Researchers in Japan have estimated that the B.1.1.7 variant strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that recently emerged in England is 40% more transmissible than strains previously circulating in the country.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus is the agent responsible for the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic that continues to pose a significant threat to global public health and has now claimed more than 2.68 million lives worldwide.
The researchers say the estimated 40% greater transmissibility of B.1.1.7 suggests that the measures implemented to control this strain need to be strengthened by 40%, compared with those used to control previously circulating strains.
For the equivalent control effects to be reached, contact rates between individuals would need to be less than 0.71 of the rates achieved using the previous measures.
Chayada Piantham and Kimihito Ito from Hokkaido University warn that the transmissibility advantage of other recently emerged strains such as those identified in Brazil and South Arica also urgently needs estimating.
A pre-print version of the research paper is available on the medRxiv* server, while the article undergoes peer review.
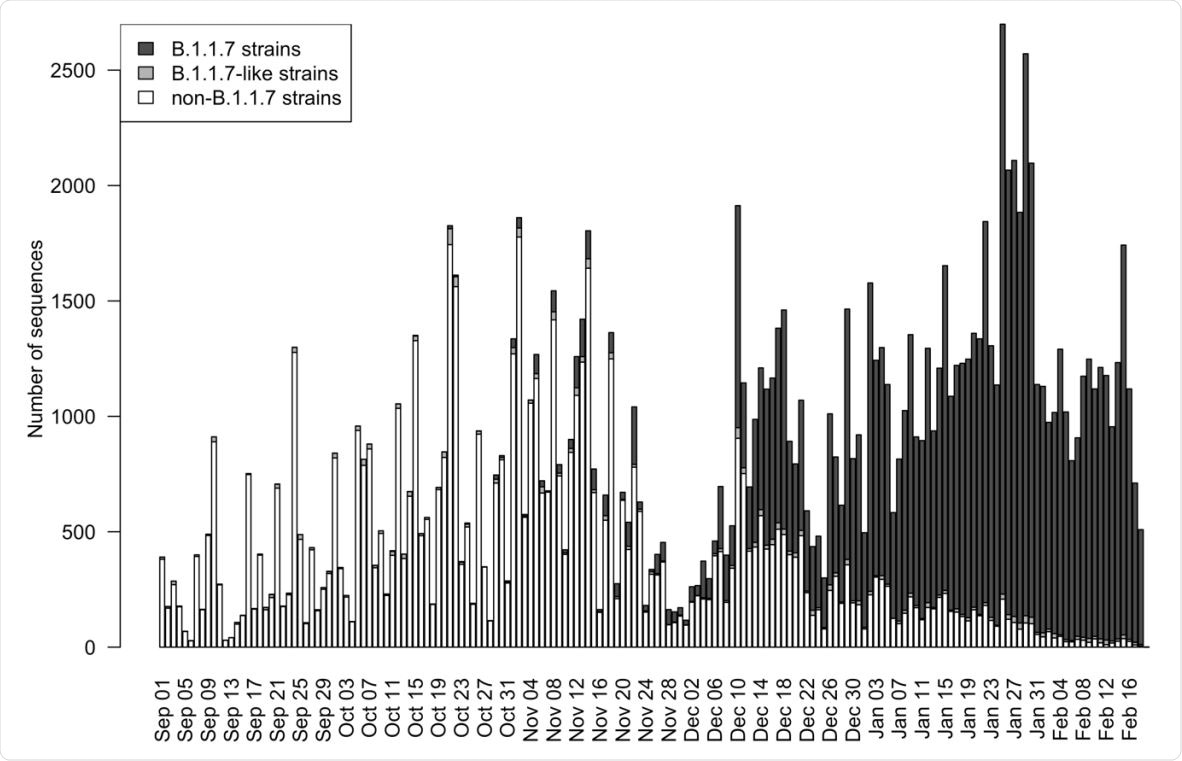
Number of sequences in England from September 1, 2020 to February 19, 2021. The nucleotide sequences were retrieved from GISAID on March 1, 2020.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
What is known so far about the B.1.1.7 lineage?
Since the COVID-19 outbreak first began in Wuhan, China, in late December 2019, the rapid spread and evolution of the causative agent SARS-CoV-2 has led to the emergence of new variants that have a transmission advantage over the original strain.
In December 2020, Public Health England identified a new cluster of viruses belonging to the lineage B.1.1.7, which the World Health Organization designated a “Variant of Concern” owing to its increased transmissibility, compared with strains previously circulating in England.
Since the lineage was first identified in the country in September 2020, the number of infections with this new strain rapidly grew during October and November. By February 2021, the B.1.1.7 viruses comprised 95% of all SARS-CoV-2 strains circulating in England.
Previous studies assumed the reproductive number is constant over time
Several studies have compared the reproduction number (R; number of secondary infections resulting from one single infection) of the B.1.1.7 lineage to that of strains previously circulating in England.
One study estimated that the R number of the B.1.1.7 strain is between 83 and 118% higher than that of previous strains, while another study estimated that it was between 40 and 75% higher.
The methods used in these studies estimated the increase in transmissibility under the assumption that R is constant over time during the target period of analysis.
However, since the increased transmissibility of the B.1.1.7 lineage was recognized, strict control measures, including lockdown, have been imposed in England.
“Thus, the constant R assumption is questionable when analyzing the increase in the reproduction number of B.1.1.7 compared to that of previously circulating strains,” say Piantham and Ito.
What did the researchers do?
The team estimated the selective advantage of the B.1.1.7 lineage over previous strains using the time course of the fraction of B.1.1.7 viruses identified in England.
Based on Wallinga-Teunis’s method for estimating instantaneous reproduction numbers, the approach allowed the reproduction number to change during the target period of analysis.
The approach was also based on a model by Maynard Smith, which assumes that the selective advantage of a mutant strain over previously circulating strains is constant over time.
The researchers downloaded nucleotide sequence data on SARS-CoV-2 viruses detected in England from the GISAID (Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data) EpiCoV database on 1st March, 2021.
The team then applied the new method to estimate the instantaneous reproduction number of B.1.1.7 strains, compared with that of previously circulating strains.
What did they find?
The researchers estimated that the selective advantage of the B.1.1.7 strains over non-B.1.1.7 strains were 0.40, indicating that the instantaneous reproduction number of the B.1.1.7 lineage is 40% higher than that of previous strains.
This suggests that the control measures used to contain the B.1.1.7 lineage need to be strengthened by 40%, compared with those used to control previous strains, says the team.
For the equivalent control effect to be reached, contact rates between individuals would need to be restricted to below 0.71 of the rates that were achieved with the previously used measures.
The selective advantage of new strains in other countries also needs assessing
The team points out that as of the 17th March 2021, the B.1.1.7 lineage has been detected in 93 countries.
“The selective advantage of the B.1.1.7 strains over previously circulating strains in other countries remains to be our future work,” say the researchers.
In addition, Piantham and Ito point out that the variants identified in Brazil and South Africa also show higher transmissibility than previous strains.
“There is also an urgent need to estimate the selective advantage of these strains,” they conclude.

 *Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
*Important notice: medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.