PD-1 + CD8 ratio and tertiary lymphoid structures with prognosis and response in advanced gastric cancer patients receiving preoperative treatment. Journal of translational medicine, (online) 22(1), p.1152. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05867-4.
- Chen, W., et al. (2025). Role of tertiary lymphoid structures and B cells in clinical immunotherapy of gastric cancer. Frontiers in Immunology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1519034.
- Schumacher, T.N. and Thommen, D.S. (2022). Tertiary lymphoid structures in cancer. Science, 375(6576). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abf9419.
- Super User (2019). High Throughput Cytometer | High Throughput Cell Scanning. (online) Tissuegnostics.com. Available at: https://tissuegnostics.com/products/high-throughput-cytometer/tissuefaxs-sl (Accessed 14 Jun. 2025).
About TissueGnostics
TissueGnostics (TG) is an Austrian company focusing on integrated solutions for high content and/or high throughput scanning and analysis of biomedical, veterinary, natural sciences, and technical microscopy samples.
TG has been founded by scientists from the Vienna University Hospital (AKH) in 2003. It is now a globally active company with subsidiaries in the EU, the USA, and China, and customers in 30 countries.
TissueGnostics portfolio
TG scanning systems are currently based on versatile automated microscopy systems with or without image analysis capabilities. We strive to provide cutting-edge technology solutions, such as multispectral imaging and context-based image analysis as well as established features like Z-Stacking and Extended Focus. This is combined with a strong emphasis on automation, ease of use of all solutions, and the production of publication-ready data.
The TG systems offer integrated workflows, i.e. scan and analysis, for digital slides or images of tissue sections, Tissue Microarrays (TMA), cell culture monolayers, smears, and other samples on slides and oversized slides, in Microtiter plates, Petri dishes and specialized sample containers. TG also provides dedicated workflows for FISH, CISH, and other dot structures.
TG analysis software apart from being integrated into full systems is fully standalone capable and supports a wide variety of scanner image formats as well as digital images taken with any microscope.
TG cooperations
TG continuously cooperates with research groups and other companies in the industry to provide novel tools and applications to its customers.
Sponsored Content Policy: News-Medical.net publishes articles and related content that may be derived from sources where we have existing commercial relationships, provided such content adds value to the core editorial ethos of News-Medical.Net which is to educate and inform site visitors interested in medical research, science, medical devices and treatments.