The gut microbiome is made up of trillions of living microbes, and more than a thousand species of bacteria. It has been known that the gut plays major roles in the body’s health. A team of university engineers may have developed a way to study and collect samples of microbes living in the gut.
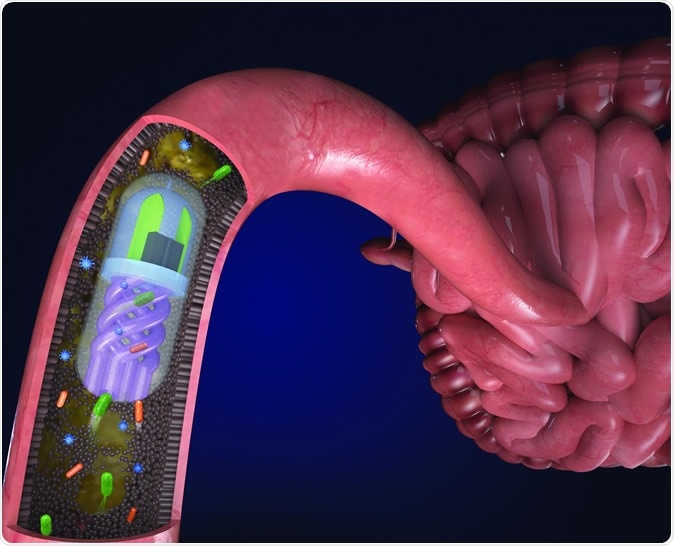
Bacteria in the gut are pulled into the helical channels by an osmotic 'pump' in the pill. Image Credit: Nano Lab, Tufts University
The 3D pill can sample gut bacteria in the entire GI tract
At present, sampling methods of the GI tract uses fecal metabolites and DNA analysis. However, these methods do not provide in-depth and comprehensive data of the GI environment, particularly in the upper part of the distal colon. It’s an area where most microbiome species differ significantly.
According to the researchers, they have tested the pill and they found that it provides accurate identification of the populations, including their abundance in various applications. The team tried the pill on both pigs and primates, but clinical trials are needed to be performed to see if the pill can be applied on humans for both diagnosis and treatment in the future.
The gut microbiome
The gut is home to trillions of microbiomes, including bacteria. That means they gut bacteria is even more abundant than the cells in the entire body. Plus, there are more than a thousand species of bacteria living in the gut. They are there for a reason and they provide many beneficial effects on the body.
First off, gut bacteria have a protective and supportive part in digestion and it helps protect the body against illness. However, once the balance of microbiome occurs in the gastrointestinal tract, called dysbiosis, occurs, it can lead to many digestive disturbance symptoms, such as constipation, bloating, indigestion, and diarrhea.
Dysbiosis can also be linked to inflammation, exacerbation of diseases like cancer, and vulnerability to certain infections. Studies have shown that microbiome metabolites work by protecting the body against disease.
“We are learning quite a lot about the role of the gut microbiome in health and disease. However, we know very little about its biogeography. The pill will improve our understanding of the role of spatial distribution in the microbiome profile to advance novel treatments and therapies for a number of diseases and conditions,” Sameer Sonkusale, study co-author and professor of electrical and computer engineering at Tufts University’s School of Engineering, said.
Sophisticated 3D pill
The new 3D pill is modern and state-of-the-art, developed through a 3D printer with microfluidic channels. The new pill can get samples from the various phases of the digestive tract. The pill’s surface has a pH-sensitive covering, so it won’t absorb any samples until it enters the small intestine. In the stomach, where acids exist, the coating melts, making it able to get samples in the small intestine.
Aside from that, it has a semi-permeable membrane that separates the pill into two chambers – one chamber comprising helical channels, is responsible for acquiring bacteria and the other is a calcium-filled chamber, which aids in making an osmotic flow across the membrane. The 3D pill also contains a tiny magnet that holds it at particular areas in the gut for more specific sampling guided by an external magnet.
The researchers located the pill in the digestive tract through a fluorescent dye in the salt chamber.
"The design of this device makes it incredibly easy to use, posing little risk to the subject being measured, yet providing so much information," Prof. Giovanni Widmer, professor of infectious diseases and global health in Tufts Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, said in a statement.
"Compared to other non-invasive diagnostic devices, this is like having an EKG for gut health,” he added.
The researchers believe that new technology can help in gastrointestinal diagnosis by analyzing bacterial populations using DNA sequencing techniques. The new non-invasive method will help not only in diagnosis but also in the treatment of various digestive disorders.
“Our results show that the bacterial populations recovered from the pills’ microfluidic channels closely resemble the bacterial population demographics of the microenvironment to which the pill was exposed,” the researchers concluded in the study.
“We believe such lab-on-a-pill devices will revolutionize our understanding of the spatial diversity of the gut microbiome and its response to medical conditions and treatments,” they added.
Journal reference:
Nejaad, H.R., Oliveira, B., Sadeqi, A., Dehkharghani, A., Kondova, I., Langermans, J., Guasto, J., Tzipori, S., Widmer, G., Sonkusal, S. (2019). Ingestible Osmotic Pill for In‐vivo Sampling of Gut Microbiome. Advanced Intelligent Systems. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/aisy.201900053