Introduction
Personalized Shopping Experiences
Automated and Smart Stores
Supply Chain and Stock Optimization
Online Grocery Shopping and Fulfillment
Challenges and Concerns
The Future of Grocery Shopping
Conclusion and Takeaway Messages
References
Discover how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the grocery experience, from hyper-personalized shopping and frictionless checkouts to smart supply chains, while also presenting new challenges for privacy, equity, and employment.
 Image Credit: nicemyphoto / Shutterstock.com
Image Credit: nicemyphoto / Shutterstock.com
Introduction
What if your grocery list could adapt to your cholesterol levels or recommend recipes that fit your family’s dietary needs? Most shoppers do not realize that machine learning (ML) is already deciding which products consumers see, what discounts they get, and when they are encouraged to buy.
The question is no longer whether artificial intelligence (AI) belongs in food retail; it is about how this technology will reshape what, when, and how we eat.
From personalized promotions to predictive logistics, AI is revolutionizing how consumers shop for food.1 By integrating AI at multiple touchpoints, grocers and retailers can offer tailored experiences, reduce waste, and respond more effectively to consumer needs.
Grocery stores are no longer just shelves and checkouts, they are dynamic, data-driven environments where algorithms guide purchasing decisions, restocking schedules, and even nutritional choices.2,3
This article explores how AI is changing how we shop for food, from personalized product recommendations and frictionless checkouts to advanced supply chain optimization. It will also explore the ethical, socio-economic, and public health challenges that come with this digital shift.
Personalized Shopping Experiences
Through AI-powered applications and algorithms, grocery retailers analyze customer data such as purchase history, dietary preferences, and allergy information to curate individualized product suggestions. Studies show that personalized shopping not only enhances user satisfaction but can also guide healthier choices by recommending low-sodium or gluten-free options.1
Loyalty programs are another area in which AI is being deployed. Retailers leverage ML to analyze customer behavior and generate tailored discounts or coupons, thereby increasing the likelihood of redemption and customer retention.2
AI-powered voice assistants integrated with smart fridges or mobile apps also enable users to manage grocery lists or place orders seamlessly, thus enhancing accessibility and convenience. These systems may also synchronize with health apps to offer insights into nutritional content and tracking consumption patterns, ultimately promoting long-term wellness and personalized dietary planning.4
Automated and Smart Stores
Automated retail environments like Amazon Go employ computer vision, sensor fusion, and deep learning to enable checkout-free shopping experiences. As customers pick up or return items, AI tracks these actions and automatically charges or updates the cart.3
Smart carts are an emerging innovation that allows customers to view their total bill in real-time, receive nutritional suggestions, and locate products within the store. These systems rely on embedded cameras, weight sensors, and computer vision algorithms to recognize items and streamline checkout processes.5
AI-enabled inventory systems have also been developed to ensure that store shelves are stocked efficiently, thereby reducing human error and waste. These technologies allow retailers to monitor foot traffic and product interactions, which informs dynamic merchandising strategies to enhance customer engagement and increase in-store sales.6
Smoother shopping is rolling your way: The Amazon Dash Cart
Supply Chain and Stock Optimization
The incorporation of AI into grocery supply chains is rapidly growing. For example, predictive analytics and ML models have been created to anticipate consumer demand based on historical sales, weather forecasts, holidays, and local events. Grocery stores then use this data to restock items in a timely manner and minimize overstocking or food spoilage, which also aligns with public health goals of reducing food waste.4,6
Inventory management systems powered by AI can also analyze real-time data across various interaction points to optimize logistics. This includes monitoring product expiration dates and dynamically adjusting prices to incentivize sales before spoilage.6
The capacity of AI to identify trends and anomalies may allow grocers to make proactive decisions, thus improving overall efficiency and sustainability. AI can also detect disruptions in the supply chain early, which will enable retailers to reroute deliveries or source alternative suppliers quickly in the event of an emergency or fluctuating demand cycles.6
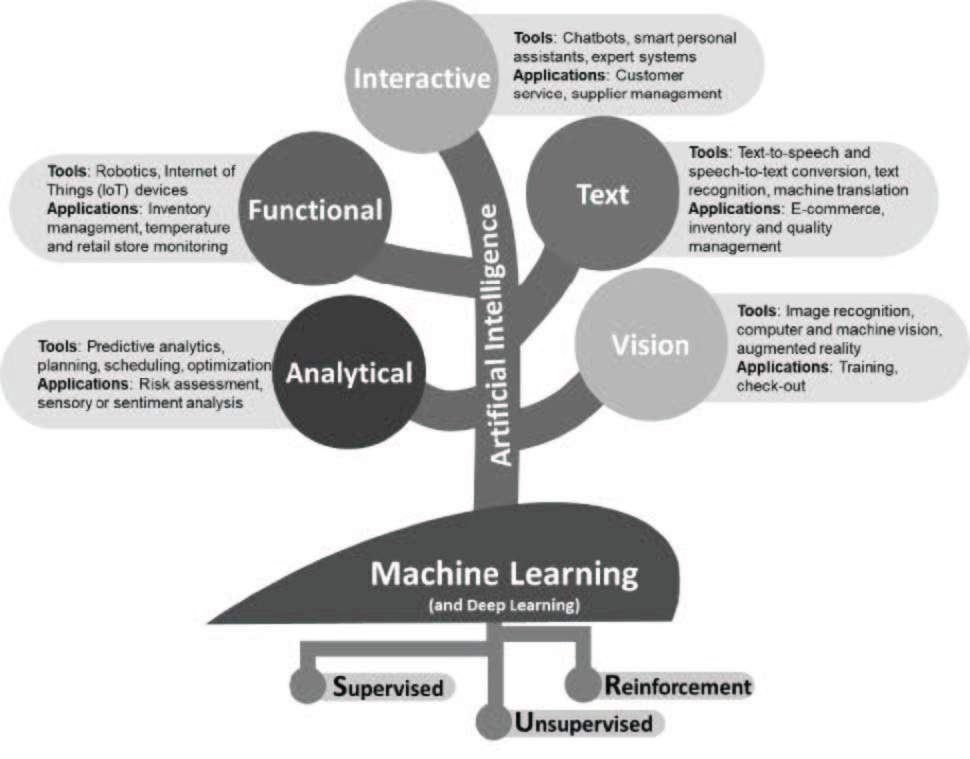
Branches of artificial intelligence tools and their applications for the retail food industry (adapted with permission from (2)). Specific branches of artificial intelligence (AI) present different solutions depending on the business problem. For purposes of this article aimed at the food retail industry, AI tools may be categorized as (i) vision, (ii) text, (iii) interactive, (iv) functional, or (v) analytical solutions. Algorithms of machine learning (ML) and more advanced deep learning programs provide the foundation for the success and dissemination of AI. ML methods are classified into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning.7
Online Grocery Shopping and Fulfillment
Within online grocery platforms, intelligent order management systems assign fulfillment centers and distribution routes based on real-time inventory and geographic proximity, thereby reducing delivery times and carbon footprints.4 Moreover, virtual assistants and chatbots handle customer inquiries, resolve complaints, and suggest products based on user profiles.
Taken together, these AI tools enhance user experience and allow human staff to focus on more complex service issues. Recommendation engines also increase sales by providing relevant product suggestions that are targeted to individual shopping behaviors.2
AI can demand forecasting, optimize packing and routing processes in micro-fulfillment centers, as well as personalize digital storefronts to ensure ease-of-access across all aspects of the consumer experience. Some platforms are even integrating augmented or virtual reality interfaces that facilitate a virtual shopping experience through grocery aisles, thereby enriching the online experience while enabling more intuitive product discovery and comparison.4
These innovations collectively reduce operational difficulties while offering a seamless and consumer-friendly shopping journey that mirrors and even expands upon the in-store experience.
Challenges and Concerns
Collecting and processing personal information to train AI systems raises various ethical questions about consent and data security. The use of personal data requires retailers to comply with data protection regulations and ensure transparency in how consumer data is used.1
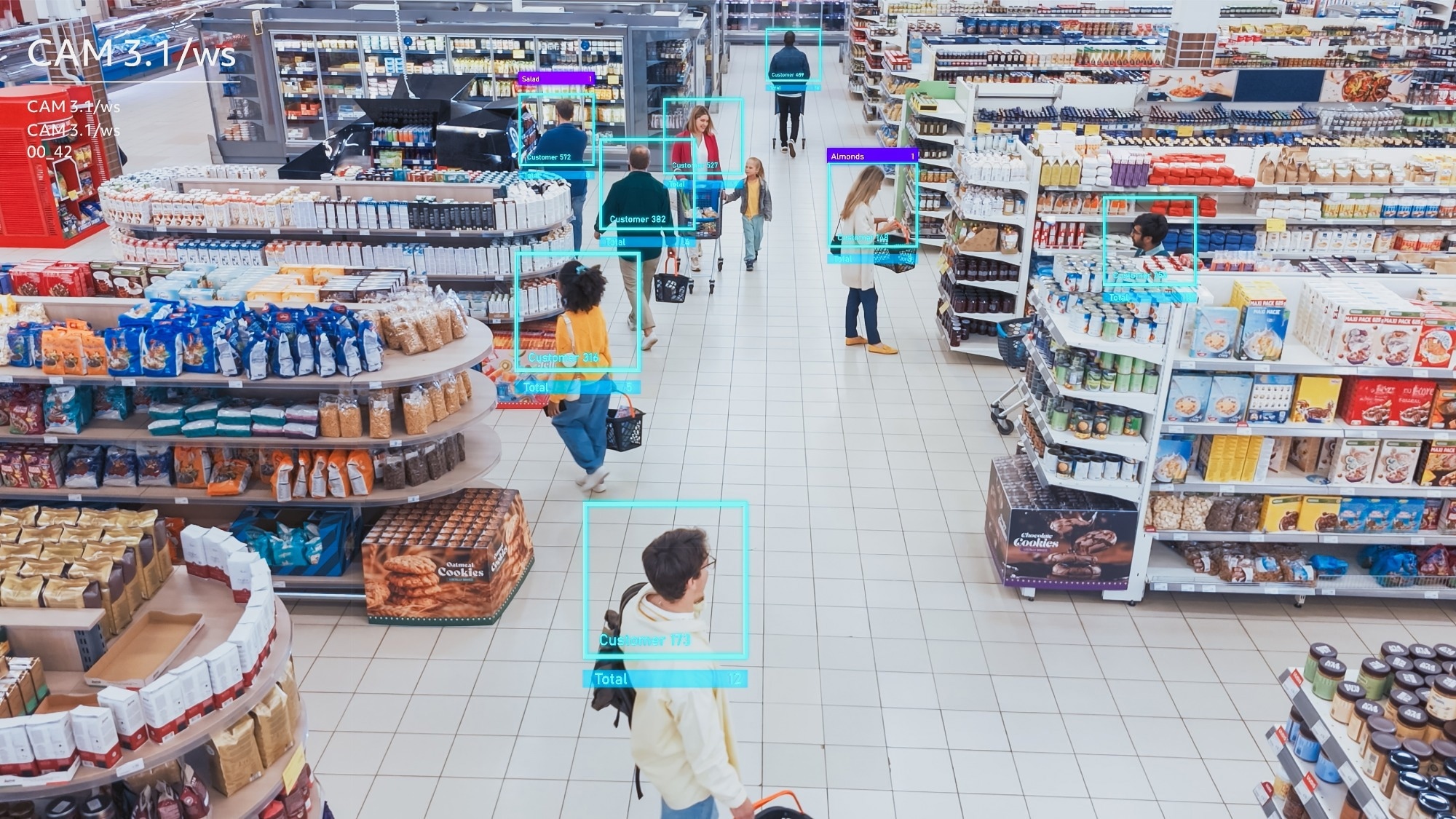 Image Credit: Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock.com
Image Credit: Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock.com
Automation due to AI implementation in retail may also displace many traditional roles, such as cashiers and stock clerks, which raises employment and equity issues.4 Furthermore, AI systems trained on biased data may inadvertently reinforce existing disparities, such as preferential product placement for higher-income demographics.6
Ethical AI design must prioritize inclusivity and fairness while ensuring continuous auditing and public oversight to protect private consumer data. There is also concern about digital accessibility, as vulnerable populations may encounter difficulties when interacting with AI-driven platforms due to a lack of digital literacy or access to smart devices.6
Therefore, policymakers and industry leaders must ensure equitable deployment that accounts for these disparities to prevent technological benefits from widening existing societal gaps.
The Future of Grocery Shopping
The role of AI in grocery shopping is predicted to grow substantially over the next decade. One potential application of AI that may overlap with retail grocery shopping is the integration of grocery retail apps with health apps and electronic medical records. Combining these two large data sets could facilitate the ability of AI to offer nutrition advice that considers the health conditions of users, such as recommending heart-healthy foods for individuals at risk of cardiovascular disease.7
AI may also assist with meal planning by generating weekly menus and auto-filling shopping lists based on dietary goals or family size. As smart kitchens and Internet of Things (IoT) devices like smart shelves are created, fully autonomous grocery ecosystems where appliances reorder items before they run out may emerge.4–6
The convergence of AI, augmented reality, and robotics has the potential to enable immersive, predictive, and even anticipatory shopping experiences by fundamentally altering consumer engagement and transforming the food retail landscape. Importantly, these revolutionary systems will inevitably encounter socio-economic difficulties, such as loss of employment for individuals working in the retail sector, which emphasizes the crucial role of federal entities in regulating these technologies.
Conclusions
From smarter carts and checkout-free stores to predictive logistics and tailored promotions, AI is redefining how we shop for food. However, this evolution raises important questions regarding privacy, equity, and loss of employment. As the public navigates this digital shift, a balanced approach that combines technological advancement with ethical oversight is essential.
References
- Ameen, N., Tarhini, A., Reppel, A., & Anand, A. (2021). Customer Experiences in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. Computers in Human Behavior, 114(106548), 106548. NCBI. DOI:10.1016/j.chb.2020.106548, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0747563220302983
- Bhatt, P., & Singh, A. K. (2025). Impact of AI on Consumers’ Purchase Intention Towards Online Grocery Shopping in India. Journal of Reliability and Statistical Studies, 17(2), 453–490. DOI:10.13052/jrss0974-8024.17210, https://journals.riverpublishers.com/index.php/JRSS/article/view/26735
- Shekokar, N., Kasat, A., Jain, S., Naringrekar, P., & Shah, M. (2020). Shop and Go: An innovative approach towards shopping using Deep Learning and Computer Vision. 2020 Third International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT). DOI:10.1109/icssit48917.2020.9214256, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9214256/
- Stecuła, K., Wolniak, R., & Aydın, B. (2024). Technology Development in Online Grocery Shopping—From Shopping Services to Virtual Reality, Metaverse, and Smart Devices: A Review. Foods, 13(23), 3959. DOI: 10.3390/foods13233959, https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/13/23/3959
- Sukhani, K., Nurul Qomariyah, N., & Andi Purwita, A. (2022). Clever Cart: An Eco-Friendly Shopping Self-Checkout System with IoT sensor. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 998(1), 012041. DOI:10.1088/1755-1315/998/1/012041, https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/998/1/012041
- Wolniak, R., Stecuła, K., & Aydın, B. (2024). Digital Transformation of Grocery In-Store Shopping-Scanners, Artificial Intelligence, Augmented Reality and Beyond: a Review. Foods, 13(18), 2948–2948, DOI:10.3390/foods13182948, https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/13/18/2948
- Friedlander, A., & Zoellner, C. (2020). Artificial Intelligence Opportunities to Improve Food Safety at Retail. Food Protection Trends, 40, 272-278, https://www.foodprotection.org/publications/food-protection-trends/archive/2020-07-artificial-intelligence-opportunities-to-improve-food-safety-at-retail/
Last Updated: May 21, 2025